The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Related Articles: The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Recycling, the process of converting waste materials into reusable objects, is a crucial aspect of environmental sustainability. It plays a vital role in conserving natural resources, reducing pollution, and mitigating the impact of our consumption on the planet. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of the materials that should be recycled, the benefits of recycling, and the best practices for maximizing its effectiveness.
Materials that Should be Recycled
The materials that can and should be recycled vary depending on local regulations and the availability of recycling facilities. However, some common materials are consistently recyclable and contribute significantly to environmental protection. These include:
Paper and Cardboard:
- Types: Newspapers, magazines, office paper, cardboard boxes, paper bags, junk mail, and paperboard packaging.
- Benefits: Recycling paper reduces the need to harvest trees, thereby protecting forests and reducing carbon emissions. It also conserves water and energy used in paper production.
- Tips: Flatten cardboard boxes to save space and remove plastic windows or tape before recycling. Ensure paper is clean and free of food residue.
Plastic:
- Types: Plastic bottles (PET), milk jugs (HDPE), grocery bags (LDPE), food containers (PP), and other recyclable plastic items.
- Benefits: Recycling plastic reduces the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills, where it can take hundreds of years to decompose. It also conserves oil resources used in plastic production.
- Tips: Rinse plastic containers thoroughly to remove food residue and ensure they are empty. Check local recycling guidelines for specific plastic types accepted in your area.
Aluminum and Steel Cans:
- Types: Aluminum beverage cans, steel food cans, and other metal containers.
- Benefits: Recycling aluminum and steel cans saves energy and reduces the need for mining new resources. It also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Tips: Rinse cans thoroughly to remove food residue and crush them to save space. Ensure cans are free of any non-recyclable materials like plastic lids.
Glass:
- Types: Glass bottles and jars, including clear, green, and brown glass.
- Benefits: Recycling glass saves energy and reduces the need for raw materials in glass production. It also reduces the amount of glass waste that ends up in landfills.
- Tips: Rinse glass containers thoroughly and remove any non-recyclable materials like metal lids. Separate glass by color if instructed by local guidelines.
Electronic Waste (E-Waste):
- Types: Computers, laptops, smartphones, televisions, printers, and other electronic devices.
- Benefits: Recycling e-waste prevents harmful substances like lead and mercury from contaminating landfills and the environment. It also recovers valuable materials for reuse.
- Tips: Dispose of e-waste responsibly through designated collection points or recycling programs. Avoid throwing e-waste in regular trash.
Other Recyclable Materials:
- Textiles: Old clothing, bedding, towels, and other fabric items.
- Batteries: Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries.
- Batteries: Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries.
- Construction and Demolition Debris: Wood, concrete, metal, and other materials from construction and renovation projects.
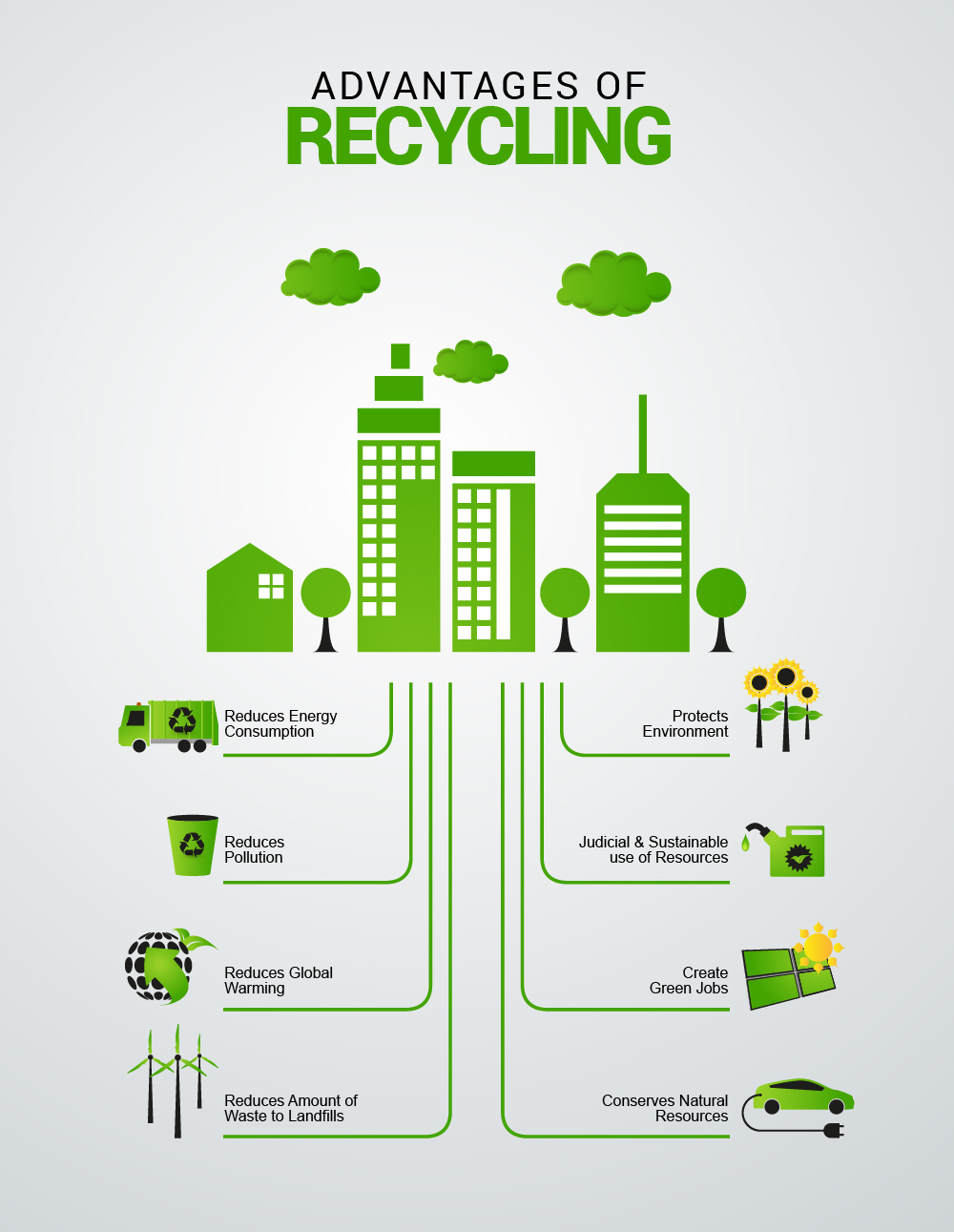
Benefits of Recycling
Recycling offers a multitude of benefits, both environmental and economic, making it a crucial practice for a sustainable future:
