The Enduring Significance of Metals: A Journey Through Their Properties and Applications
Related Articles: The Enduring Significance of Metals: A Journey Through Their Properties and Applications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Significance of Metals: A Journey Through Their Properties and Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Significance of Metals: A Journey Through Their Properties and Applications
Metals, a class of elements characterized by their unique physical and chemical properties, have been integral to human civilization since its dawn. Their malleability, ductility, conductivity, and strength have enabled the development of tools, weapons, infrastructure, and countless other innovations that have shaped our world. This article delves into the multifaceted realm of metals, exploring their characteristics, applications, and the enduring significance they hold in modern society.
The Nature of Metals: A Look at Their Defining Characteristics
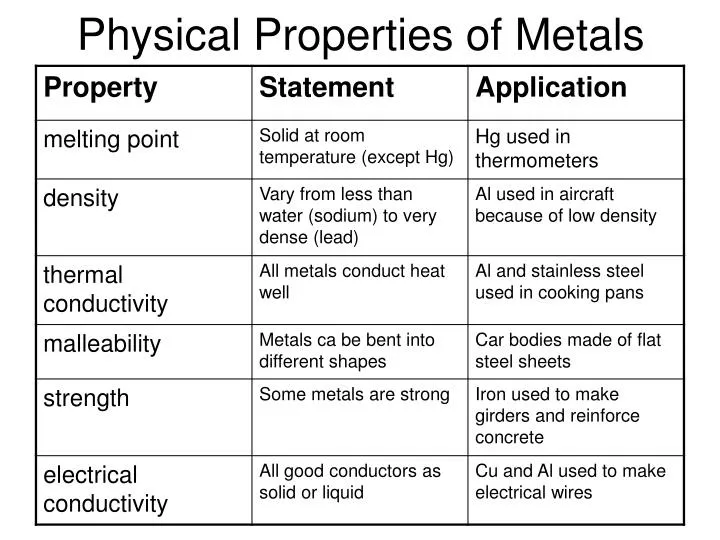
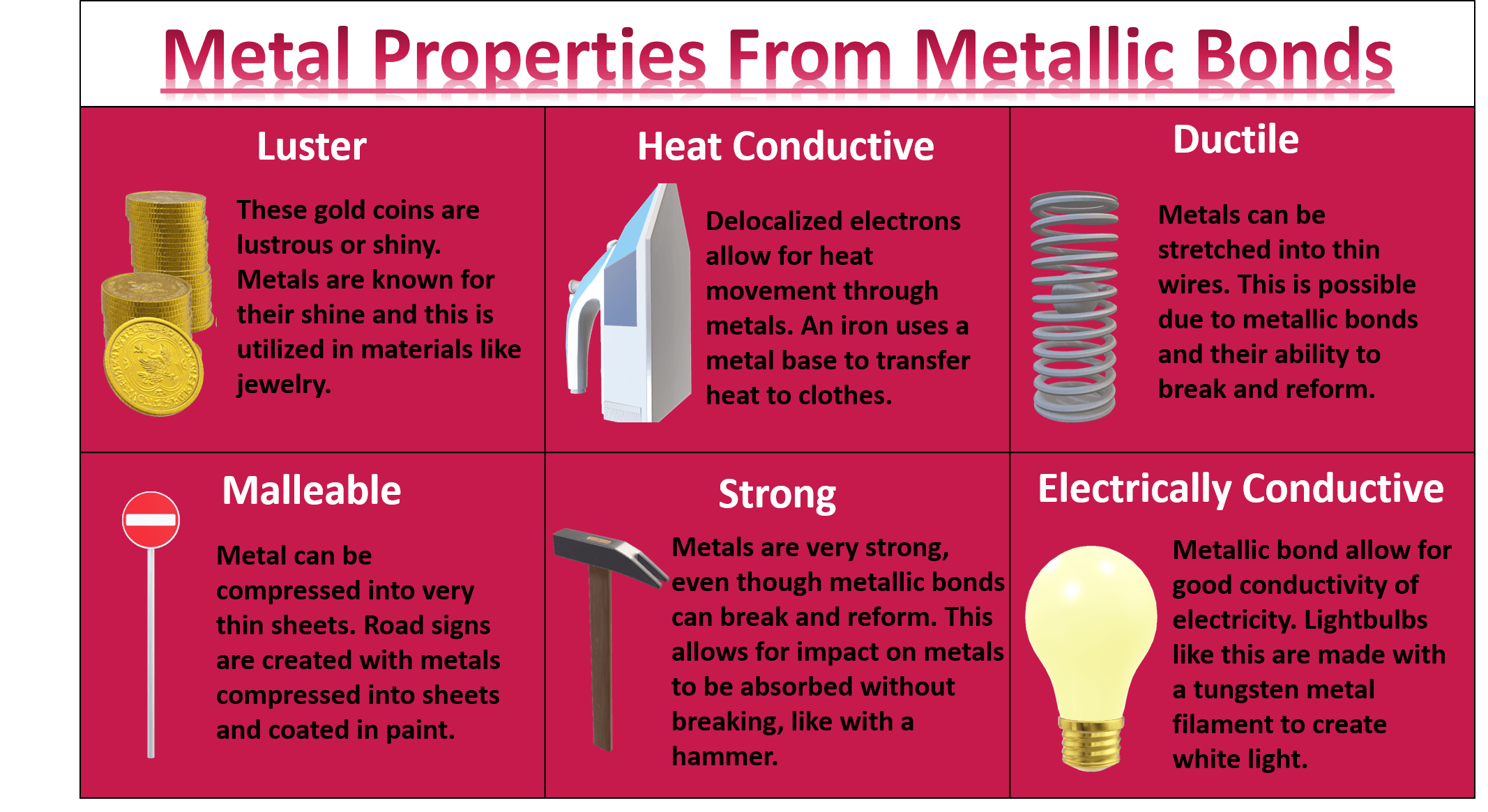
Metals, typically found on the left side of the periodic table, share a common thread: their atomic structure. Their atoms readily lose electrons, forming positive ions, and are bound together by a "sea" of delocalized electrons. This arrangement accounts for many of their defining properties:
- Malleability and Ductility: Metals can be hammered into thin sheets (malleability) or drawn into wires (ductility) without breaking. This property arises from the ability of metal atoms to slide past each other without disrupting the metallic bond.
