Understanding Household Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Household Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide

Household power consumption, the amount of electricity used by a home, is a crucial aspect of modern life. It directly impacts our energy bills, environmental footprint, and overall energy efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the factors influencing household power consumption, its breakdown across different appliances and activities, and strategies for optimizing energy use.
Factors Influencing Household Power Consumption
Several key factors contribute to a household’s energy consumption, including:
- Household Size and Composition: The number of occupants and their lifestyle habits directly affect power usage. Larger families naturally consume more energy due to increased appliance usage, lighting needs, and heating/cooling requirements.
- Climate and Geographic Location: The climate plays a significant role in heating and cooling demands. Homes in colder regions require more energy for heating during winter, while those in warmer climates need more energy for cooling during summer.
- Housing Size and Insulation: The size of the home and its insulation level significantly impact energy consumption. Larger homes need more energy for heating and cooling, while well-insulated homes minimize energy loss.
- Appliance Usage: Different appliances consume varying amounts of energy. For example, refrigerators and air conditioners are known for their high power consumption compared to lighting or small electronics.
- Lifestyle Habits: Individual behaviors, such as leaving lights on, using excessive hot water, or running appliances unnecessarily, can significantly influence power consumption.
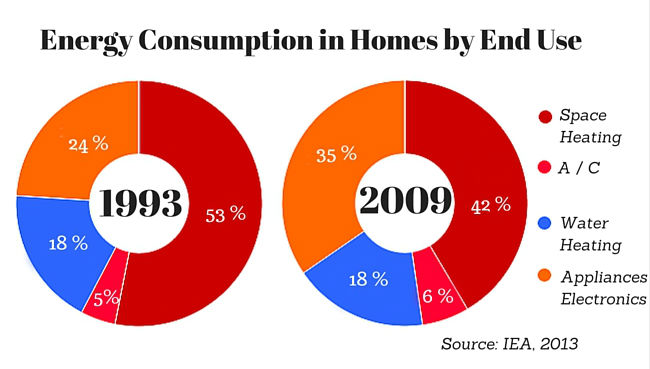
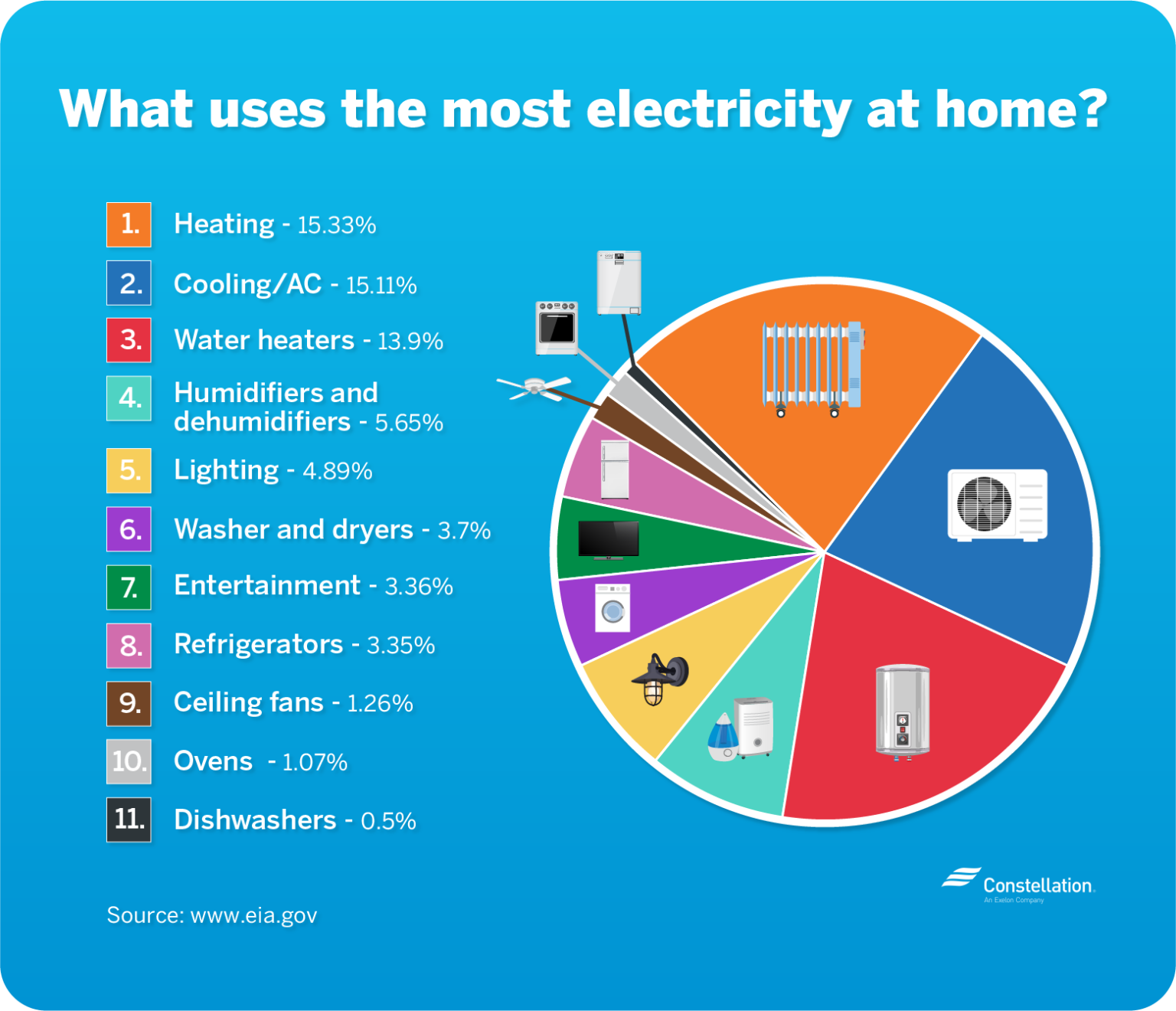
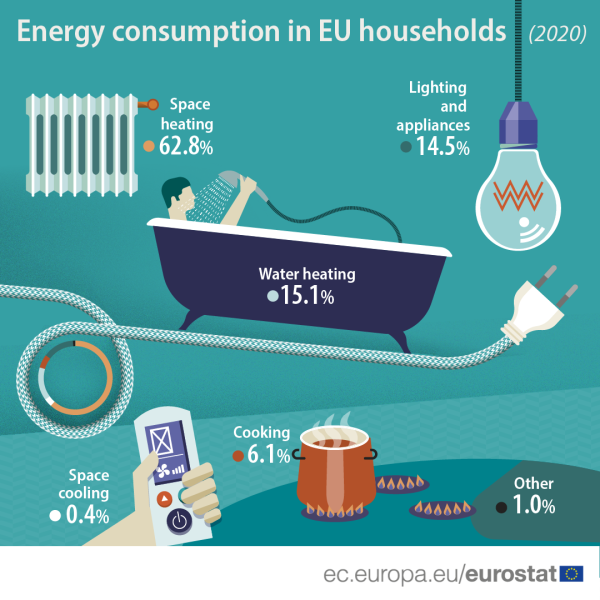
Breakdown of Household Power Consumption
Understanding how energy is consumed across different areas within a home provides valuable insights for optimizing usage. Here’s a typical breakdown of power consumption in a modern household:
- Heating and Cooling: This often accounts for the largest portion of household energy consumption, especially in regions with extreme temperatures. Efficient HVAC systems, proper insulation, and smart thermostats can significantly reduce energy use in this area.
- Water Heating: Heating water for showers, dishwashing, and other household tasks consumes a substantial amount of energy. Installing energy-efficient water heaters, using cold water washing cycles, and minimizing water usage can help reduce this consumption.
- Appliance Usage: Appliances such as refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, and dryers consume significant energy. Choosing energy-efficient models, using appliances appropriately, and optimizing their settings can make a noticeable difference in overall energy consumption.
- Lighting: While individual light bulbs may not consume much energy, the cumulative effect of numerous lights can be significant. Switching to energy-efficient LED bulbs and using natural light whenever possible can significantly reduce lighting-related energy consumption.
- Electronics and Gadgets: Modern homes are filled with electronics like televisions, computers, and gaming consoles. While these devices may not consume as much energy as appliances, their cumulative effect can be substantial, especially if left on standby mode. Unplugging devices when not in use and opting for energy-efficient models can help reduce this consumption.
Importance of Understanding Household Power Consumption
