The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Double-Edged Sword of Modern Life
Related Articles: The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Double-Edged Sword of Modern Life
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Double-Edged Sword of Modern Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Double-Edged Sword of Modern Life
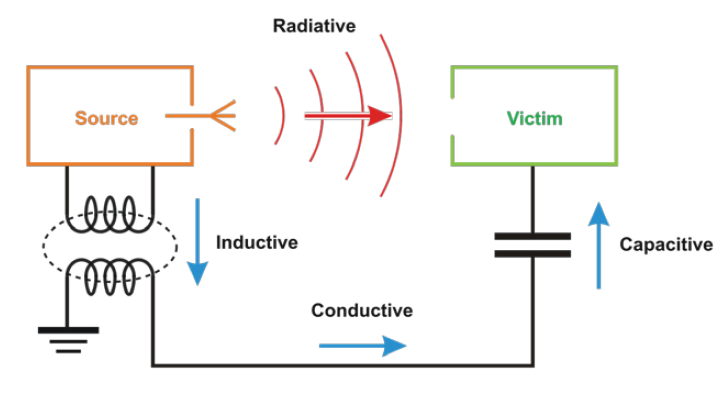
Electromagnetic (EM) waves, invisible ripples in the fabric of space, are a fundamental aspect of the universe. They encompass a vast spectrum of wavelengths, each carrying unique properties and applications. From the warmth of the sun to the signals that power our communication networks, EM waves permeate our lives, shaping our understanding of the cosmos and driving technological advancements. However, this pervasive presence also necessitates an understanding of their potential dangers.
A Spectrum of Possibilities: The Uses of Electromagnetic Waves
The EM spectrum, a continuous range of frequencies, can be broadly categorized into seven regions: radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each region possesses distinct characteristics that dictate its specific uses and applications.
1. Radio Waves: The Backbone of Communication
Radio waves, the longest wavelength EM radiation, are the cornerstone of wireless communication. Their ability to travel long distances through the atmosphere makes them ideal for broadcasting, radio navigation, and satellite communication. AM and FM radio, television broadcasting, and mobile phone networks all rely on the transmission and reception of radio waves.
2. Microwaves: Heating and Communication
Microwaves, with wavelengths shorter than radio waves, find applications in both heating and communication. Microwave ovens utilize their ability to excite water molecules, generating heat for cooking. Satellite communication, radar systems, and wireless internet networks also leverage the properties of microwaves for data transmission.
3. Infrared Radiation: Heat and Sensing
Infrared radiation, invisible to the human eye, is associated with heat. It is used in remote sensing, thermal imaging, and night vision technology. Infrared spectroscopy, a technique that analyzes the absorption and emission of infrared radiation, is employed in various fields, including chemistry, medicine, and materials science.
4. Visible Light: The Spectrum of Color
Visible light, the narrow band of the EM spectrum perceptible to human eyes, is responsible for our perception of color. It plays a crucial role in photography, optical microscopy, and various optical technologies. Lasers, which emit highly focused beams of visible light, are utilized in diverse applications, ranging from medical surgery to barcode scanning.
5. Ultraviolet Radiation: Sterilization and Medical Imaging
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, with wavelengths shorter than visible light, possesses germicidal properties. UV lamps are used to sterilize medical equipment and purify water. Medical imaging techniques, such as fluorescent microscopy and UV spectroscopy, employ UV radiation for diagnostic purposes.
6. X-rays: Medical Imaging and Security
X-rays, with even shorter wavelengths than UV radiation, have the ability to penetrate materials, making them indispensable for medical imaging. X-ray machines are used to diagnose bone fractures, detect tumors, and examine internal organs. Security checkpoints at airports and other locations utilize X-ray scanners to inspect luggage and identify potential threats.
7. Gamma Rays: Medical Treatment and Research
Gamma rays, the highest energy and shortest wavelength EM radiation, are highly penetrating and can cause significant damage to living tissues. However, their destructive nature is also harnessed for medical treatment. Gamma radiation is used in radiotherapy to destroy cancerous cells. Additionally, gamma ray spectroscopy is employed in nuclear physics research and astrophysics.
The Shadow Side: The Dangers of Electromagnetic Waves
While EM waves are essential for modern life, their use comes with inherent risks. Understanding the potential dangers associated with different regions of the EM spectrum is crucial for minimizing exposure and mitigating adverse effects.
1. Non-Ionizing Radiation: The Debate on Low-Level Exposure
Radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, and visible light are classified as non-ionizing radiation, meaning they do not have enough energy to directly break chemical bonds in biological molecules. However, prolonged or intense exposure to these forms of radiation can still have harmful effects.
a. Radio Frequency Radiation and Health Concerns
Radio frequency (RF) radiation emitted by mobile phones, Wi-Fi routers, and other wireless devices has been a subject of ongoing debate. Some studies suggest potential links between RF exposure and health issues like cancer, infertility, and neurological disorders. However, the evidence is inconclusive, and further research is needed to establish definitive causal relationships.
b. Microwave Radiation and Tissue Heating
Exposure to high levels of microwave radiation can cause tissue heating, leading to burns and other injuries. Microwave ovens are designed to contain radiation, but leaks can occur, necessitating safety precautions.
c. Infrared Radiation and Eye Damage
Prolonged exposure to intense infrared radiation, such as from welding torches or industrial ovens, can damage the eyes, leading to cataracts and other vision problems.