Environmental Benefits:
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Recycling conserves valuable natural resources like trees, minerals, and fossil fuels, which are used in the production of new materials.
- Pollution Reduction: Recycling reduces pollution from manufacturing new products, including air, water, and land pollution.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Recycling helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing and waste disposal.
- Landfill Space Reduction: Recycling reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, extending their lifespan and minimizing environmental impacts.
Economic Benefits:
- Job Creation: Recycling creates jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing industries.
- Resource Recovery: Recycling recovers valuable materials from waste, reducing the need for new resources and saving costs.
- Energy Savings: Recycling saves energy compared to manufacturing new products from raw materials.
- Economic Growth: Recycling contributes to a circular economy, where resources are used more efficiently and waste is minimized, promoting sustainable economic growth.
Best Practices for Recycling
To maximize the effectiveness of recycling efforts, it is essential to follow best practices:
- Check Local Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with local recycling guidelines and regulations, as they vary by region.
- Clean and Empty Containers: Rinse and empty containers to remove food residue and other contaminants.
- Separate Materials: Separate different materials for recycling, such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
- Avoid Contamination: Do not mix recyclable materials with non-recyclable items.
- Use Recycling Bins: Use designated recycling bins or containers for recyclable materials.
- Support Recycling Programs: Participate in local recycling programs and initiatives to promote recycling.
- Reduce Waste Generation: Reduce waste generation in the first place by using reusable items and purchasing products with minimal packaging.
FAQs on Recycling
Q: What happens to recycled materials?
A: Recycled materials are collected, sorted, and processed into new products. Paper is recycled into new paper products, plastic is recycled into new plastic items, glass is recycled into new glass containers, and metals are recycled into new metal products.
Q: Why is it important to recycle properly?
A: Improper recycling can contaminate recyclable materials, making them unusable. It is essential to follow guidelines and ensure that only recyclable materials are placed in recycling bins.
Q: Can I recycle everything?
A: Not all materials are recyclable. Some items, such as plastic bags, food wrappers, and certain types of plastic, may not be accepted in local recycling programs.
Q: What are some challenges to recycling?
A: Challenges to recycling include the cost of collection and processing, the need for advanced sorting technologies, and the lack of public awareness and participation.
Conclusion
Recycling is an essential practice for environmental protection and sustainable development. By understanding the materials that should be recycled, the benefits of recycling, and the best practices for maximizing its effectiveness, we can collectively contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. Recycling is not just about throwing away waste; it is about transforming waste into valuable resources, reducing our environmental footprint, and creating a more sustainable world for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!