The Essential Tools and Techniques of Successful Planting
Related Articles: The Essential Tools and Techniques of Successful Planting
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Essential Tools and Techniques of Successful Planting. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Tools and Techniques of Successful Planting

Planting, the act of introducing seeds or seedlings into the soil to cultivate plants, is a fundamental practice in agriculture, horticulture, and forestry. It involves a series of steps and employs a diverse range of tools and techniques, all contributing to the successful establishment and growth of plants. This article delves into the various components involved in planting, highlighting their significance and benefits in nurturing life from seed to maturity.
1. Soil Preparation:
The foundation of successful planting lies in the preparation of the soil. This involves creating a suitable environment for root development and plant growth.
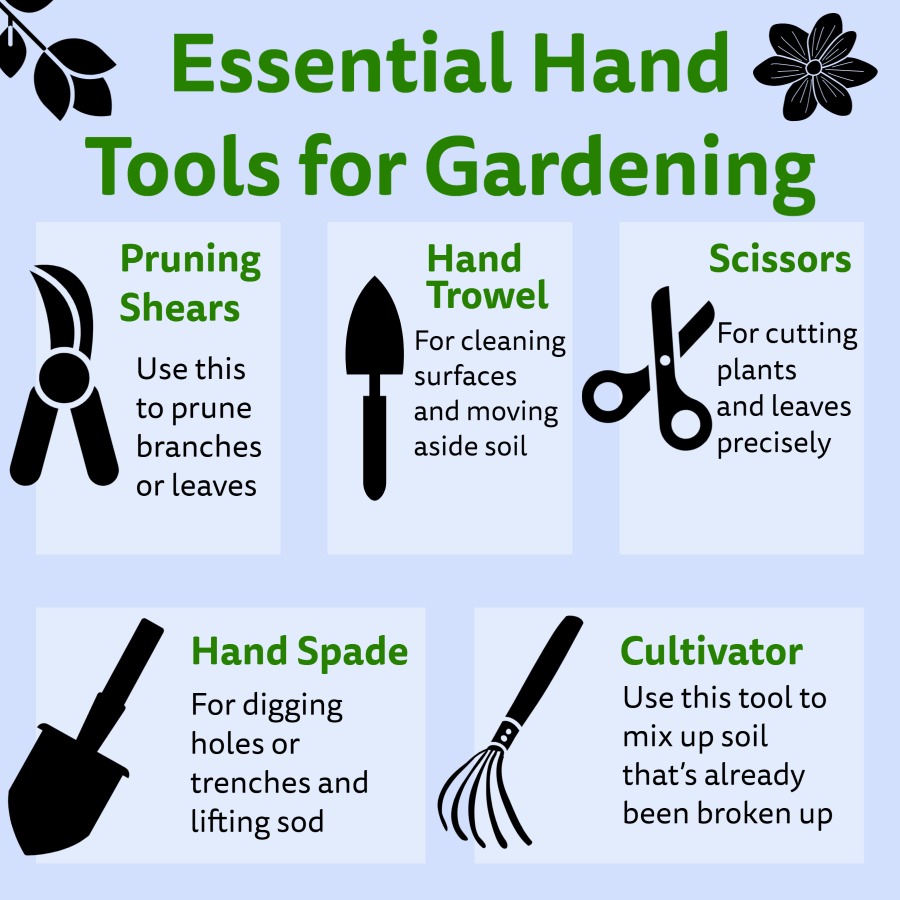
- Tilling: Breaking up compacted soil, removing weeds, and incorporating organic matter is achieved through tilling. This can be done manually with a hand rake or hoe, or mechanically with a rototiller. Tilling improves soil aeration, drainage, and nutrient availability, promoting healthy root growth.
- Composting: The addition of compost, a decomposed organic matter, enriches the soil with nutrients, improves its structure, and enhances water retention. Compost provides a slow-release source of nutrients, fostering sustainable plant growth.
- Soil Amendments: Incorporating amendments like peat moss, vermiculite, or perlite improves soil texture and drainage. These materials enhance soil aeration and water retention, creating an ideal environment for root growth.
- pH Adjustment: Soil pH plays a crucial role in plant growth, as it influences nutrient availability. Applying lime to acidic soils or sulfur to alkaline soils can adjust the pH to a suitable range for specific plant species.
2. Seed Selection and Preparation:
The choice of seeds and their preparation are vital for successful germination and plant establishment.
- Seed Viability: Selecting high-quality seeds with good viability ensures a higher germination rate and healthy seedlings. Seeds should be stored properly to maintain their viability.
- Seed Scarification: Some seeds have hard seed coats that prevent water absorption and germination. Scarification, a process of mechanically or chemically weakening the seed coat, enhances germination. Methods include nicking, sanding, or soaking in hot water.
