Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Electricity Consumption
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Electricity Consumption

Electricity, the lifeblood of modern society, powers our homes, businesses, and infrastructure. While its benefits are undeniable, understanding where our energy goes is crucial for responsible consumption and a sustainable future. This article delves into the primary consumers of electricity, examining their impact and exploring strategies for efficient usage.
Residential Consumption: The Everyday Energy Users
Within the walls of our homes, a multitude of appliances and devices contribute to our overall electricity consumption. While the specific breakdown varies based on individual habits and regional climates, some key contributors stand out:
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC): In many regions, HVAC systems represent the largest electricity draw. During colder months, heating systems like furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps consume significant energy to maintain comfortable temperatures. Conversely, in warmer climates, air conditioning units work tirelessly to combat the heat, often accounting for a substantial portion of the energy bill.
- Water Heating: The process of heating water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry requires substantial energy. Traditional water heaters, especially those powered by electricity, contribute significantly to residential energy consumption.
- Refrigeration and Food Storage: Refrigerators and freezers are essential for food preservation, but their constant operation consumes a noticeable amount of electricity. This energy usage is influenced by factors like appliance efficiency, frequency of door openings, and the temperature setting.
- Lighting: While advancements in LED technology have significantly reduced energy consumption for lighting, it still represents a notable portion of residential electricity usage. The number of lights, their wattage, and the duration of use all influence the overall energy consumption.
- Electronics and Appliances: Our modern lives are filled with electronic devices, from televisions and computers to washing machines and dryers. These appliances contribute to electricity consumption, with varying levels of energy efficiency depending on their age and technology.
Commercial and Industrial Consumption: The Powerhouses of Industry
Beyond residential use, electricity plays a critical role in powering businesses and industries. The energy demands of these sectors are often significantly higher, with large-scale operations requiring substantial power. Some of the key contributors to commercial and industrial electricity consumption include:
- Manufacturing: Industrial processes like machinery operation, metal processing, and chemical production require substantial electricity. The scale of these operations and the types of equipment used heavily influence the overall energy consumption.
- Commercial Buildings: Offices, retail spaces, and other commercial buildings utilize electricity for lighting, HVAC, and a variety of equipment. The size of the building, its occupancy, and the specific needs of its occupants all contribute to its energy footprint.
- Data Centers: The rapid growth of digital technologies has led to a surge in the demand for data centers. These facilities require significant electricity to power servers, storage systems, and cooling infrastructure.
- Transportation: While electric vehicles are gaining traction, the majority of transportation still relies on fossil fuels. However, charging stations for electric vehicles and the electrification of public transportation networks are increasing electricity demand in this sector.
Understanding the Importance of Efficient Electricity Use
The importance of understanding electricity consumption goes beyond simply reducing our energy bills. It is directly linked to a multitude of crucial factors:
- Environmental Sustainability: Generating electricity often relies on fossil fuels, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Efficient electricity use reduces our reliance on these fuels, promoting a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
- Economic Benefits: Lowering electricity consumption translates to reduced energy costs for individuals, businesses, and governments. This economic benefit can be channeled towards other priorities, fostering economic growth and development.
- Energy Security: By reducing our dependence on external energy sources, efficient electricity use enhances energy security and reduces vulnerability to global energy market fluctuations.
- Resource Conservation: Efficient energy use extends the lifespan of energy resources, ensuring their availability for future generations.
FAQs about Electricity Consumption
Q: How can I track my electricity consumption?
A: Many utilities offer online portals or apps that allow customers to track their energy usage in real-time. Smart meters can also provide detailed data on electricity consumption patterns.
Q: What are some simple ways to reduce my electricity consumption?
A: Simple measures like turning off lights when leaving a room, unplugging appliances when not in use, and adjusting thermostat settings can significantly reduce energy consumption.
Q: How can businesses reduce their electricity consumption?
A: Businesses can implement energy-efficient technologies, optimize HVAC systems, promote energy-conscious practices among employees, and explore renewable energy sources to reduce their electricity consumption.
Q: What are the benefits of using renewable energy sources?
A: Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro power are sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives to fossil fuels. They contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a cleaner energy future.
