Understanding the Energy Landscape of the Modern Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Energy Landscape of the Modern Home: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Energy Landscape of the Modern Home: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Energy Landscape of the Modern Home: A Comprehensive Guide

The modern home is a complex ecosystem of energy consumption, fueled by a diverse array of appliances, devices, and systems. Understanding how energy is used within a household is crucial for promoting responsible energy consumption, reducing environmental impact, and optimizing financial well-being. This article delves into the multifaceted world of typical household energy use, offering a comprehensive overview of key energy consumers, factors influencing consumption patterns, and strategies for achieving greater energy efficiency.
The Energy Consumption Landscape
Household energy consumption is primarily driven by the use of electricity and natural gas, with varying proportions depending on regional factors, climate, and the specific mix of appliances and systems within a home.
Major Energy Consumers:
- Heating and Cooling: This category represents the largest portion of energy consumption in most households, particularly in regions with extreme climates. Heating systems, including furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps, rely on natural gas, electricity, or propane to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Air conditioning units, essential for cooling during summer months, also contribute significantly to energy consumption.
- Water Heating: Water heaters, typically fueled by natural gas, electricity, or propane, are responsible for heating water for showers, baths, dishwashing, and laundry. The size of the water heater and the frequency of hot water use directly impact energy consumption.
- Lighting: While the energy consumption of individual light bulbs has significantly decreased with the advent of energy-efficient technologies, the sheer number of light fixtures in a home can still contribute considerably to overall energy use.
- Appliances: Refrigerators, freezers, ovens, dishwashers, washing machines, and dryers are major energy consumers, accounting for a significant portion of household energy use. The energy efficiency of these appliances, their usage frequency, and operating settings all play a role in their energy consumption.
- Electronics and Gadgets: The increasing prevalence of electronic devices, including computers, televisions, gaming consoles, and mobile phones, has added a new dimension to household energy consumption. While individual devices may consume relatively little energy, the cumulative effect of multiple devices operating simultaneously can be substantial.
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption:
- Climate and Weather: The climate in which a home is located significantly influences energy consumption. Regions with extreme temperatures require more energy for heating and cooling, impacting overall energy use.
- Home Size and Insulation: Larger homes with poor insulation require more energy to maintain comfortable temperatures, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Occupancy and Lifestyle: The number of occupants in a home and their habits, such as shower duration, appliance usage, and thermostat settings, directly influence energy consumption.
- Appliance Efficiency: The energy efficiency of appliances, measured by Energy Star ratings, plays a crucial role in determining energy consumption. Newer, more energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to older models.
- Behavioral Choices: Energy-conscious behaviors, such as turning off lights when leaving a room, using energy-efficient appliances, and adopting sustainable practices, can significantly impact energy consumption.
Benefits of Understanding Household Energy Use:
- Reduced Energy Costs: By identifying and addressing areas of high energy consumption, households can significantly reduce their energy bills, saving money in the long run.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption directly translates to lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Increased Energy Independence: By adopting energy-efficient practices and utilizing renewable energy sources, households can reduce their dependence on traditional energy sources, promoting energy independence and resilience.
FAQs on Household Energy Use:
Q: What are the most common energy sources used in homes?
A: The most common energy sources used in homes are electricity and natural gas. However, other sources such as propane, fuel oil, and solar energy are also used in specific regions or for specific purposes.
Q: How can I track my household energy consumption?
A: Several methods can be used to track household energy consumption, including:
- Energy Meters: These devices, installed on individual appliances or the main electrical panel, provide real-time data on energy consumption.
- Smart Meters: These digital meters provide detailed information on energy consumption patterns and can be accessed remotely through online platforms.
- Utility Bills: Analyzing utility bills provides a historical overview of energy consumption trends and can help identify potential areas for improvement.
Q: How can I reduce my household energy consumption?
A: Several strategies can be implemented to reduce household energy consumption, including:
- Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing old appliances with newer, energy-efficient models can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Weatherization: Sealing air leaks, adding insulation, and installing energy-efficient windows and doors can improve home energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs.
- Smart Thermostats: Programmable thermostats can automatically adjust temperatures based on occupancy schedules, optimizing heating and cooling systems and reducing energy consumption.
- LED Lighting: Switching to LED lighting can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Water Conservation: Installing low-flow showerheads, fixing leaks, and using water-efficient appliances can reduce water heating energy consumption.
- Energy Audits: Professional energy audits can identify areas of energy waste and provide tailored recommendations for improvement.
Tips for Reducing Energy Consumption:
- Unplug Electronics: Unplug electronic devices when not in use to prevent phantom load, which occurs when devices are plugged in but not actively used.
- Use Natural Lighting: Utilize natural lighting during the day to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Most clothes can be washed in cold water, significantly reducing the energy needed for heating water.
- Air Dry Clothes: Air drying clothes instead of using a dryer can save a considerable amount of energy.
- Use a Dishwasher Efficiently: Run the dishwasher only when it’s full and use the air-dry setting to reduce energy consumption.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Lowering the thermostat during winter and raising it during summer can significantly reduce heating and cooling energy consumption.
- Consider Renewable Energy: Explore renewable energy options, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to generate electricity for your home.
Conclusion:
Understanding typical household energy use is essential for promoting responsible energy consumption, reducing environmental impact, and achieving financial savings. By identifying key energy consumers, analyzing factors influencing consumption patterns, and implementing energy-efficient strategies, households can significantly reduce their energy footprint, contributing to a more sustainable future. Embracing energy-conscious practices and adopting innovative technologies will play a vital role in shaping a more energy-efficient and environmentally responsible future for generations to come.
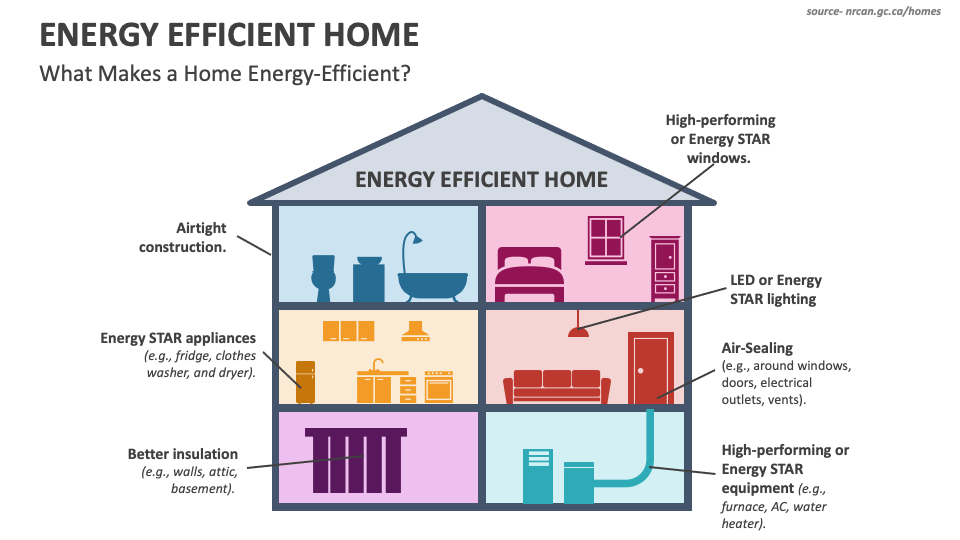





