Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Related Articles: Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
The average household consumes a significant amount of electricity daily, powering everything from lights and appliances to entertainment systems and heating/cooling. This energy consumption, measured in watts (W), is crucial to understand for several reasons. It directly impacts energy bills, environmental sustainability, and even the overall functionality of a home.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of typical household wattage use, exploring the various appliances and devices that contribute to overall energy consumption. It delves into the importance of understanding wattage, highlighting its significance in making informed decisions about energy efficiency and cost savings.
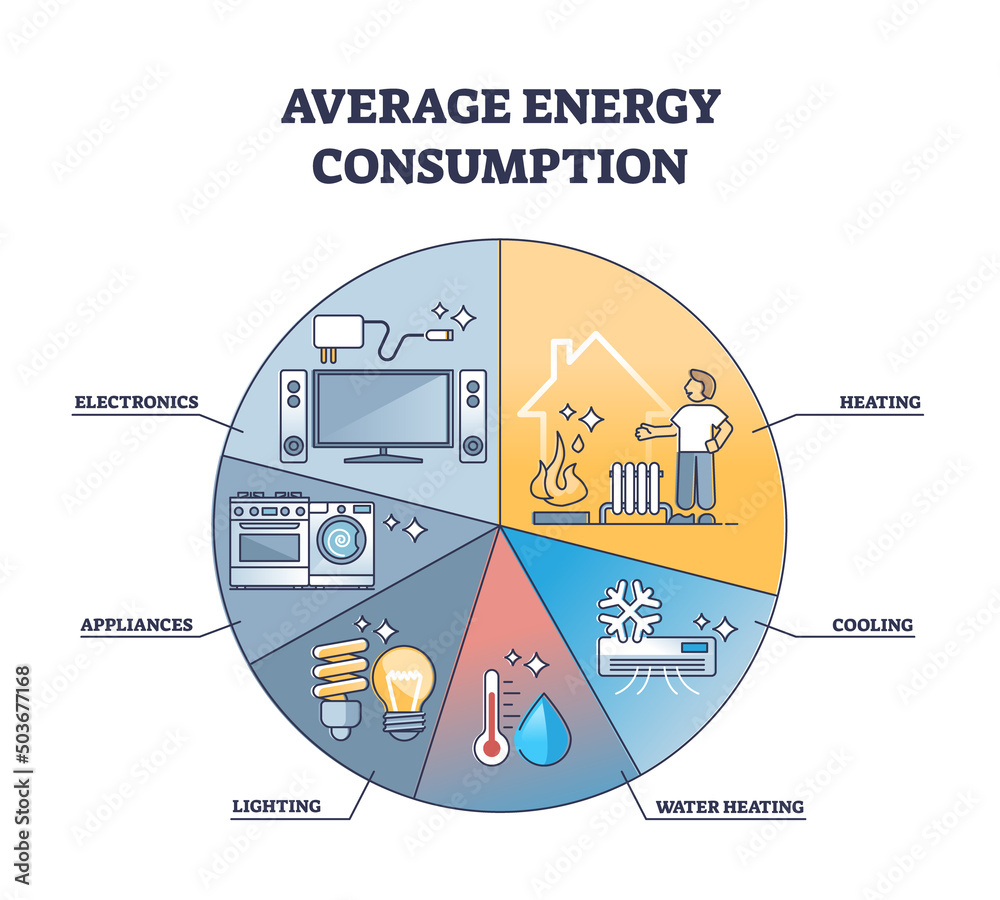
A Breakdown of Typical Household Wattage Use
Understanding the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices is essential for managing energy usage effectively. Here’s a breakdown of common household items and their typical wattage ranges:
1. Lighting
- Incandescent Bulbs: These traditional bulbs are known for their high wattage consumption, typically ranging from 40W to 100W.
- Halogen Bulbs: Similar to incandescent bulbs, halogen bulbs consume a slightly lower wattage, ranging from 20W to 75W.
- Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs): CFLs are significantly more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, consuming between 5W and 15W.
- Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): LEDs are the most energy-efficient lighting option, consuming only 3W to 10W.
2. Appliances
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators are among the highest energy consumers in a household, with wattage ranging from 100W to 200W. Energy-efficient models can reduce this consumption significantly.
- Freezers: Similar to refrigerators, freezers consume a considerable amount of energy, typically ranging from 100W to 200W.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers consume around 1200W to 1800W during operation.
- Washing Machines: Washing machines consume approximately 500W to 1500W depending on the load size and cycle.
- Dryers: Clothes dryers are significant energy consumers, with wattage ranging from 1500W to 5000W.
- Ovens: Electric ovens consume a substantial amount of energy, typically ranging from 2000W to 5000W.
- Microwaves: Microwaves are relatively energy-efficient, consuming around 700W to 1500W during operation.
- Coffee Makers: Coffee makers consume between 500W and 1000W depending on the size and features.
