The Energy-Hungry Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Electricity Consumption
Related Articles: The Energy-Hungry Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Electricity Consumption
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Energy-Hungry Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Electricity Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Energy-Hungry Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Electricity Consumption
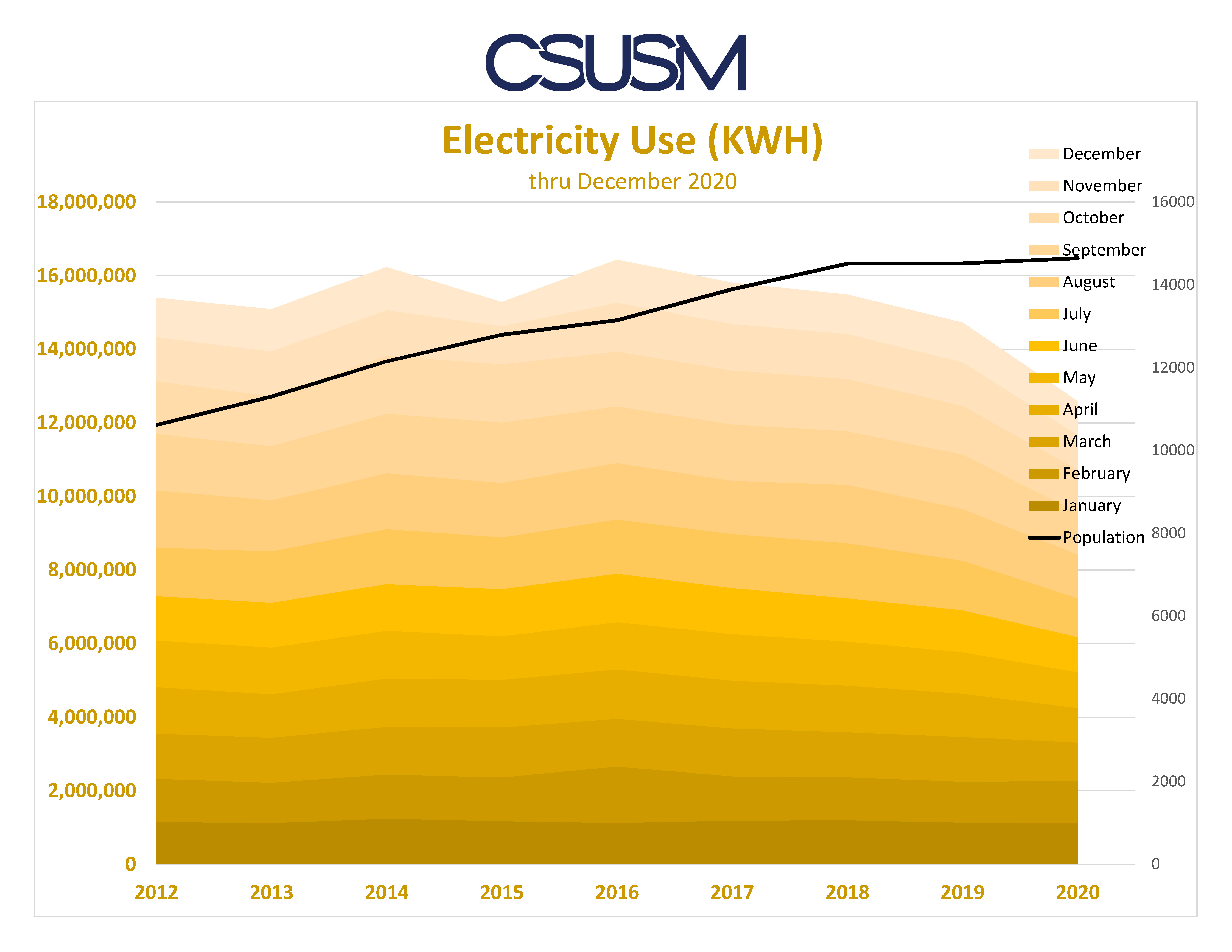
Electricity, the invisible force that powers our modern world, is a ubiquitous necessity, but its generation and consumption come with a significant environmental footprint. Understanding which sectors and appliances consume the most electricity is crucial for developing sustainable energy strategies and mitigating our impact on the planet.
This article delves into the major electricity consumers, examining their significance, benefits, and potential for efficiency improvements.
Residential Consumption: The Silent Power Drains
While often overlooked, residential electricity consumption accounts for a substantial portion of overall energy use. The primary culprits are:
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC): HVAC systems, especially in regions with extreme temperatures, are significant electricity consumers. Efficient HVAC systems, including heat pumps and programmable thermostats, can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Water Heating: Water heaters, both electric and gas, consume a considerable amount of energy. Energy-efficient models, tankless water heaters, and solar water heating systems offer substantial savings.