- Conductivity: Metals excel as conductors of heat and electricity due to the free movement of electrons throughout their structure. This characteristic makes them essential in electrical wiring, heating elements, and other applications requiring efficient energy transfer.
- Luster: The smooth surface of metals reflects light, giving them a characteristic shine or luster. This property is a result of the delocalized electrons interacting with light waves.
- Strength and Hardness: Many metals possess significant strength and hardness, making them suitable for structural components, tools, and other applications requiring resistance to deformation and wear.
A Spectrum of Metals: From Everyday Essentials to High-Tech Wonders
The world of metals is diverse, encompassing a wide range of elements, each with its unique properties and applications. Here are some prominent examples:
- Iron: The most abundant metal in the Earth’s crust, iron is renowned for its strength and durability. It is the primary component of steel, a versatile alloy used in construction, transportation, and countless other industries.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum finds widespread use in aircraft, beverage containers, building materials, and consumer products.
- Copper: An excellent conductor of heat and electricity, copper is indispensable in electrical wiring, plumbing, and electronics.
- Gold: A precious metal prized for its beauty, resistance to corrosion, and high conductivity. Gold is used in jewelry, electronics, and as a monetary reserve.
- Titanium: Known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion, titanium finds application in aerospace, medical implants, and sporting goods.
- Silver: A highly reflective metal with excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Silver is used in jewelry, mirrors, and electrical contacts.
- Platinum: A rare and valuable metal, platinum is prized for its resistance to corrosion and high melting point. It is used in jewelry, catalytic converters, and laboratory equipment.
The Metal Revolution: Shaping Modern Society
Metals have played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history, driving technological advancements and transforming our lives. Their impact can be seen in various domains:
- Construction: Steel, concrete reinforced with steel, and aluminum are foundational materials in modern construction, enabling the creation of skyscrapers, bridges, and other large-scale structures.
- Transportation: Automobiles, airplanes, and ships rely heavily on metals for their structural integrity, engine components, and other essential parts.
- Electronics: Metals are essential components in electronic devices, from the copper wires in circuits to the gold contacts in microchips.
- Medicine: Titanium and stainless steel are widely used in medical implants, surgical instruments, and dental work.
- Energy: Copper and aluminum are vital in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity.
- Manufacturing: Metals are used in a vast array of manufacturing processes, from stamping and forging to machining and welding.
The Future of Metals: A Look at Emerging Trends and Innovations
The field of metallurgy continues to evolve, with ongoing research and development focused on:
- Advanced Alloys: Creating new alloys with enhanced properties, such as increased strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
- Nanomaterials: Developing metal-based nanomaterials with unique properties, such as improved conductivity, catalytic activity, and mechanical strength.
- Sustainable Extraction and Processing: Exploring environmentally friendly methods for extracting and processing metals, minimizing waste and reducing environmental impact.
- Recycling and Reuse: Promoting the recycling and reuse of metals to conserve resources and reduce reliance on virgin materials.
FAQs About Metals
Q: What is the difference between a metal and a non-metal?
A: Metals typically exhibit high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, ductility, and luster. Non-metals, on the other hand, are generally poor conductors of heat and electricity, brittle, and lack metallic luster.
Q: How are metals extracted from the Earth?
A: Metals are typically extracted from ores, which are naturally occurring rocks containing a significant concentration of metal. The extraction process involves various steps, including mining, crushing, grinding, and chemical processing.
Q: What are alloys, and why are they important?
A: Alloys are mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. They are often created to enhance the properties of the constituent metals, such as increasing strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance.
Q: What are the environmental impacts of metal extraction and processing?
A: Metal extraction and processing can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable mining practices and responsible recycling are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
Tips for Understanding Metals
- Explore the periodic table: Familiarize yourself with the location and properties of different metals on the periodic table.
- Learn about common alloys: Research the composition and properties of common alloys, such as steel, brass, and bronze.
- Consider the applications of metals: Observe how metals are used in everyday objects and structures.
- Stay informed about new developments: Keep abreast of emerging trends and innovations in the field of metallurgy.
Conclusion
Metals, with their unique properties and versatility, have played an indispensable role in human civilization. From the earliest tools to the intricate components of modern technology, metals continue to shape our world. As we navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, understanding the properties, applications, and environmental implications of metals remains essential for a sustainable and technologically advanced future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Significance of Metals: A Journey Through Their Properties and Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!