The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Symphony of Waves Shaping Our World
Related Articles: The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Symphony of Waves Shaping Our World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Symphony of Waves Shaping Our World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Symphony of Waves Shaping Our World

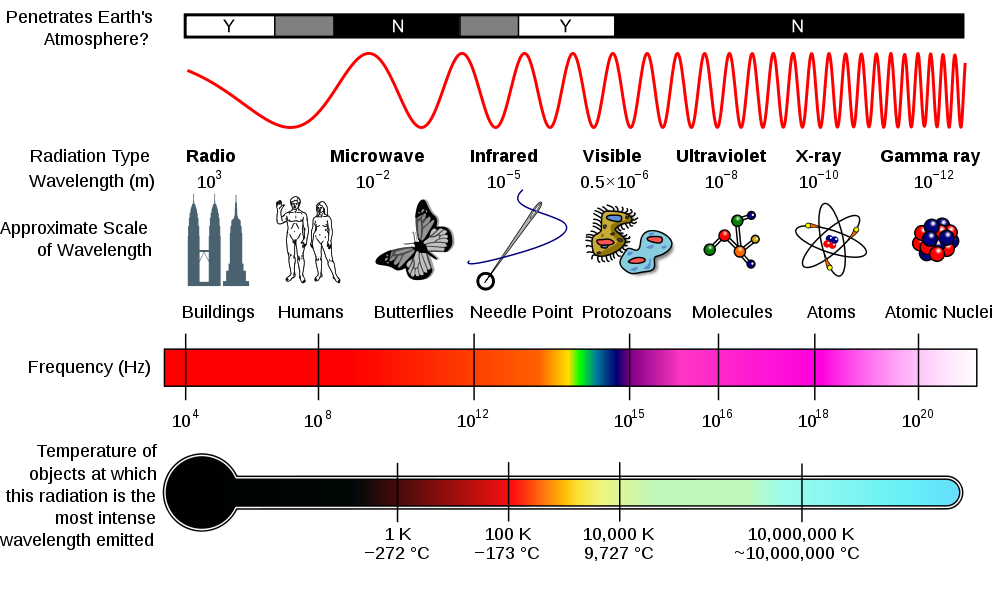
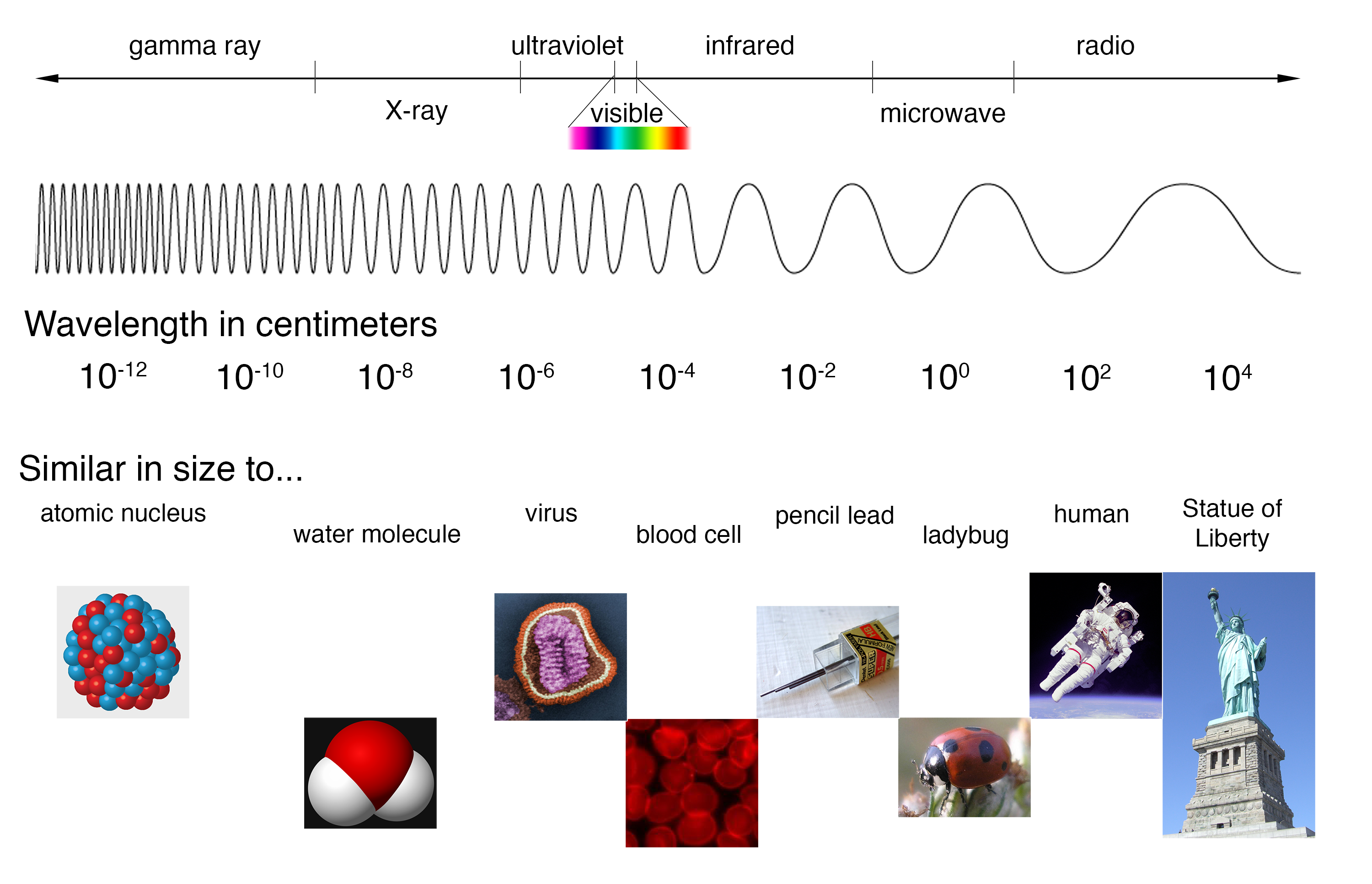
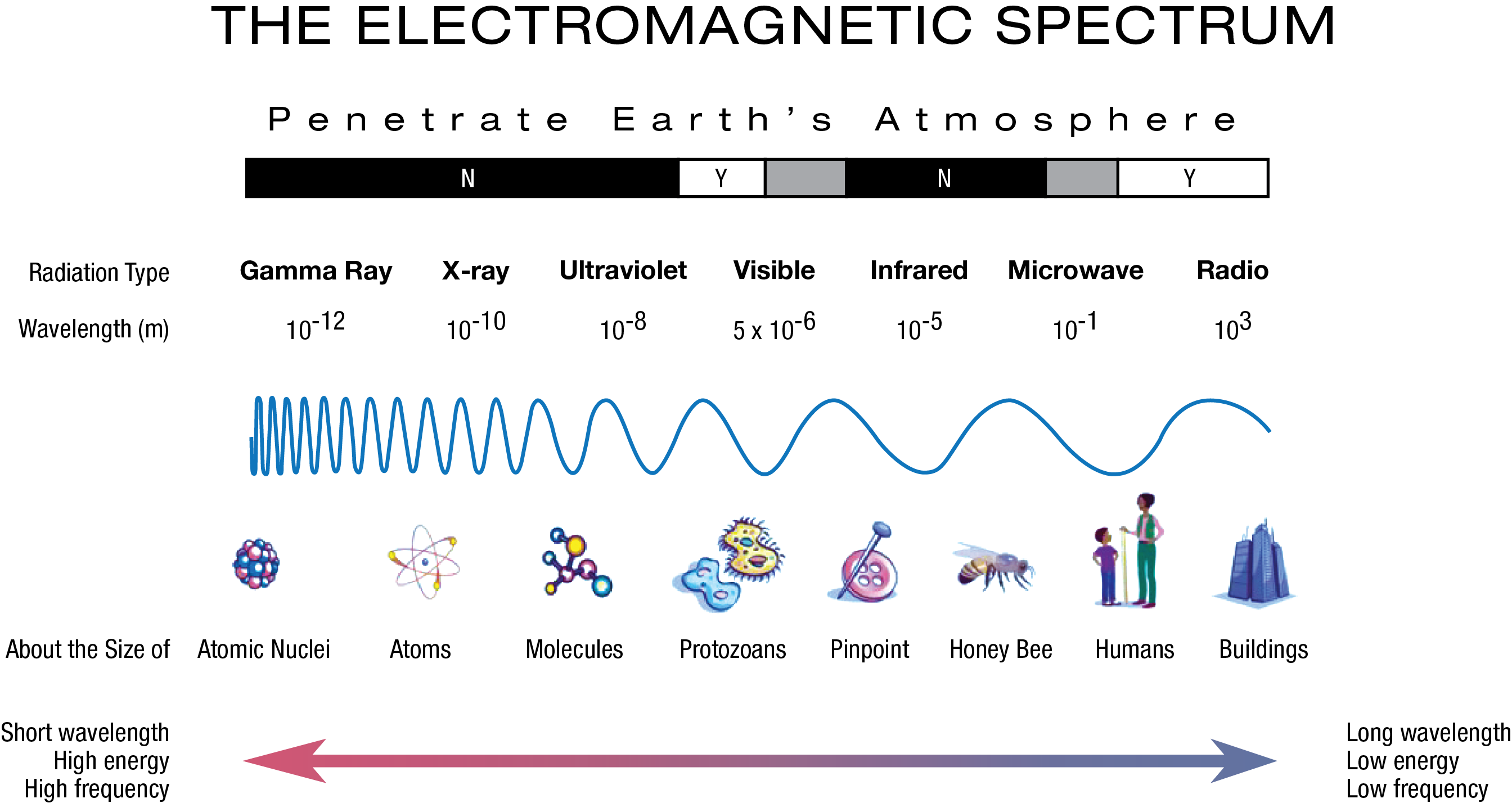
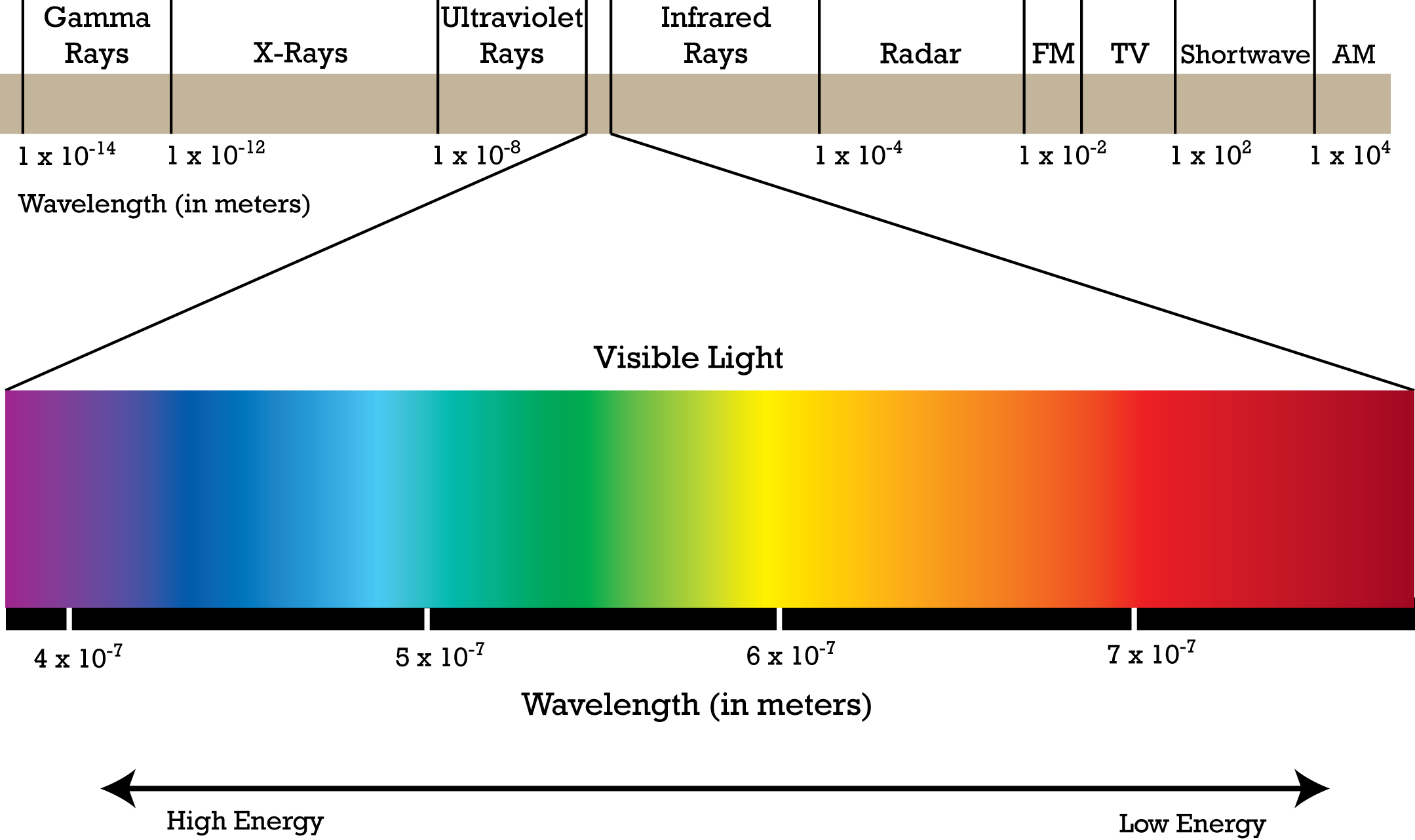
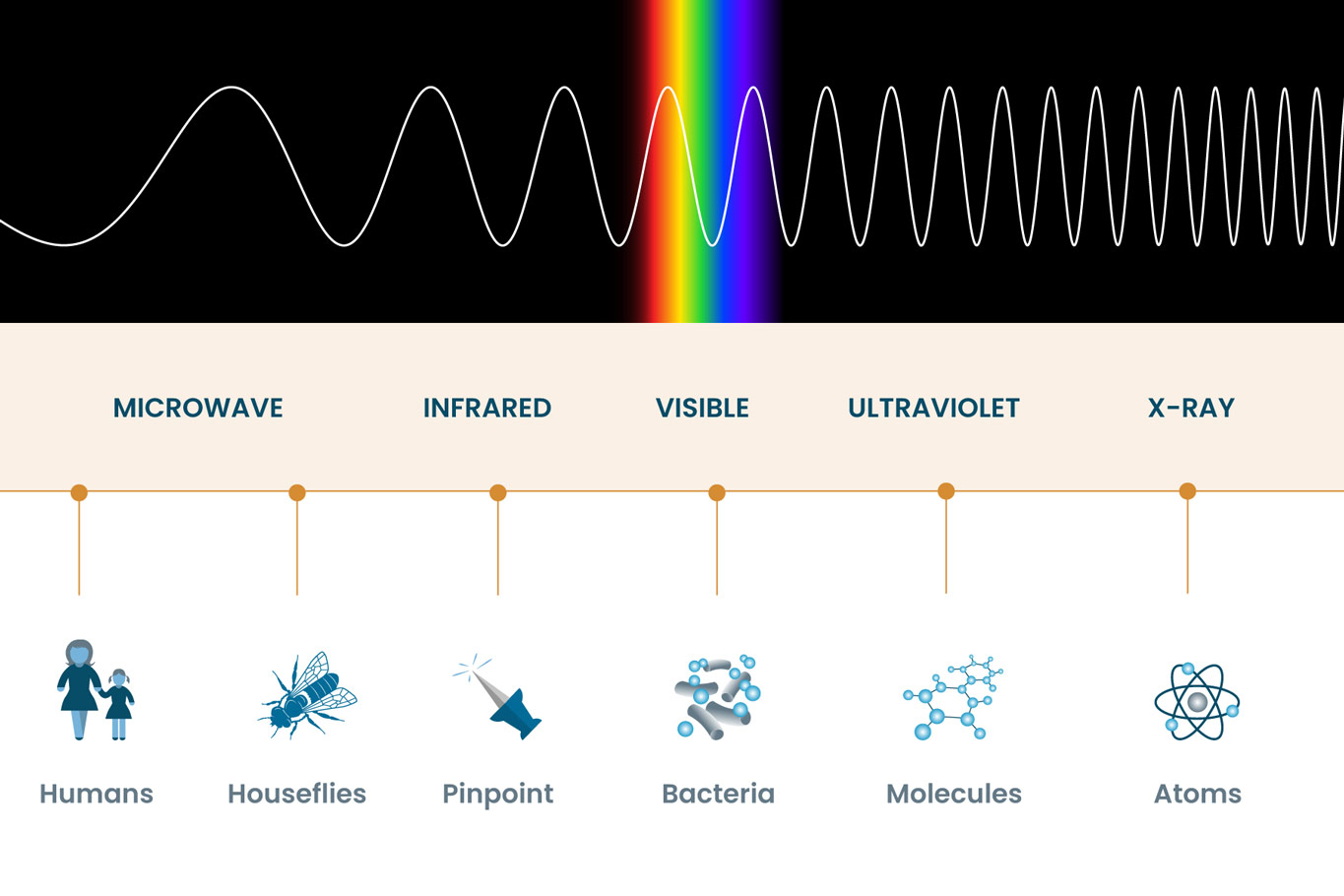
The electromagnetic spectrum, a vast expanse of energy spanning from low-frequency radio waves to high-energy gamma rays, is a fundamental aspect of our universe. These waves, each characterized by its unique wavelength and frequency, permeate our existence, driving countless technologies and shaping our understanding of the cosmos.