Tips for Efficient Electricity Use
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Invest in appliances with Energy Star ratings, as they consume significantly less energy than older models.
- Optimize HVAC Systems: Regularly maintain and service your HVAC systems to ensure optimal efficiency. Consider using programmable thermostats to adjust temperatures automatically when you are away from home.
- Choose LED Lighting: LED bulbs consume significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs and last much longer.
- Unplug Electronics: When not in use, unplug electronic devices and chargers, as they can consume energy even when turned off.
- Practice Water Conservation: Reduce water heating energy consumption by taking shorter showers, using low-flow showerheads, and fixing leaky faucets.
Conclusion
Understanding the key contributors to electricity consumption is crucial for responsible energy use. By implementing energy-efficient practices in our homes, businesses, and industries, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, mitigate environmental impact, and foster a more sustainable future. As technology continues to evolve, new solutions for efficient energy consumption will emerge, further empowering us to harness the benefits of electricity while minimizing its environmental footprint.
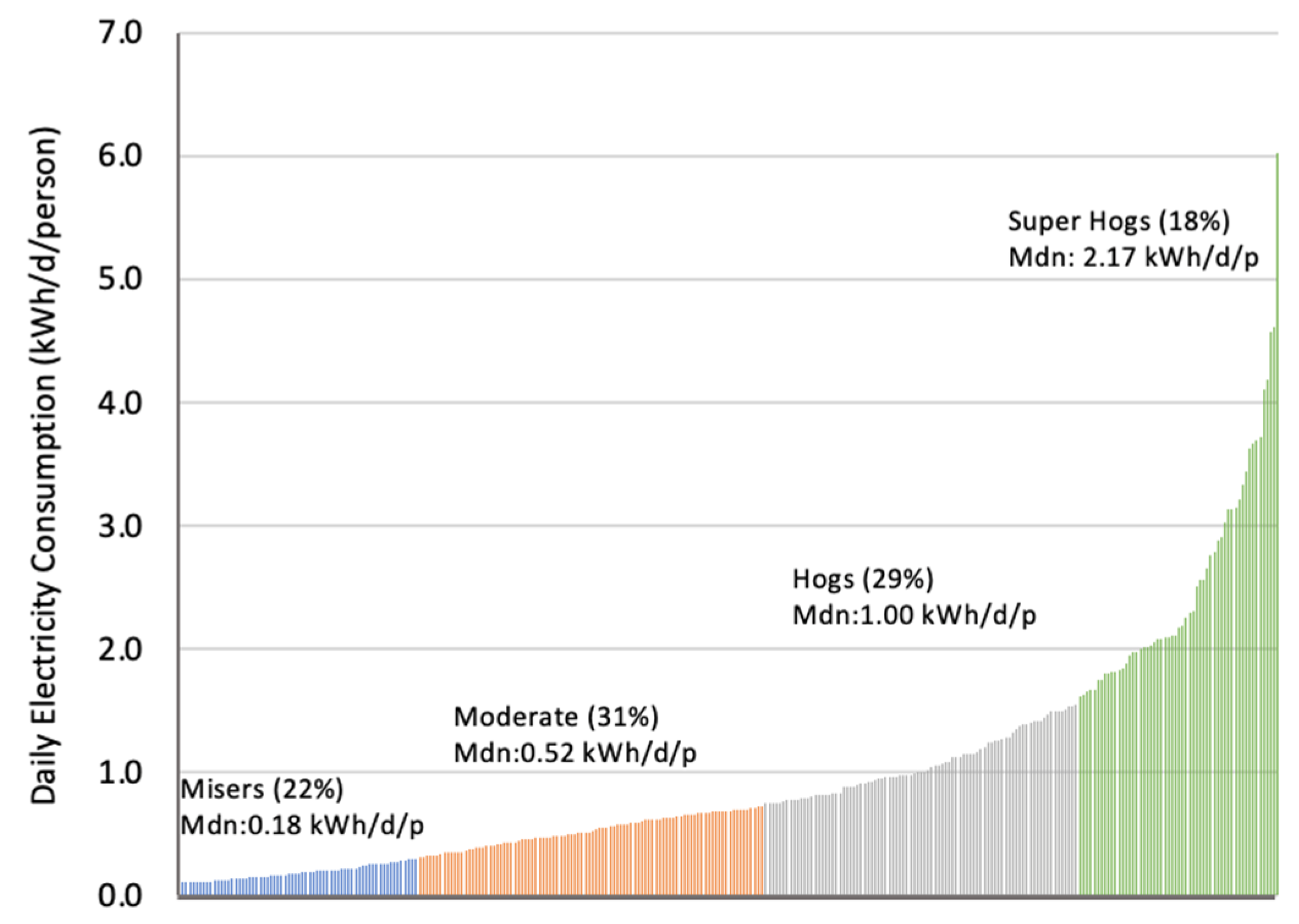

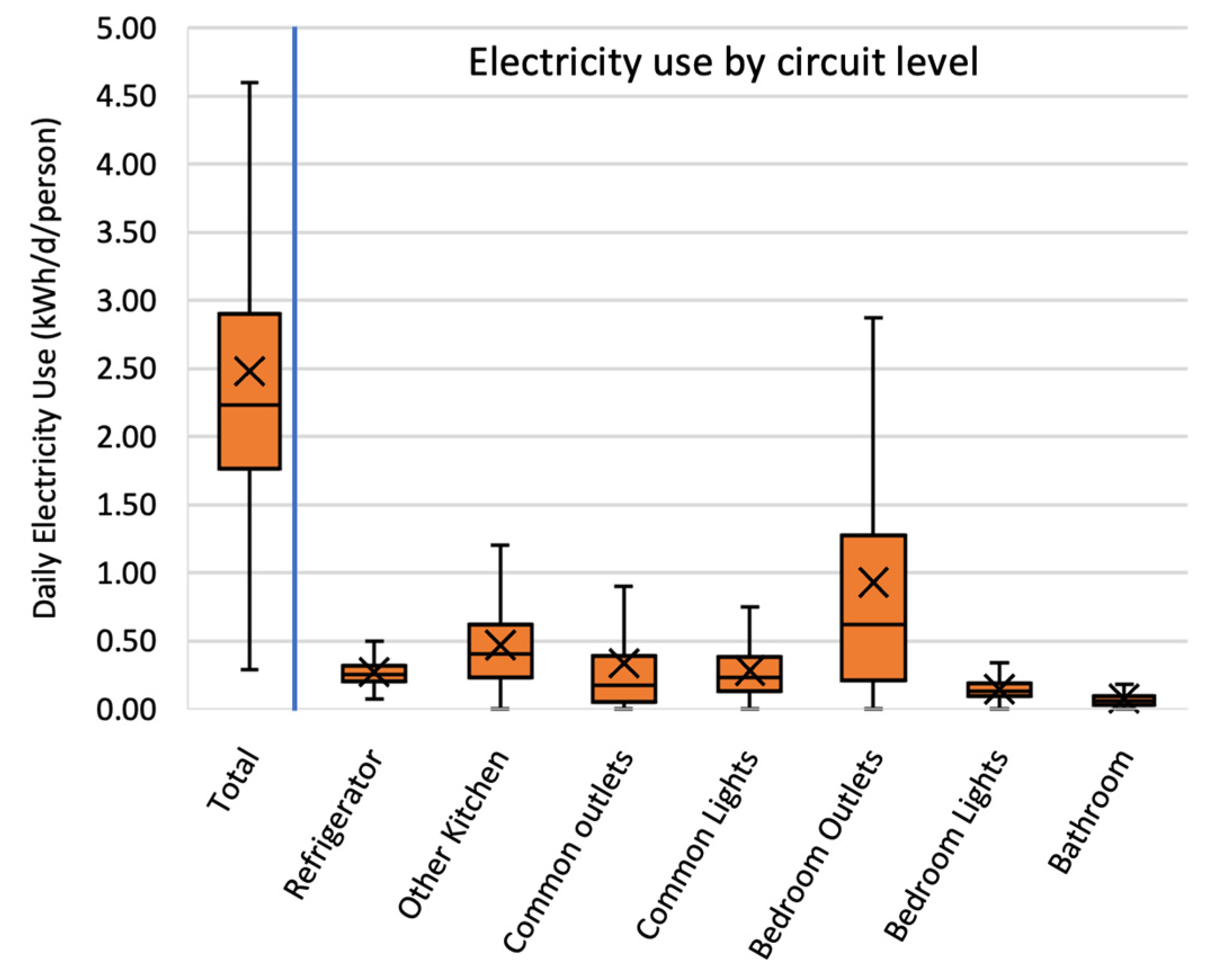
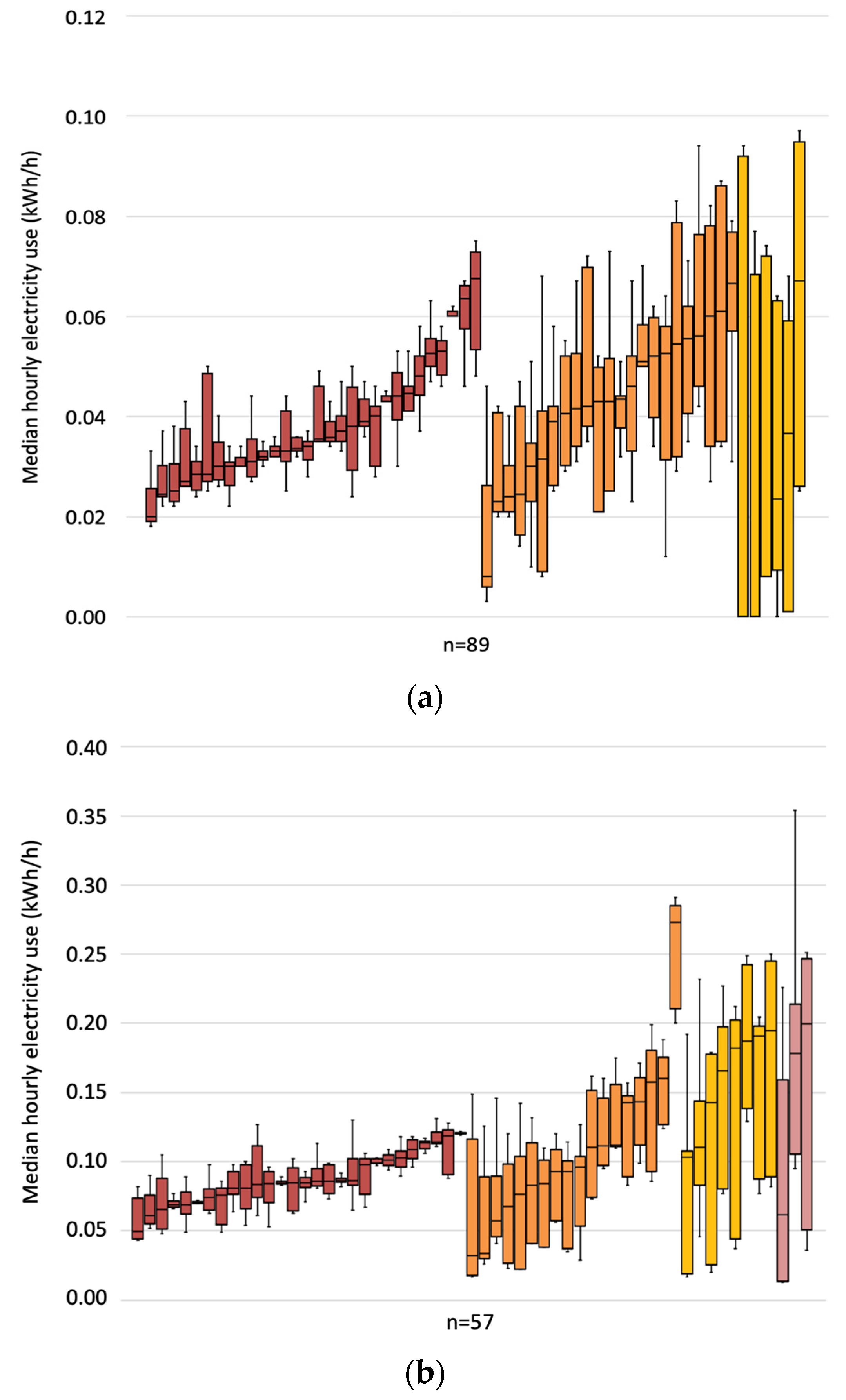
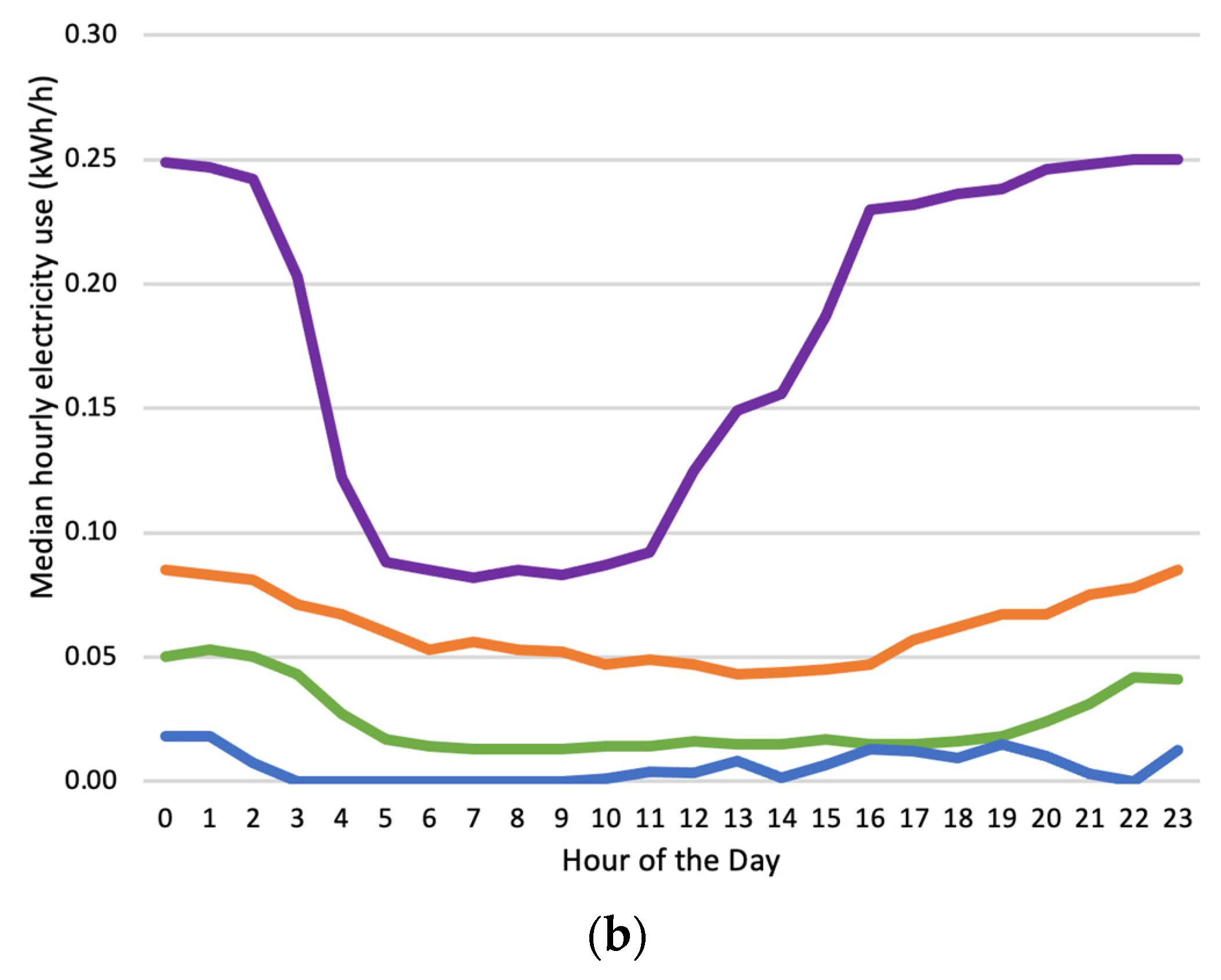


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unmasking the Energy Hogs: A Comprehensive Guide to Electricity Consumption. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!