Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide

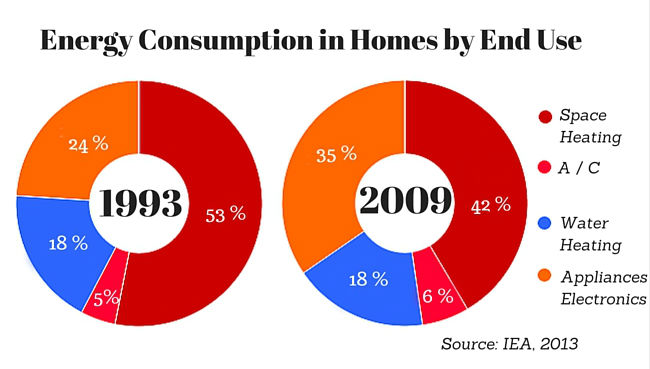
Electricity is the lifeblood of modern households, powering everything from lighting and heating to appliances and entertainment systems. Understanding how electricity is used within a home is crucial for both financial and environmental sustainability. This article provides a comprehensive overview of typical household electricity usage, exploring its key components, influencing factors, and strategies for optimization.
Components of Household Electricity Consumption:
Household electricity usage can be categorized into various components, each with its unique contribution to overall consumption:
1. Lighting:
Lighting accounts for a significant portion of household electricity usage, particularly in homes with older, less energy-efficient incandescent bulbs. Modern LED bulbs offer substantial energy savings, consuming significantly less power while providing comparable brightness.
2. Appliances:
Appliances, ranging from refrigerators and washing machines to ovens and microwaves, are major electricity consumers. Their energy efficiency varies considerably, with older models often consuming significantly more energy than newer, more energy-efficient counterparts.
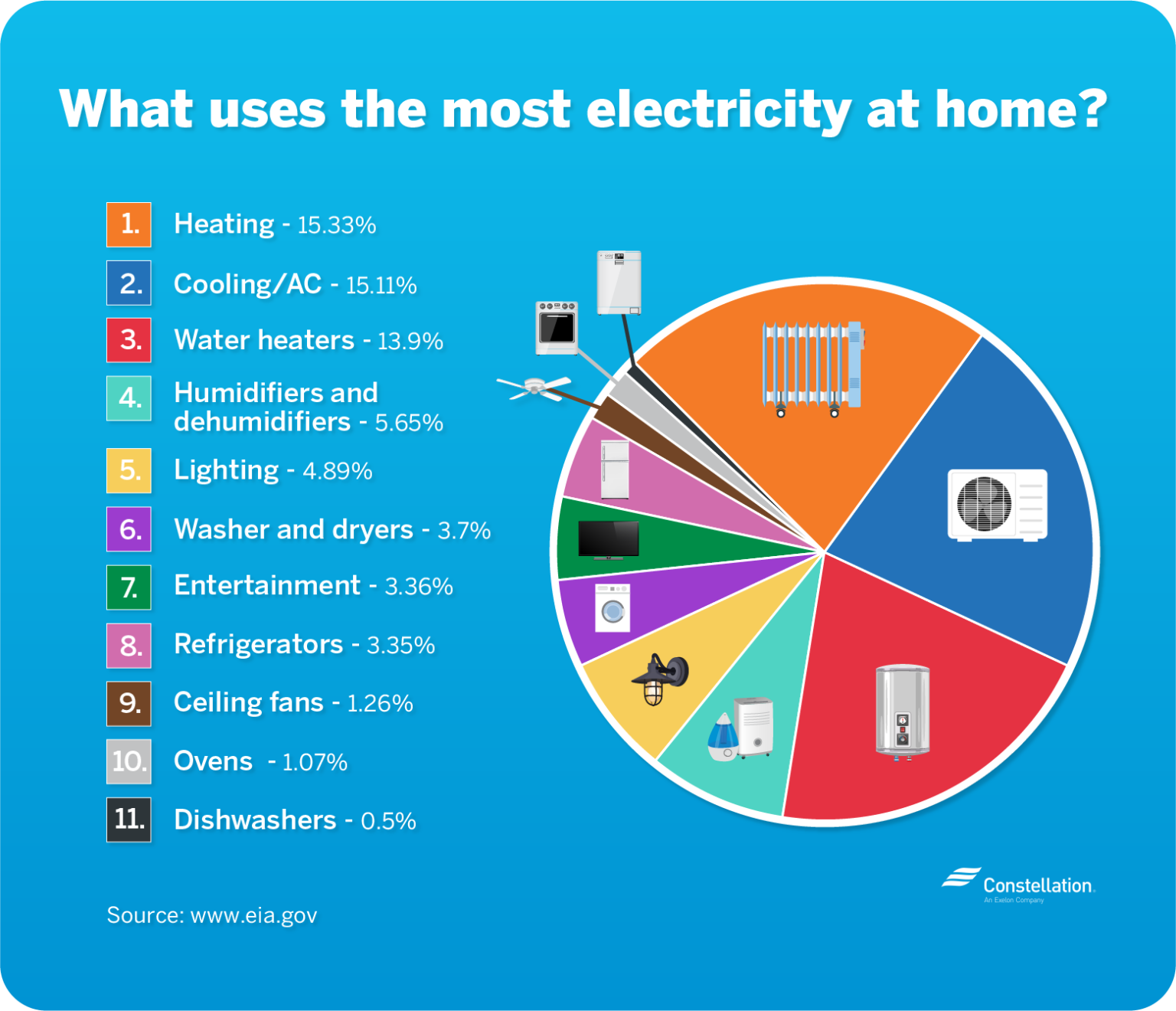
3. Heating and Cooling:
Heating and cooling systems, including furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps, are significant electricity consumers, especially in regions with extreme temperatures. Efficient insulation, proper ventilation, and programmable thermostats can help optimize energy usage for temperature control.