- Seed Stratification: Certain seeds require a period of cold treatment to break dormancy and stimulate germination. This process, known as stratification, involves exposing seeds to cold temperatures for a specific duration.
- Seed Treatment: Applying fungicides or insecticides to seeds can protect them from diseases and pests during germination. These treatments minimize early seedling losses and promote healthy growth.
3. Planting Techniques:
Planting techniques vary depending on the type of plant, soil conditions, and climate.
- Direct Sowing: Seeds are directly sown into the prepared soil, allowing them to germinate and develop in place. This method is commonly used for vegetables, flowers, and herbs.
- Transplanting: Seedlings grown in containers or trays are transferred to their permanent locations. This method is suitable for plants with delicate roots or those that require a longer growing period before transplanting.
- Spacing: Proper spacing between plants is crucial for optimal growth and development. Adequate spacing ensures sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients for each plant.
- Depth: Planting seeds at the correct depth is essential for successful germination. Too shallow planting can expose seeds to drying conditions, while planting too deep can hinder emergence.
- Watering: Consistent watering after planting is crucial for seed germination and seedling establishment. Water deeply and infrequently to encourage root growth and prevent surface dryness.
4. Plant Support and Protection:
Providing support and protection to plants can enhance their growth and yield.
- Trellises and Stakes: Climbing plants benefit from trellises or stakes that provide vertical support for growth. This promotes air circulation and prevents stems from becoming tangled.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of mulch around plants helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Mulch can be organic, like straw or wood chips, or inorganic, like plastic or fabric.
- Pest and Disease Control: Monitoring for pests and diseases is essential for healthy plant growth. Implementing integrated pest management practices, including biological control and cultural control, minimizes the need for chemical pesticides.
- Fertilization: Supplying plants with nutrients through fertilization is crucial for optimal growth. Fertilizers can be organic, like compost or manure, or inorganic, like synthetic fertilizers.
5. Harvesting and Post-Harvest Care:
The final stage of planting involves harvesting and post-harvest care.
- Harvesting: Harvesting plants at the appropriate time maximizes yield and quality. This involves recognizing signs of maturity and using appropriate harvesting techniques.
- Post-Harvest Handling: Proper handling after harvesting is crucial for preserving the quality and shelf life of produce. This includes cleaning, sorting, and storing harvested products under optimal conditions.
FAQs by Things Used in Planting:
Q: What are the benefits of using compost in planting?
A: Compost enriches the soil with nutrients, improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and promotes beneficial microbial activity. It is a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic fertilizers.
Q: How do I choose the right seed for my planting needs?
A: Consider factors such as plant type, growing conditions, desired characteristics, and seed viability. Look for seeds from reputable suppliers and check their germination rates.
Q: What are the advantages of transplanting seedlings?
A: Transplanting allows for a longer growing period before planting in the garden, enabling seedlings to develop strong root systems. It also provides control over spacing and allows for selective planting.
Q: What are the different types of mulch and their benefits?
A: Organic mulches, such as straw, wood chips, and bark, decompose over time, adding nutrients to the soil. Inorganic mulches, such as plastic and fabric, suppress weeds and retain moisture but do not decompose.
Q: How do I determine the appropriate fertilizer for my plants?
A: Consider the specific nutrient requirements of your plants, the soil type, and the stage of plant growth. Soil testing can provide valuable information about nutrient levels and guide fertilizer selection.
Tips by Things Used in Planting:
- Choose the right tools for the job. Invest in quality tools that are appropriate for the size and type of planting you are undertaking.
- Understand the needs of your plants. Research the specific requirements of the plants you are growing, including sunlight, water, and nutrient needs.
- Prepare the soil properly. Tilling, composting, and amending the soil create an optimal environment for root growth and plant development.
- Select healthy seeds and seedlings. Choose seeds with good viability and seedlings that are free from pests and diseases.
- Space plants appropriately. Adequate spacing ensures sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients for each plant.
- Water consistently and deeply. Encourage root growth by watering deeply and infrequently.
- Protect plants from pests and diseases. Implement integrated pest management practices to minimize the need for chemical pesticides.
- Fertilize according to plant needs. Provide plants with the necessary nutrients through organic or inorganic fertilizers.
- Harvest at the right time. Recognize signs of maturity and use appropriate harvesting techniques to maximize yield and quality.
- Practice sustainable gardening techniques. Minimize waste, conserve water, and use environmentally friendly methods to promote a healthy ecosystem.
Conclusion by Things Used in Planting:
Planting is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, preparation, and execution. By understanding the various tools and techniques involved, gardeners and farmers can cultivate healthy and productive plants. From soil preparation and seed selection to planting methods and post-harvest care, each step plays a vital role in ensuring successful plant growth. By adopting sustainable practices and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques, we can foster a vibrant and productive agricultural landscape, providing sustenance and beauty for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Tools and Techniques of Successful Planting. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!