The Ubiquitous Presence of Benzene: A Look at its Applications and Considerations
Related Articles: The Ubiquitous Presence of Benzene: A Look at its Applications and Considerations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Ubiquitous Presence of Benzene: A Look at its Applications and Considerations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ubiquitous Presence of Benzene: A Look at its Applications and Considerations
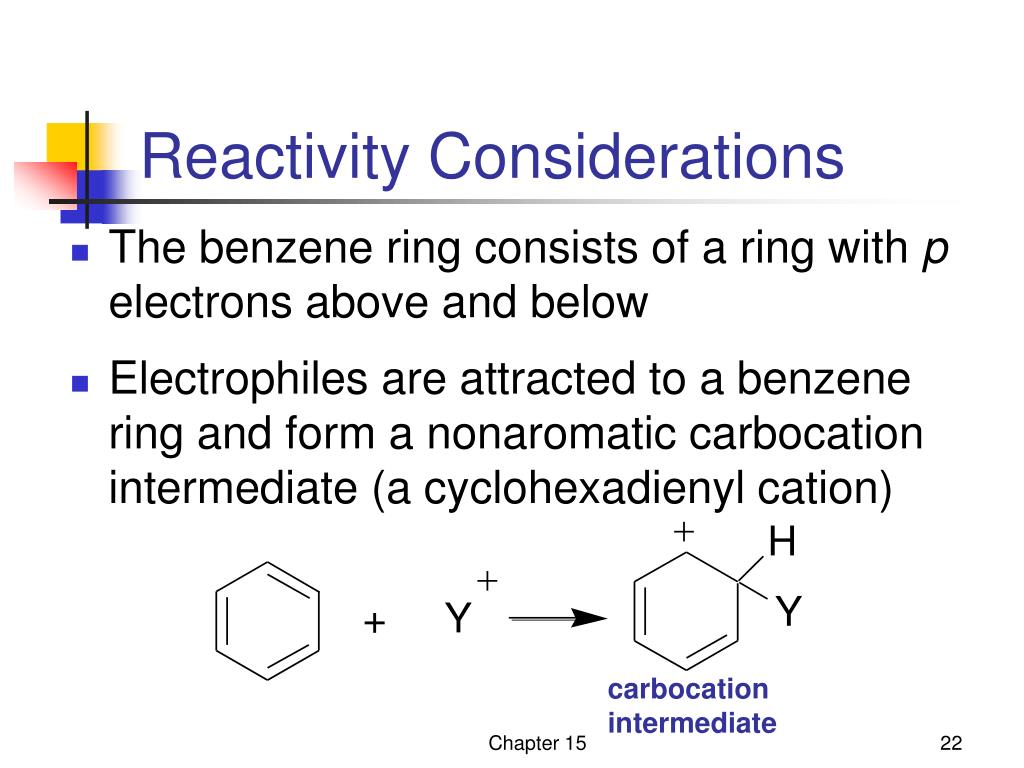
Benzene, a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet odor, is a fundamental building block in the chemical industry. Its unique molecular structure, a six-carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds, grants it remarkable versatility, making it a key ingredient in the production of countless everyday products. While its benefits are undeniable, the inherent toxicity of benzene requires careful handling and awareness of its potential risks.
Benzene’s Journey from the Lab to Everyday Life:
Benzene’s journey from the laboratory to everyday life is a testament to its multifaceted nature. It serves as a raw material for the synthesis of a vast array of chemicals, including:
- Plastics: Benzene is a precursor to polystyrene, a versatile plastic used in packaging, insulation, and disposable cups.
- Synthetic Rubber: Styrene, derived from benzene, is a crucial component in the production of synthetic rubber, a vital material in tires, hoses, and other rubber products.
- Dyes and Pigments: Benzene derivatives find applications in the vibrant world of dyes and pigments, contributing to the color of textiles, paints, and inks.
- Detergents and Cleaning Agents: Benzene’s derivatives, such as alkylbenzenesulfonates, are essential components in detergents and cleaning agents, enhancing their cleaning power.
- Pharmaceuticals: Benzene-derived compounds are incorporated into numerous pharmaceuticals, including pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, and antibiotics.