4. Electronics and Entertainment:
Televisions, computers, gaming consoles, and other electronics contribute to household electricity usage. While these devices typically consume less power than appliances, their cumulative impact can be significant, especially when left on standby mode.
5. Water Heating:
Water heating is another major electricity consumer, especially in homes with electric water heaters. Tankless water heaters, which heat water on demand, offer greater energy efficiency compared to traditional tank-style heaters.
Factors Influencing Household Electricity Consumption:
Several factors influence household electricity consumption, including:
1. Household Size and Composition:
Larger households with more individuals generally consume more electricity, as they require more lighting, appliances, and heating/cooling. The presence of children and teenagers can also increase energy consumption due to increased use of electronics and appliances.
2. Climate and Location:
Climate significantly impacts electricity usage for heating and cooling. Homes in regions with extreme temperatures require more energy to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. Location can also influence electricity usage, as energy prices and availability vary across regions.
3. Home Size and Insulation:
Larger homes generally require more energy for heating, cooling, and lighting. Adequate insulation plays a crucial role in reducing energy loss, minimizing the need for heating and cooling, and lowering overall electricity consumption.
4. Lifestyle and Habits:
Individual lifestyle and habits can significantly influence electricity usage. For example, frequent use of appliances, leaving lights on in unoccupied rooms, and keeping electronics plugged in when not in use can all contribute to higher electricity consumption.
5. Appliance Efficiency:
The energy efficiency of appliances plays a significant role in electricity consumption. Newer, energy-efficient models consume significantly less power compared to older, less efficient counterparts.
Optimizing Household Electricity Consumption:
Several strategies can help optimize household electricity consumption and reduce energy costs:
1. Energy-Efficient Lighting:
Replacing traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs can significantly reduce lighting energy consumption. LED bulbs consume significantly less power while providing comparable brightness, resulting in substantial energy savings over their lifetime.
2. Appliance Efficiency:
Choosing energy-efficient appliances can significantly reduce electricity usage. Look for appliances with Energy Star certification, which indicates they meet specific energy efficiency standards.
3. Smart Home Technology:
Smart home technology, such as programmable thermostats and smart plugs, can help optimize energy usage by automatically adjusting appliance settings based on occupancy and usage patterns.
4. Home Insulation and Weatherization:
Proper home insulation and weatherization can significantly reduce energy loss, minimizing the need for heating and cooling and reducing overall electricity consumption.
5. Energy Audits:
Conducting an energy audit can identify specific areas of energy waste within a home. Professional energy auditors can assess insulation, ventilation, and appliance efficiency, providing recommendations for improvement.
6. Behavioral Changes:
Simple behavioral changes can also significantly impact electricity consumption. Turning off lights in unoccupied rooms, unplugging electronics when not in use, and avoiding unnecessary appliance usage can all contribute to energy savings.