2. Ionizing Radiation: A Significant Health Risk
Ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays are classified as ionizing radiation, capable of removing electrons from atoms and molecules, potentially causing damage to DNA and other cellular components.
a. Ultraviolet Radiation and Skin Cancer
Excessive exposure to UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds increases the risk of skin cancer, premature aging, and eye damage.
b. X-rays and Radiation Sickness
Medical X-rays are generally considered safe at low doses. However, repeated or high-dose exposures can increase the risk of cancer and other health problems.
c. Gamma Rays and Radioactivity
Gamma rays emitted from radioactive sources are highly dangerous. Exposure to high levels of gamma radiation can cause radiation sickness, leading to nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and even death.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q1: Are cell phones dangerous?
The potential health risks associated with cell phone use are a subject of ongoing research. While some studies suggest possible links to brain tumors and other health issues, the evidence is not conclusive. It is generally recommended to minimize exposure to RF radiation, especially for children and pregnant women.
Q2: Is Wi-Fi harmful?
Wi-Fi routers emit RF radiation, but at levels significantly lower than cell phones. The health risks associated with Wi-Fi exposure are considered minimal, but it is still advisable to maintain a safe distance from routers and limit exposure, especially for children.
Q3: Are microwave ovens safe?
Microwave ovens are designed to contain radiation, but leaks can occur. It is important to use microwave ovens safely, ensuring the door seals properly and avoiding using damaged or cracked appliances.
Q4: How can I protect myself from UV radiation?
Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen when outdoors, especially during peak sunlight hours. Avoid tanning beds and other artificial UV sources.
Q5: What are the safety precautions for X-ray procedures?
Medical professionals take precautions to minimize radiation exposure during X-ray procedures. Patients should inform their doctors of any relevant medical history and follow any instructions provided by the technician.
Tips for Minimizing Exposure and Risks
- Limit Exposure to Wireless Devices: Reduce screen time, use speakerphone or headphones, and keep wireless devices away from your body, especially during sleep.
- Use Microwave Ovens Safely: Ensure the door seals properly, avoid using damaged appliances, and keep children away from operating ovens.
- Protect Yourself from UV Radiation: Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen when outdoors, and avoid tanning beds.
- Follow Safety Guidelines for X-rays: Inform your doctor of any medical history and follow instructions provided by the technician.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of research and recommendations regarding EM radiation safety.
Conclusion: Balancing Benefits and Risks
Electromagnetic waves are an integral part of our technological world, enabling communication, medical advancements, and countless other innovations. However, their use comes with inherent risks, particularly for ionizing radiation. By understanding the potential dangers and taking appropriate precautions, we can mitigate risks while harnessing the benefits of this powerful force. Responsible use and continued research are essential to ensure the safe and sustainable application of electromagnetic waves in the future.







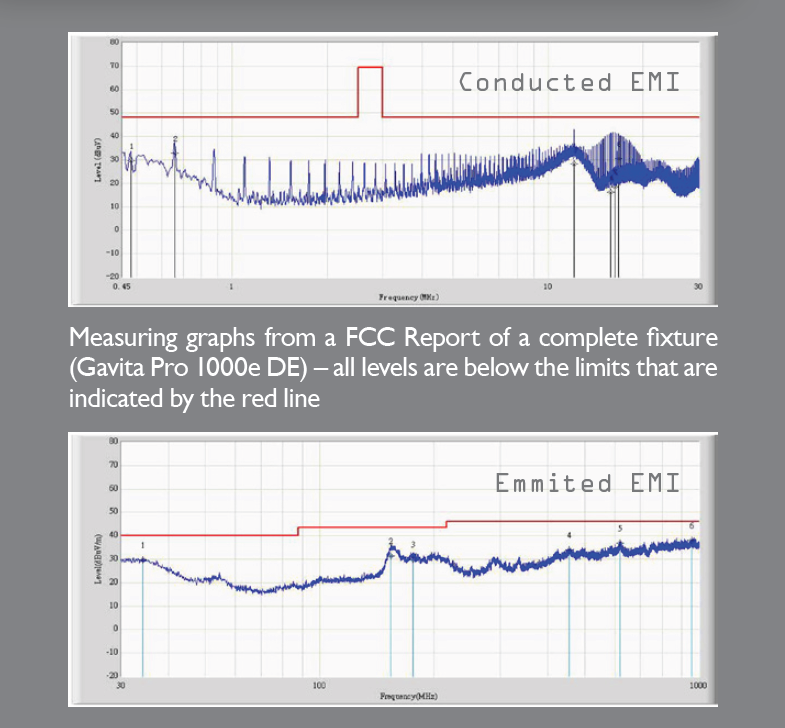
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Double-Edged Sword of Modern Life. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!