- Appliances: Refrigerators, dishwashers, washing machines, and dryers are major electricity consumers. Choosing energy-efficient models with Energy Star certification can significantly reduce energy usage.
- Lighting: While traditional incandescent bulbs have been largely replaced by more efficient LEDs, lighting still accounts for a notable portion of residential energy consumption. Choosing energy-efficient LED bulbs and using smart lighting systems can save energy and reduce costs.
- Electronics: Televisions, computers, and other electronic devices, while seemingly low-power consumers, contribute significantly to overall energy consumption when left on standby or plugged in. Using power strips and unplugging devices when not in use can reduce "phantom" energy consumption.
Industrial Consumption: The Engines of Economic Growth
Industrial sectors, encompassing manufacturing, mining, and construction, are the largest consumers of electricity.
- Manufacturing: Heavy industries like steel production, chemical manufacturing, and aluminum smelting require vast amounts of electricity for processes like melting, refining, and processing.
- Mining: Extracting minerals and ores often involves energy-intensive processes like crushing, grinding, and separating, requiring substantial electricity consumption.
- Construction: Construction sites rely heavily on electricity for power tools, lighting, and equipment like cranes and pumps.
- Data Centers: The booming digital economy has led to a surge in data center construction, which consume vast amounts of electricity for server operations, cooling, and data processing.
Commercial Consumption: The Power Behind Businesses
Commercial buildings, including offices, retail stores, restaurants, and hotels, also consume significant amounts of electricity.
- Lighting: Large commercial buildings often require extensive lighting systems, contributing significantly to their energy consumption.
- HVAC: Maintaining comfortable temperatures in large commercial spaces necessitates high-power HVAC systems, leading to substantial energy use.
- Refrigeration: Retail stores, restaurants, and hotels rely heavily on refrigeration systems to store food and beverages, consuming a considerable amount of electricity.
- Equipment: Commercial buildings use a wide range of equipment, including computers, servers, printers, and kitchen appliances, which consume electricity.
Transportation: The Shifting Gears of Electrification
The transportation sector, traditionally reliant on fossil fuels, is undergoing a significant shift towards electric vehicles (EVs).
- Electric Vehicles: EVs are rapidly gaining popularity due to their environmental benefits and lower operating costs. However, charging EVs requires substantial electricity, putting a strain on existing power grids.
- Electric Buses and Trains: Electrifying public transportation systems can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, charging large fleets of electric buses and trains requires substantial infrastructure investments.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency
Reducing electricity consumption is crucial for environmental sustainability, economic prosperity, and energy security.
- Environmental Impact: Generating electricity often involves burning fossil fuels, releasing greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change. Reducing electricity consumption helps mitigate these emissions.
- Economic Benefits: Lowering electricity consumption reduces energy bills, saving money for individuals, businesses, and governments.
- Energy Security: Reducing reliance on fossil fuels enhances energy security by diversifying energy sources and reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations.
FAQs by Things That Use a Lot of Electricity
1. How can I reduce my home’s electricity consumption?
- Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: Look for Energy Star-certified appliances that use less energy.
- Install a programmable thermostat: Set your thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures when you’re away or asleep.
- Use LED light bulbs: LEDs use significantly less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Unplug devices when not in use: Even when turned off, many electronics continue to draw power.
- Use power strips: Turn off power strips when not in use to reduce "phantom" energy consumption.
2. What are the benefits of electric vehicles?
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping to reduce air pollution and climate change.
- Lower operating costs: EVs are cheaper to operate than gasoline-powered vehicles due to lower fuel costs and maintenance requirements.
- Quiet operation: EVs are significantly quieter than gasoline-powered vehicles, reducing noise pollution.
3. How can businesses reduce their electricity consumption?
- Upgrade to energy-efficient lighting: Replace traditional lighting with LEDs, which use significantly less energy.
- Optimize HVAC systems: Use programmable thermostats, adjust temperature settings, and ensure proper maintenance to reduce HVAC energy consumption.
- Implement energy-efficient practices: Turn off lights and equipment when not in use, use energy-saving devices, and encourage employees to adopt energy-saving habits.
4. What are the challenges of electrifying transportation?
- Infrastructure investment: Building out charging stations for EVs requires significant investment in infrastructure.
- Battery range: The range of EVs is still limited compared to gasoline-powered vehicles, which can be a concern for long-distance travel.