3. Electronics
- Televisions: Televisions consume a varying amount of wattage depending on screen size and technology. Older models can consume up to 200W, while newer LED TVs consume significantly less, around 50W to 100W.
- Computers: Desktop computers consume a considerable amount of energy, ranging from 100W to 500W. Laptops, on the other hand, consume much less, typically between 30W and 100W.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles consume a significant amount of energy, ranging from 100W to 200W.
- Streaming Devices: Streaming devices like Roku and Chromecast consume relatively low wattage, typically around 5W to 15W.
4. Heating and Cooling
- Heating Systems: Heating systems are major energy consumers, with wattage ranging from 1000W to 5000W depending on the type and size of the system.
- Air Conditioners: Air conditioners consume a considerable amount of energy, typically ranging from 1000W to 5000W.
5. Other Devices
- Hair Dryers: Hair dryers consume a significant amount of energy, ranging from 1000W to 2000W.
- Vacuum Cleaners: Vacuum cleaners consume between 500W and 1500W depending on the type and features.
- Electric Kettles: Electric kettles consume around 1000W to 1500W during operation.
The Importance of Understanding Wattage
Understanding wattage consumption is crucial for several reasons:
1. Reducing Energy Bills: By being aware of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can make informed decisions about their energy usage. Choosing energy-efficient models and using appliances sparingly can significantly reduce energy bills.
2. Promoting Environmental Sustainability: Excessive energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. Reducing wattage consumption through energy efficiency measures is crucial for mitigating climate change.
3. Ensuring Safe and Efficient Operation: Understanding wattage consumption is essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation of electrical appliances. Overloading electrical circuits can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
4. Optimizing Home Performance: By understanding the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can optimize their home’s energy performance. This can involve implementing energy-efficient upgrades, such as installing LED lighting or upgrading to energy-efficient appliances.
FAQs about Typical Household Wattage Use
1. What is the average wattage consumption of a typical household?
The average wattage consumption of a typical household varies significantly depending on factors such as the size of the home, the number of occupants, and their energy usage habits. However, it is estimated that the average household in the United States consumes around 10,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year.
2. How can I calculate my household’s wattage consumption?
You can calculate your household’s wattage consumption by monitoring your energy bill and keeping track of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices. You can also use a wattmeter to measure the actual wattage consumption of specific appliances.
3. How can I reduce my household’s wattage consumption?
There are several ways to reduce your household’s wattage consumption:
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Opt for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate energy efficiency.
- Unplug Devices When Not in Use: Unplug devices like phone chargers, laptops, and televisions when not in use to prevent phantom load.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with CFLs or LEDs.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature and avoid unnecessary heating or cooling.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Washing clothes in cold water can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Air Dry Clothes: Air drying clothes instead of using a dryer can save a considerable amount of energy.
- Use a Power Strip: Use a power strip for electronics and turn it off when not in use.
Tips for Reducing Household Wattage Consumption
- Prioritize Energy Efficiency: When purchasing new appliances, prioritize energy efficiency over initial cost.
- Implement a "Power Down" Routine: Make it a habit to turn off lights and appliances when leaving a room.
- Use Natural Light: Maximize natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds.
- Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal air leaks around windows and doors to prevent heat loss.
- Maintain Appliances Regularly: Regular maintenance can improve the efficiency of appliances.
- Consider Solar Energy: Explore the possibility of installing solar panels to generate renewable energy.
Conclusion
Understanding typical household wattage consumption is crucial for managing energy usage effectively. By being aware of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can make informed decisions about their energy usage, reducing energy bills, promoting environmental sustainability, and ensuring safe and efficient operation of their home. Implementing energy efficiency measures can significantly reduce wattage consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future. By adopting these strategies, homeowners can make a positive impact on both their wallets and the environment.