Understanding the Spectrum:
Electromagnetic waves are disturbances that propagate through space at the speed of light, carrying energy and information. They are comprised of oscillating electric and magnetic fields, synchronized and perpendicular to each other. The spectrum is a continuous range, with distinct regions categorized by their wavelength or frequency.
Radio Waves:
The longest waves in the spectrum, radio waves, are utilized in a myriad of applications, from communication to navigation and medical imaging. Their low energy levels make them ideal for transmitting information over long distances.
- Broadcasting: Radio waves are the backbone of terrestrial radio broadcasting, enabling the transmission of audio signals to receivers across vast geographical areas.
- Telecommunications: Radio waves are crucial for mobile phone networks, satellite communication, and Wi-Fi, facilitating seamless connectivity and information exchange.
- Navigation: Radio waves power Global Positioning Systems (GPS) by transmitting signals from satellites to receivers on Earth, enabling precise location tracking.
- Medical Imaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) utilizes radio waves to generate detailed images of internal organs and tissues, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Microwaves:
Microwaves, with their shorter wavelengths, find applications in heating, communication, and radar systems.
- Microwave Ovens: These appliances utilize microwave radiation to heat food by exciting water molecules, generating heat through molecular friction.
- Satellite Communication: Microwaves are used in satellite communication systems, transmitting signals between satellites and ground stations for long-distance communication.
- Radar Systems: Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging) systems use microwave pulses to detect objects and measure their distance, speed, and direction, employed in air traffic control, weather forecasting, and military applications.
Infrared Radiation:
Infrared radiation, invisible to the human eye, is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero.
- Thermal Imaging: Infrared cameras detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, creating images that reveal temperature variations, aiding in night vision, security surveillance, and medical diagnostics.
- Remote Sensing: Infrared satellites are used to monitor Earth’s surface temperature, vegetation health, and atmospheric conditions, providing valuable data for environmental research and disaster management.
- Heating and Drying: Infrared radiation is employed in industrial heating and drying processes, effectively transferring heat to materials for applications like paint drying and food processing.
Visible Light:
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum visible to the human eye, encompassing the colors of the rainbow, plays a crucial role in our perception of the world.
- Vision: Our eyes are designed to detect visible light, allowing us to perceive colors and shapes, enabling our interaction with the environment.
- Photography: Cameras capture visible light to create images, preserving memories and documenting events.
