Understanding Financial Habits: A Deeper Look at Spending Patterns in Low-Income Households
Related Articles: Understanding Financial Habits: A Deeper Look at Spending Patterns in Low-Income Households
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Financial Habits: A Deeper Look at Spending Patterns in Low-Income Households. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Financial Habits: A Deeper Look at Spending Patterns in Low-Income Households

While the term "waste" can be subjective and dependent on individual circumstances, there are certain spending habits prevalent in low-income households that can hinder financial stability and limit opportunities for progress. These habits, often driven by immediate needs, lack of access to resources, or limited financial literacy, can contribute to a cycle of poverty. This article aims to shed light on these spending patterns, providing a comprehensive understanding of their underlying causes and potential solutions.
The Complexities of Spending in Low-Income Households:
It is crucial to approach this topic with sensitivity and understanding. Low-income individuals often face significant challenges, including limited access to affordable housing, healthcare, and education. These challenges can lead to financial pressures that force them to prioritize immediate needs over long-term financial planning.
Common Spending Patterns:
1. High-Cost Credit:
Low-income households often rely on high-cost credit, such as payday loans or rent-to-own agreements, to meet immediate financial needs. These options, while seemingly convenient, come with exorbitant interest rates and fees, trapping individuals in a cycle of debt.
2. Overspending on Food:
Food insecurity is a significant concern for low-income families. However, limited access to affordable and nutritious food options can lead to overspending on processed and less healthy foods, which can contribute to health problems and further strain finances.
3. Utility Bills:
High energy costs can disproportionately impact low-income households. Lack of insulation, inefficient appliances, and limited access to energy assistance programs can lead to high utility bills, further reducing disposable income.
4. Transportation Costs:
Lack of reliable transportation can significantly impact employment opportunities and access to essential services. Relying on expensive taxis or car payments can consume a large portion of income, leaving little room for savings or other necessities.
5. Entertainment and Recreation:
While entertainment and recreation are essential for well-being, excessive spending in these areas can negatively impact financial stability. This can be particularly challenging for families with children, who may be subject to peer pressure or societal expectations regarding entertainment.
6. Lack of Financial Literacy:
Limited financial literacy can hinder individuals’ ability to manage their finances effectively. This includes a lack of understanding about budgeting, saving, investing, and navigating the complexities of the financial system.
Understanding the Underlying Causes:
Several factors contribute to these spending patterns:
- Lack of Resources: Limited access to affordable housing, healthcare, and education can create financial burdens that leave little room for savings or long-term planning.
- Financial Stress: Living paycheck to paycheck and facing unexpected expenses can lead to impulsive spending and reliance on high-cost credit.
- Limited Financial Literacy: Lack of knowledge about budgeting, saving, and investing can make it difficult for individuals to make informed financial decisions.
- Social and Cultural Factors: Societal pressures and expectations regarding consumerism and entertainment can influence spending habits, even when financial resources are limited.
The Importance of Addressing These Spending Patterns:
Breaking these cycles requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both individual and systemic factors:
- Financial Education: Programs that provide financial literacy training can equip individuals with the skills and knowledge to manage their finances effectively.
- Access to Resources: Expanding access to affordable housing, healthcare, and education can alleviate financial burdens and create opportunities for economic advancement.
- Government Assistance: Expanding access to food assistance, energy assistance, and other government programs can help mitigate financial hardship and provide a safety net for low-income families.
- Community-Based Initiatives: Community organizations can provide support and resources, such as financial counseling, job training, and affordable housing options.
FAQs:
Q: What are some common examples of high-cost credit that low-income households use?
A: Common examples include payday loans, rent-to-own agreements, and pawn shop loans. These options often come with exorbitant interest rates and fees, trapping individuals in a cycle of debt.
Q: How can overspending on food impact low-income households?
A: Overspending on processed and less healthy foods can lead to health problems, such as obesity and diabetes, which can further strain finances through increased healthcare costs.
Q: What are some ways to reduce utility bills for low-income households?
A: Implementing energy-efficient measures, such as insulation and efficient appliances, can significantly reduce energy consumption and utility bills. Accessing energy assistance programs can also provide financial relief.
Q: How can lack of reliable transportation impact financial stability?
A: Lack of reliable transportation can limit employment opportunities and access to essential services, leading to lost income and increased expenses for alternative transportation options.
Q: What are some strategies for improving financial literacy among low-income individuals?
A: Financial literacy programs offered through community organizations, schools, and government agencies can provide individuals with the skills and knowledge to manage their finances effectively.
Tips for Managing Finances:
- Create a Budget: Track income and expenses to identify areas for potential savings.
- Prioritize Needs Over Wants: Focus on essential expenses, such as housing, food, and healthcare, before allocating funds to discretionary spending.
- Explore Affordable Options: Seek out affordable alternatives for transportation, food, and entertainment.
- Negotiate Bills: Contact utility companies and creditors to discuss payment plans or potential discounts.
- Seek Financial Counseling: Consult with a financial counselor for personalized advice and support in managing finances.
Conclusion:
Understanding the spending patterns in low-income households requires acknowledging the complex factors that contribute to these habits. Addressing these patterns through financial education, access to resources, and government assistance can empower individuals to break the cycle of poverty and achieve financial stability. By promoting financial literacy and providing support, we can create a more equitable society where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.






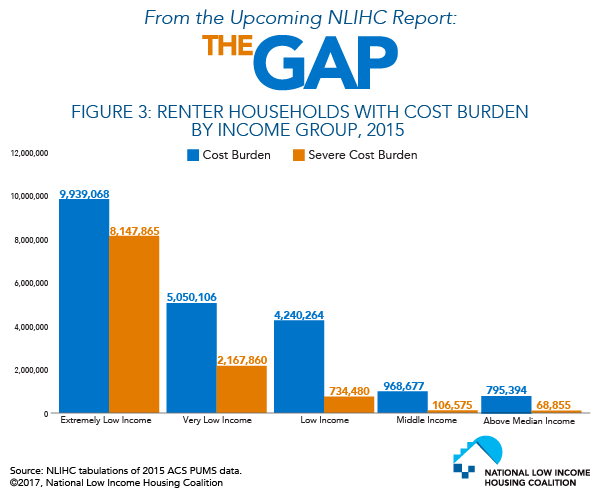
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Financial Habits: A Deeper Look at Spending Patterns in Low-Income Households. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!