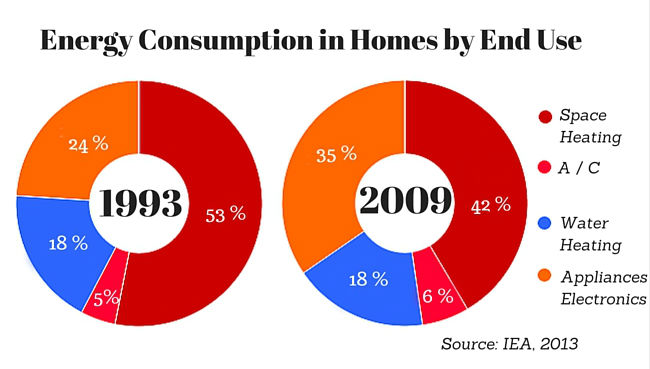
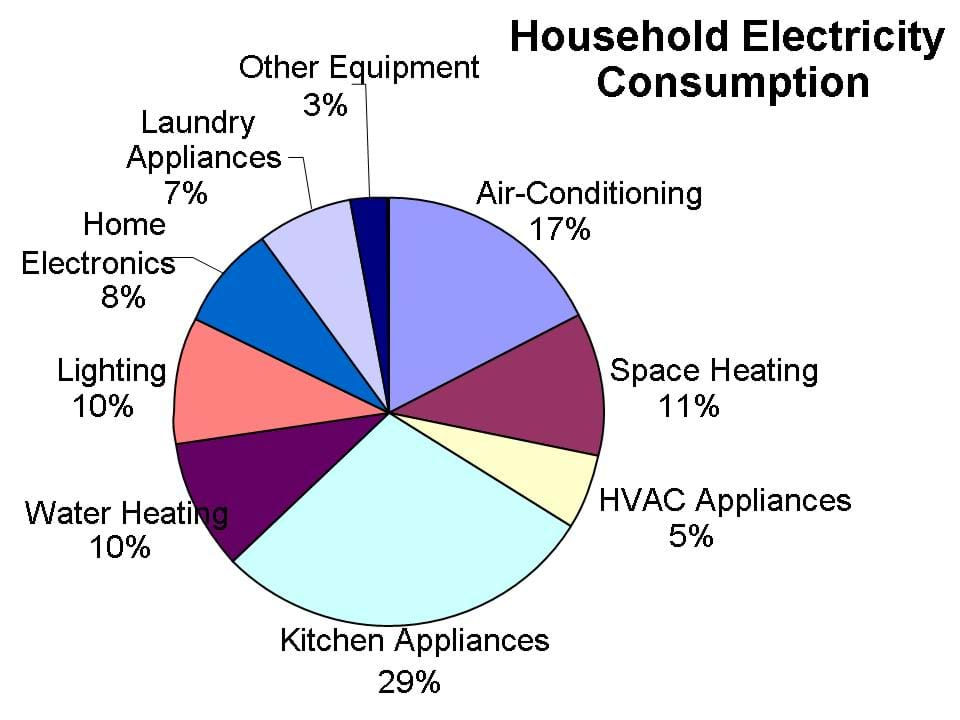
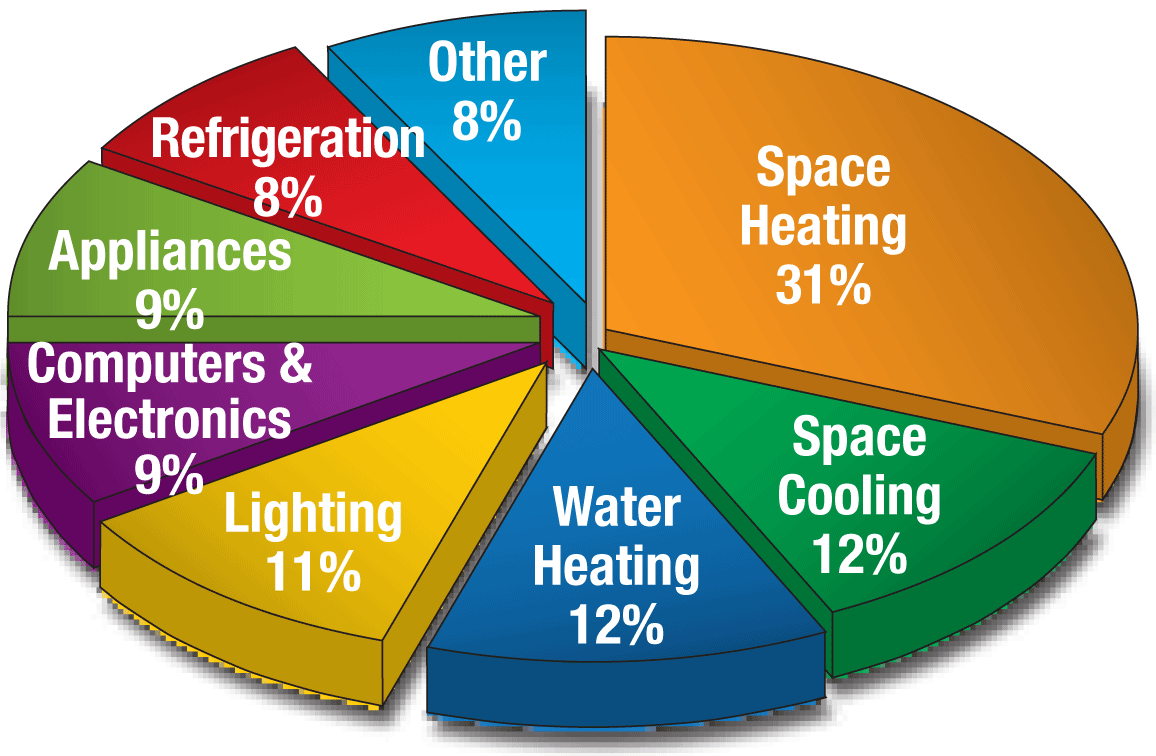



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!