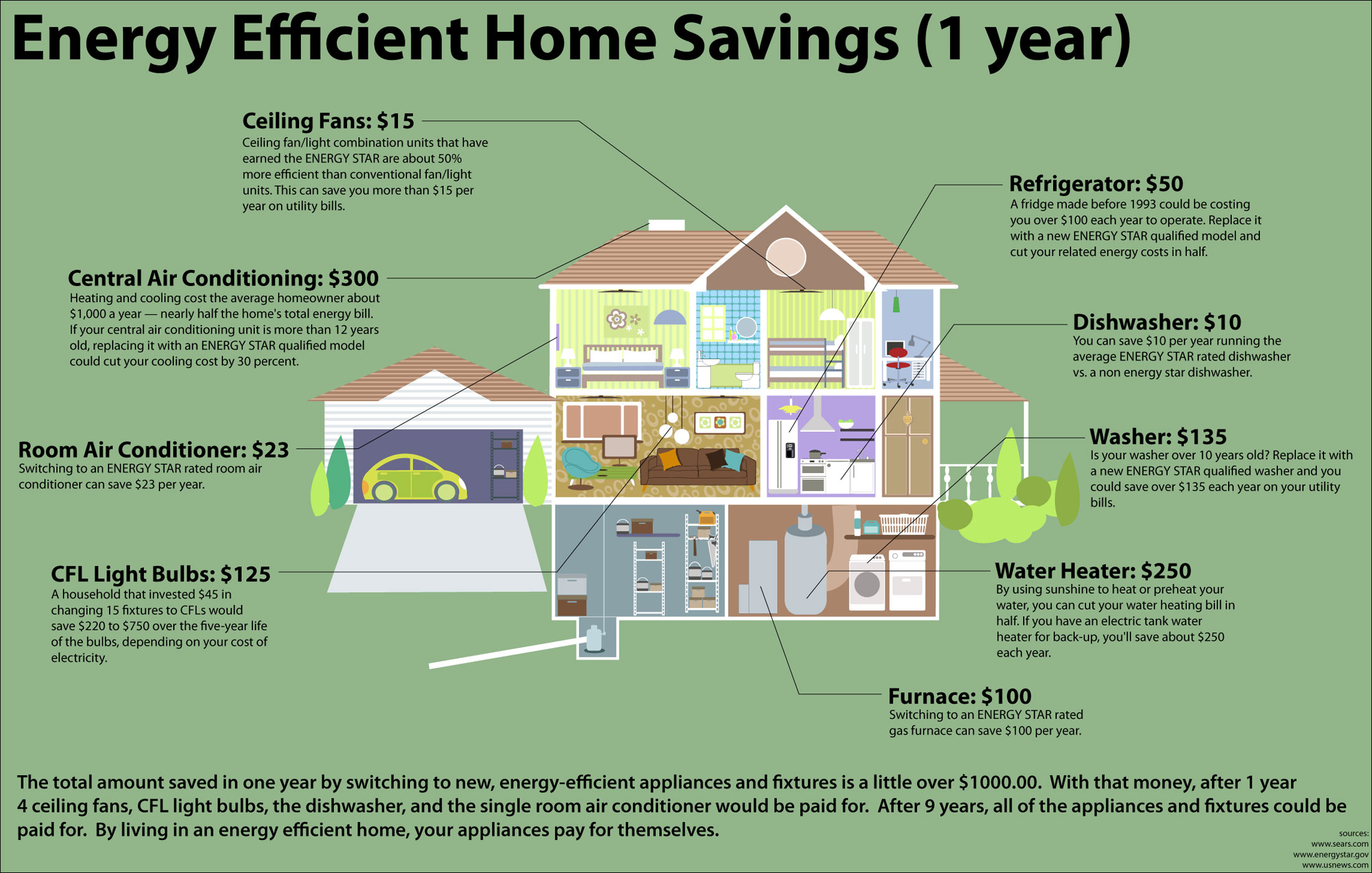

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Energy Landscape of the Modern Home: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!