Understanding household power consumption is crucial for several reasons:
- Reducing Energy Costs: By identifying areas of high energy usage and implementing energy-saving measures, households can significantly reduce their electricity bills, resulting in substantial financial savings over time.
- Promoting Environmental Sustainability: Reducing household power consumption directly contributes to lowering greenhouse gas emissions, minimizing our environmental impact, and promoting a more sustainable future.
- Improving Energy Efficiency: Understanding power consumption patterns allows for informed decisions regarding appliance upgrades, home insulation, and energy-saving practices, resulting in a more energy-efficient and sustainable home.
FAQs on Household Power Consumption
Q: What is the average household power consumption in the United States?
A: The average American household consumes approximately 10,972 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year. However, this figure varies significantly depending on factors such as household size, climate, and energy efficiency practices.
Q: How can I track my household power consumption?
A: Several methods can help track household power consumption:
- Smart Meters: Many utilities offer smart meters that provide real-time energy usage data, allowing homeowners to monitor their consumption patterns.
- Energy Monitoring Devices: Various devices, such as plug-in energy monitors and home energy management systems, can track the energy consumption of individual appliances and provide detailed insights into household power usage.
- Utility Bills: Analyzing past utility bills can reveal trends in energy consumption and identify potential areas for improvement.
Q: What are some effective ways to reduce household power consumption?
A: Several strategies can help reduce household power consumption:
- Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances: Replacing older appliances with energy-efficient models can significantly reduce energy consumption. Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate high energy efficiency.
- Improve Home Insulation: Proper insulation helps minimize heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Switch to LED bulbs, which use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Unplug Devices When Not in Use: Even when turned off, many electronics continue to consume energy in standby mode. Unplugging them when not in use can significantly reduce energy waste.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Optimize thermostat settings for heating and cooling, and consider using smart thermostats that can automatically adjust temperatures based on occupancy and weather conditions.
- Practice Water Conservation: Take shorter showers, install low-flow showerheads, and fix leaks to reduce water heating energy consumption.
- Utilize Natural Light: Maximize natural light during the day by keeping curtains open and using task lighting only when necessary.
- Reduce Appliance Usage: Use appliances efficiently, such as washing full loads of laundry and running the dishwasher only when it’s full.
Conclusion
Understanding household power consumption is essential for managing energy costs, promoting environmental sustainability, and improving energy efficiency. By identifying areas of high consumption, implementing energy-saving strategies, and making informed choices regarding appliances and home improvements, households can significantly reduce their energy footprint, contributing to a more sustainable future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Power Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!