7. Renewable Energy Sources:
Exploring renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, can help reduce reliance on traditional electricity sources and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
FAQs Regarding Household Electricity Usage:
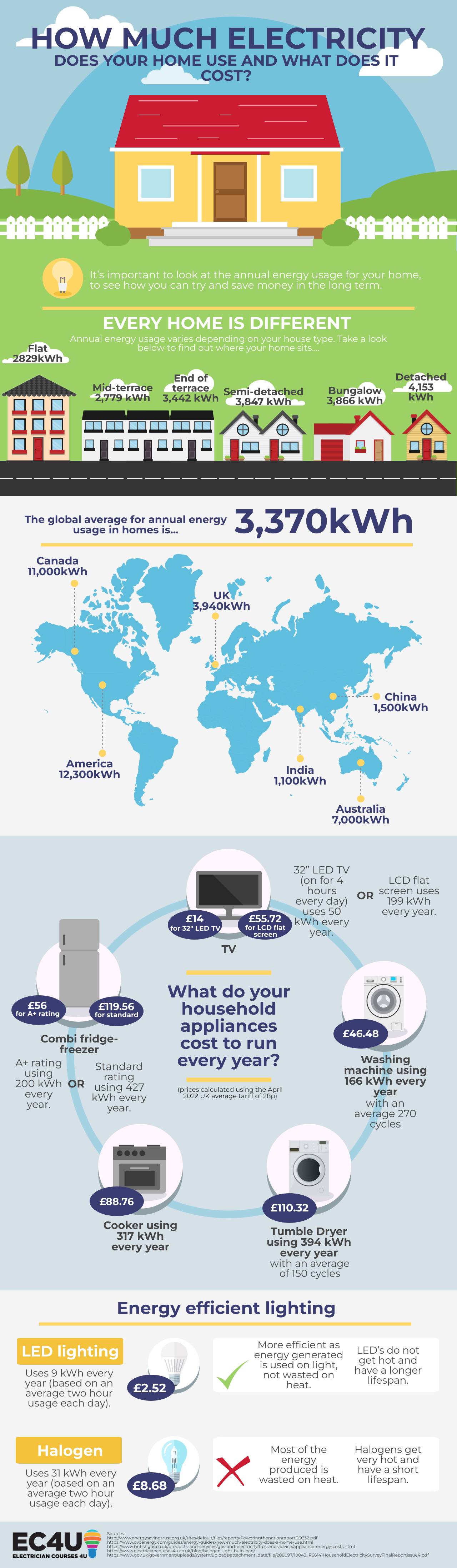
1. What is the average household electricity consumption in the United States?
The average household in the United States consumes approximately 10,972 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year. However, this figure can vary significantly based on factors such as home size, climate, and individual usage habits.
2. How can I track my household electricity consumption?
Many utility companies provide online portals or mobile apps that allow customers to track their electricity usage in real-time. Smart meters can also provide detailed consumption data, helping identify areas for potential energy savings.
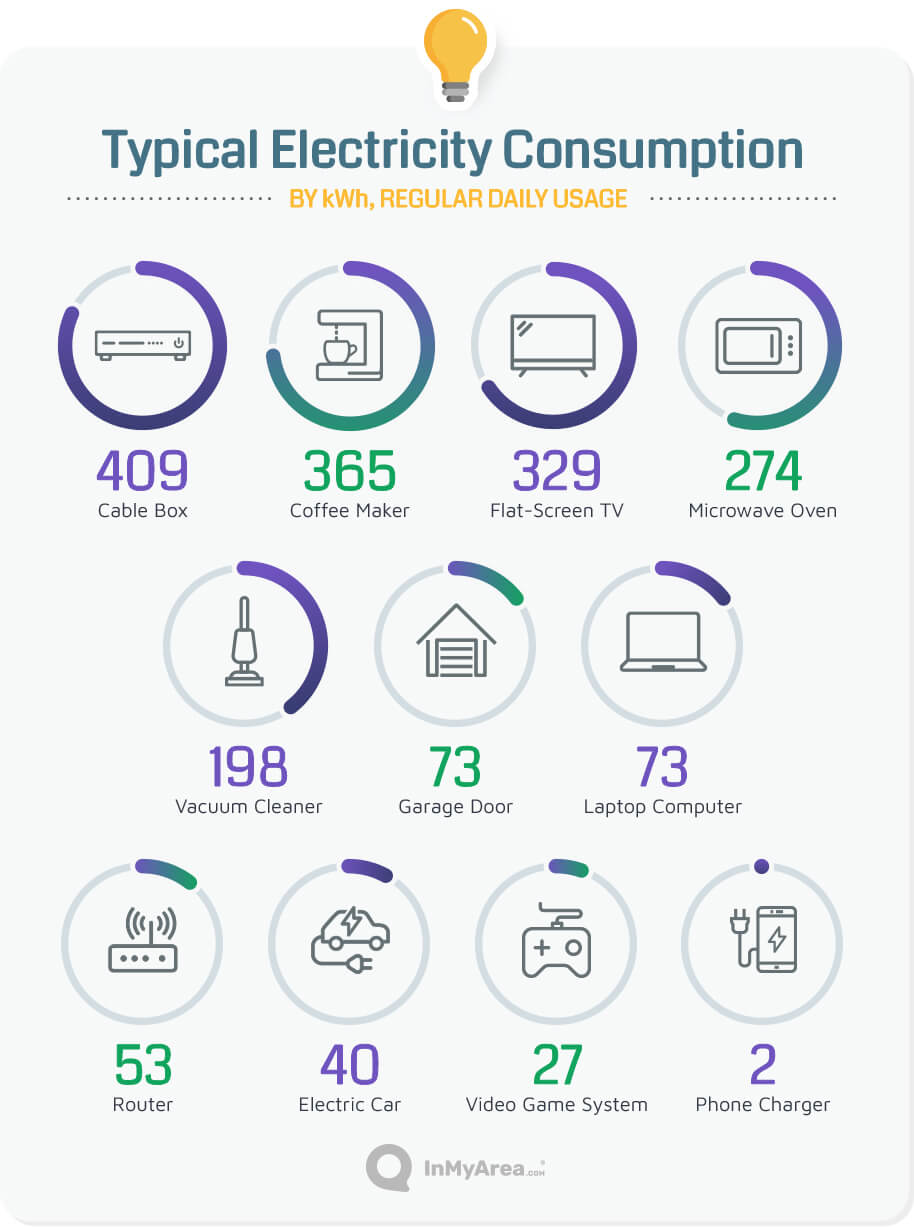
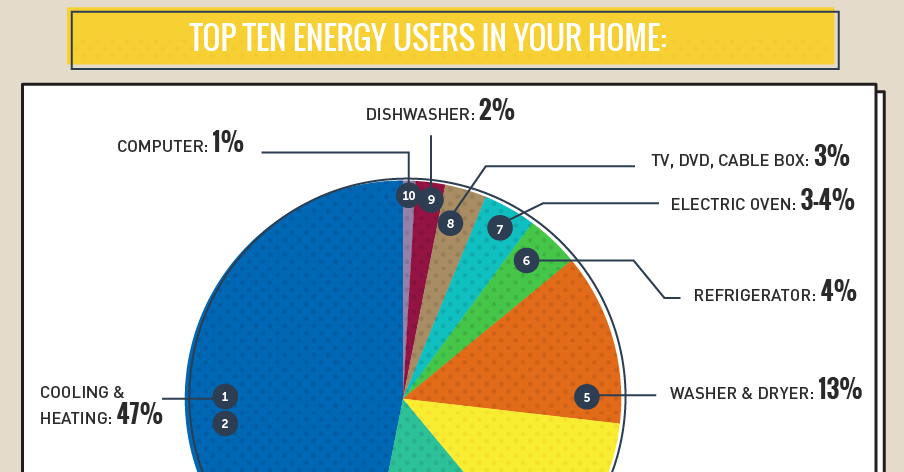
3. What are the most energy-consuming appliances in a typical household?
The most energy-consuming appliances in a typical household typically include refrigerators, water heaters, ovens, and air conditioners. The specific appliances with the highest energy consumption will vary depending on individual usage patterns and appliance efficiency.
4. How can I reduce my electricity bill?
By implementing energy-saving strategies, such as upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, optimizing heating and cooling systems, and adopting energy-conscious behaviors, you can significantly reduce your electricity bill.
5. What are the benefits of reducing household electricity consumption?
Reducing household electricity consumption not only saves money on energy bills but also contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
Tips for Reducing Household Electricity Consumption:
1. Unplug Unused Electronics:
Unplug electronics when not in use, as they continue to consume energy in standby mode.
2. Use Natural Light:
Maximize natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
3. Optimize Heating and Cooling:
Set thermostats to optimal temperatures and use programmable thermostats to adjust settings based on occupancy and usage patterns.
4. Wash Clothes in Cold Water:
Washing clothes in cold water significantly reduces energy consumption for water heating.
5. Air Dry Clothes:
Air drying clothes instead of using a dryer saves energy and reduces reliance on electricity.
Conclusion:
Understanding household electricity consumption is essential for both financial and environmental sustainability. By adopting energy-efficient practices, optimizing appliance usage, and implementing behavioral changes, individuals can significantly reduce their electricity consumption and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
This comprehensive overview provides valuable insights into the components, influencing factors, and optimization strategies for household electricity usage, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and contribute to a more energy-conscious lifestyle.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Electricity Consumption: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!