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Certain benzene derivatives, such as chlorobenzene, are used in the formulation of pesticides and herbicides, aimed at protecting crops and controlling pests.
Beyond its Direct Use: The Role of Benzene in Industrial Processes:
Benzene’s influence extends beyond its direct use in consumer products. It plays a vital role in various industrial processes:
- Fuel Production: Benzene is a component of gasoline, contributing to its octane rating and improving engine performance.
- Solvent Applications: Its solvent properties make benzene suitable for dissolving various substances, including resins, oils, and fats, finding applications in various industries.
- Chemical Intermediates: Benzene serves as a crucial intermediate in the production of numerous chemicals, including nylon, polyester, and other synthetic fibers.
Navigating the Complexities: Understanding Benzene’s Risks and Benefits:
While benzene’s contributions to modern life are undeniable, its inherent toxicity poses a significant concern. Prolonged exposure to benzene can lead to various health problems, including:
- Leukemia: Benzene is a known carcinogen, increasing the risk of developing leukemia, a type of blood cancer.
- Bone Marrow Suppression: Exposure to benzene can suppress bone marrow function, leading to a decrease in the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Reproductive Health Issues: Benzene exposure has been linked to reproductive health problems, including infertility and miscarriage.
- Respiratory Issues: Inhalation of benzene can cause respiratory problems, including coughing, shortness of breath, and pneumonia.
Minimizing Risks: Safe Handling and Exposure Control:
To mitigate the risks associated with benzene, stringent safety protocols are crucial:
- Proper Ventilation: Ensuring adequate ventilation in areas where benzene is handled is essential to prevent the buildup of harmful vapors.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Workers handling benzene should wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, respirators, and protective clothing, to minimize skin and respiratory exposure.
- Safe Storage and Transportation: Benzene should be stored in tightly sealed containers in well-ventilated areas, and its transportation should adhere to strict safety regulations.
- Exposure Monitoring: Regular monitoring of benzene levels in the workplace and environment is crucial to ensure that exposure remains below safe limits.
FAQs About Benzene:
1. What are the symptoms of benzene poisoning?
Symptoms of benzene poisoning can vary depending on the level of exposure and individual sensitivity. Common symptoms include headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and skin irritation. In severe cases, benzene poisoning can lead to coma and death.
2. How is benzene exposure monitored?
Benzene exposure can be monitored through various methods, including air sampling, urine testing, and blood testing. These methods provide valuable insights into the levels of benzene exposure and help in identifying potential risks.
3. Is benzene used in household products?
Benzene is not typically used directly in household products. However, some products, such as paints, glues, and cleaning agents, may contain small amounts of benzene as a component of their ingredients.
4. What are the alternatives to benzene in industrial processes?
Researchers and industry leaders are continually exploring alternative chemicals and processes to reduce the reliance on benzene. Some promising alternatives include toluene, xylene, and cyclohexane, which offer similar properties with lower toxicity.
5. What are the long-term health effects of benzene exposure?
Prolonged or repeated exposure to benzene can have serious long-term health consequences, including an increased risk of leukemia, bone marrow suppression, reproductive health issues, and other chronic illnesses.
Tips for Reducing Benzene Exposure:
- Avoid using products containing benzene whenever possible.
- Ensure adequate ventilation in areas where benzene is handled or stored.
- Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, respirators, and protective clothing, when handling benzene.
- Store benzene in tightly sealed containers in well-ventilated areas.
- Dispose of benzene-containing products properly, following local regulations.
- Be aware of potential benzene sources in your environment, such as vehicle exhaust and industrial emissions.
Conclusion:
Benzene’s journey from the laboratory to everyday life highlights its remarkable versatility and importance in the chemical industry. However, its inherent toxicity demands careful handling and awareness of potential risks. By adhering to safety protocols, minimizing exposure, and exploring alternative chemicals and processes, we can harness the benefits of benzene while safeguarding human health and the environment. Continuous research and innovation are crucial to minimizing the risks associated with benzene and ensuring its responsible use in a sustainable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ubiquitous Presence of Benzene: A Look at its Applications and Considerations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!