- Lighting: Artificial light sources, from incandescent bulbs to LED lamps, emit visible light, illuminating our homes, streets, and workplaces.
Ultraviolet Radiation:
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, invisible to the human eye, has both beneficial and harmful effects.
- Sun Tanning: Exposure to UV radiation from the sun causes skin to tan, a protective response to prevent further damage.
- Medical Treatments: UV radiation is used in phototherapy to treat skin conditions like psoriasis and vitiligo.
- Sterilization: UV radiation effectively kills bacteria and viruses, making it useful for sterilizing medical equipment and water purification.
X-rays:
X-rays, with their high energy and ability to penetrate matter, are widely used in medical imaging and material analysis.
- Medical Imaging: X-rays are used to create images of bones, teeth, and internal organs, aiding in diagnosis and treatment of injuries and diseases.
- Security Screening: X-ray scanners are used in airports and other security checkpoints to detect concealed objects and weapons.
- Material Analysis: X-ray diffraction techniques are used to analyze the structure of materials, aiding in materials science, chemistry, and crystallography.
Gamma Rays:
Gamma rays, the highest energy waves in the electromagnetic spectrum, are emitted by radioactive materials and cosmic events.
- Medical Treatments: Gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells.
- Sterilization: Gamma radiation is highly effective in sterilizing medical equipment, food products, and pharmaceutical materials.
- Astronomy: Gamma ray telescopes detect gamma rays from distant objects in space, providing insights into high-energy phenomena such as supernovae and black holes.
The Importance of Electromagnetic Waves:
Electromagnetic waves are indispensable to modern life, driving advancements in communication, healthcare, technology, and scientific exploration. Their versatility allows them to be harnessed for a wide range of applications, from transmitting information to diagnosing diseases and exploring the universe. Understanding the properties of electromagnetic waves and their interactions with matter is crucial for developing new technologies and addressing global challenges.
FAQs by Uses and Applications of EM Waves:
Q: How are radio waves used in communication?
A: Radio waves are used to transmit information over long distances because they can travel through the atmosphere and penetrate many materials. Radio signals are modulated, meaning their amplitude or frequency is altered to carry information. Receivers then decode these modulated signals to retrieve the original information.
Q: What are the advantages of using microwaves for satellite communication?
A: Microwaves are ideal for satellite communication because they can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere with minimal loss of signal strength. They also have a relatively short wavelength, enabling high bandwidth for transmitting large amounts of data.
Q: How are infrared cameras used in security surveillance?
A: Infrared cameras detect heat emitted by objects, allowing them to create images even in low-light conditions. This makes them effective for security surveillance, as they can detect intruders and monitor activity in the dark.
Q: What are the risks associated with exposure to ultraviolet radiation?
A: Exposure to excessive UV radiation can cause skin damage, including sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. It is essential to protect oneself from prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak UV hours.
Q: How are X-rays used in medical imaging?
A: X-rays are used to create images of bones and other dense structures because they can penetrate soft tissues but are absorbed by bone. The resulting image shows the distribution of bone density, allowing doctors to identify fractures, infections, and other abnormalities.
Q: What are the applications of gamma rays in medicine?
A: Gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to kill cancerous cells. They are also used in medical sterilization, where they are used to sterilize medical equipment and pharmaceuticals.
Tips by Uses and Applications of EM Waves:
- Safety Precautions: When using devices that emit electromagnetic radiation, such as cell phones, microwave ovens, and X-ray machines, it is important to follow safety guidelines and minimize exposure.
- Understanding the Spectrum: Familiarize yourself with the different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and their respective properties to better understand the applications of these waves.
- Technological Advancements: Stay informed about new technologies and applications that utilize electromagnetic waves, as this field is constantly evolving.
Conclusion by Uses and Applications of EM Waves:
Electromagnetic waves are a fundamental force in our universe, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and driving countless technologies that enhance our lives. From communication and navigation to medical imaging and material analysis, these waves play a vital role in modern society. As our understanding of electromagnetic waves continues to grow, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, transforming our world in exciting new ways.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Symphony of Waves Shaping Our World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!