- Battery recycling: The disposal of EV batteries poses environmental challenges, requiring responsible recycling practices.
Tips by Things That Use a Lot of Electricity
1. HVAC Systems:
- Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance to ensure your HVAC system is operating efficiently.
- Proper insulation: Ensure your home is properly insulated to reduce heat loss and gain.
- Use ceiling fans: Ceiling fans can help circulate air and reduce the need for air conditioning.
2. Water Heaters:
- Install a tankless water heater: Tankless water heaters heat water on demand, reducing energy waste.
- Lower the thermostat setting: Lowering the thermostat setting by a few degrees can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Insulate your hot water pipes: Insulating hot water pipes reduces heat loss and saves energy.
3. Appliances:
- Choose energy-efficient models: Look for Energy Star-certified appliances that use less energy.
- Wash clothes in cold water: Most laundry detergents are effective in cold water, saving energy on heating.
- Air-dry clothes: Air-drying clothes instead of using a dryer can save significant energy.
4. Lighting:
- Use LED bulbs: LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Turn off lights when leaving a room: This simple habit can save a significant amount of energy.
- Use motion-sensor lights: Motion-sensor lights turn on only when needed, reducing energy waste.
5. Electronics:
- Use power strips: Turn off power strips when not in use to reduce "phantom" energy consumption.
- Unplug devices when not in use: Even when turned off, many electronics continue to draw power.
- Choose energy-efficient models: Look for energy-efficient models of televisions, computers, and other electronics.
Conclusion by Things That Use a Lot of Electricity
Electricity is a vital resource that powers our modern world, but its consumption comes with environmental and economic costs. By understanding the major electricity consumers and adopting energy-efficient practices, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, mitigate climate change, and save money. From individual actions like choosing energy-efficient appliances to large-scale initiatives like electrifying transportation, every effort to reduce electricity consumption contributes to a more sustainable and prosperous future.
![The Energy-Hungry House [Infographic]](https://infographicjournal.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/01/energy-hungy-house1.png)



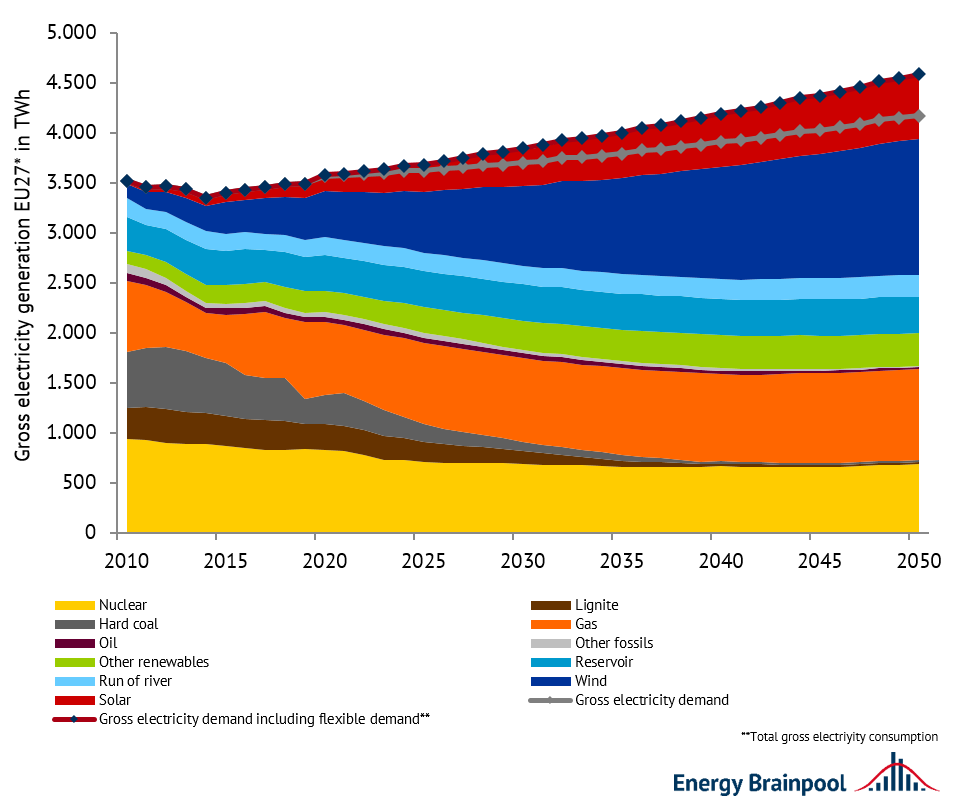



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Energy-Hungry Giants: A Comprehensive Look at Electricity Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!