Understanding the Power of pH in the Home
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of pH in the Home
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of pH in the Home. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of pH in the Home
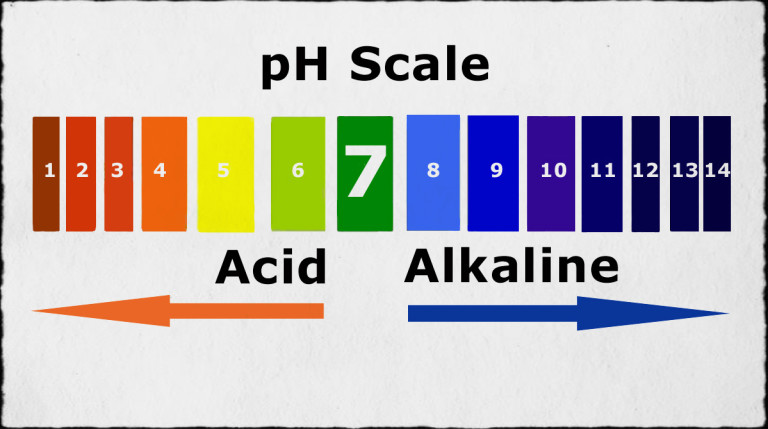
The pH scale, a measure of acidity and alkalinity, plays a critical role in various aspects of our daily lives, especially within the confines of our homes. While the concept of pH might seem abstract, its practical implications are far-reaching, impacting everything from the cleanliness of our dishes to the health of our plants. This article delves into the world of pH in the home, exploring common household items with strong pH values and their diverse applications.
The pH Spectrum: A Fundamental Understanding
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 representing neutral. Values below 7 indicate acidity, with lower numbers signifying stronger acids, while values above 7 indicate alkalinity, with higher numbers signifying stronger bases.
Strong Household Acids
Several household products possess strong acidic properties, often employed for cleaning and disinfecting purposes.
- Vinegar: This common kitchen staple boasts a pH of around 2.4, making it a potent natural cleaner. Its acidic nature effectively tackles mineral deposits, grime, and even mildew.
- Lemon Juice: With a pH of approximately 2.0, lemon juice is another natural acidic agent. Its citric acid acts as a powerful cleaning and deodorizing agent, particularly effective in removing stains and brightening surfaces.
- Battery Acid: This highly corrosive liquid, typically sulfuric acid, possesses a pH close to 0. Its extreme acidity makes it dangerous for direct handling and necessitates careful storage and disposal.
- Toilet Bowl Cleaner: These commercially available cleaners, often containing hydrochloric acid, boast a pH of around 1.0. Their potent acidity effectively removes tough stains and mineral deposits from toilets.
- Drain Cleaner: Many drain cleaners rely on strong acids like sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid to dissolve clogs. Their pH values can be extremely low, making them highly corrosive and requiring cautious use.
Strong Household Bases
Household bases, also known as alkalis, are commonly used for cleaning and degreasing tasks.
- Baking Soda: This versatile kitchen ingredient boasts a pH of around 8.3, making it a mild base. Its alkaline properties are effective for cleaning and deodorizing, tackling stains and removing grease.
- Ammonia: This pungent liquid, with a pH of around 11.5, is a powerful cleaning agent. Its alkalinity effectively cuts through grease, grime, and even removes stubborn stains.
- Lye (Sodium Hydroxide): This highly caustic substance, with a pH of around 14, is used in drain cleaners and soap-making. Its extreme alkalinity requires careful handling and protective measures.
- Oven Cleaner: Many oven cleaners contain strong bases like sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, with pH values approaching 14. Their potent alkalinity effectively breaks down baked-on grease and food residue.
The Importance of pH Balance in the Home
Maintaining a balanced pH in various aspects of our homes is crucial for both efficiency and safety.
- Cleaning: The appropriate pH level for cleaning varies depending on the surface and the type of dirt or stain. Acidic cleaners are effective for mineral deposits and hard water stains, while alkaline cleaners excel at cutting grease and grime.
- Gardening: Plants thrive in specific pH ranges, and understanding soil pH is essential for optimal growth. Acidic soils favor plants like blueberries and rhododendrons, while alkaline soils suit plants like roses and tomatoes.
- Swimming Pools: Maintaining a balanced pH in swimming pools is critical for water clarity, swimmer comfort, and preventing corrosion. A slightly alkaline pH, around 7.2 to 7.6, is ideal for most pools.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I determine the pH of a household product?
A: While pH testing strips are readily available, it’s generally advisable to consult the product label for its pH information.
Q: What safety precautions should I take when handling strong acids and bases?
A: Always wear protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and long sleeves, when handling strong acids and bases. Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes, and ensure adequate ventilation.
Q: What happens if I mix strong acids and bases?
A: Mixing strong acids and bases can lead to a violent reaction, generating heat and potentially harmful fumes.
Q: How can I safely dispose of strong acids and bases?
A: Never pour strong acids or bases down the drain. Consult local regulations and disposal guidelines for safe disposal.
Tips for Using Strong Acids and Bases Safely
- Read and follow all product instructions carefully.
- Wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, goggles, and long sleeves.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing.
- Store strong acids and bases separately and securely.
- Never mix strong acids and bases.
- Dispose of strong acids and bases properly.
Conclusion
Understanding the pH of household products and their impact on our daily lives is crucial for maintaining a safe and efficient home environment. From cleaning and gardening to maintaining a swimming pool, pH plays a significant role in achieving desired outcomes. By utilizing the power of pH responsibly and adhering to safety precautions, we can effectively leverage the benefits of strong acids and bases while minimizing potential risks.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of pH in the Home. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
