The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Canvas for Innovation
Related Articles: The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Canvas for Innovation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Canvas for Innovation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Canvas for Innovation

The world around us is awash in invisible energy, a symphony of electromagnetic waves (EM waves) that permeate our existence. From the warmth of the sun to the clarity of a radio broadcast, from the power of a microwave oven to the precision of a medical scan, EM waves are the silent architects of countless technologies that shape our lives.
This article delves into the fascinating world of EM waves, exploring their fundamental properties and the diverse ways in which they are harnessed for human advancement. We will examine the spectrum of EM waves, from the low-energy radio waves to the high-energy gamma rays, and discuss the technologies that leverage their unique characteristics.
Understanding the Spectrum
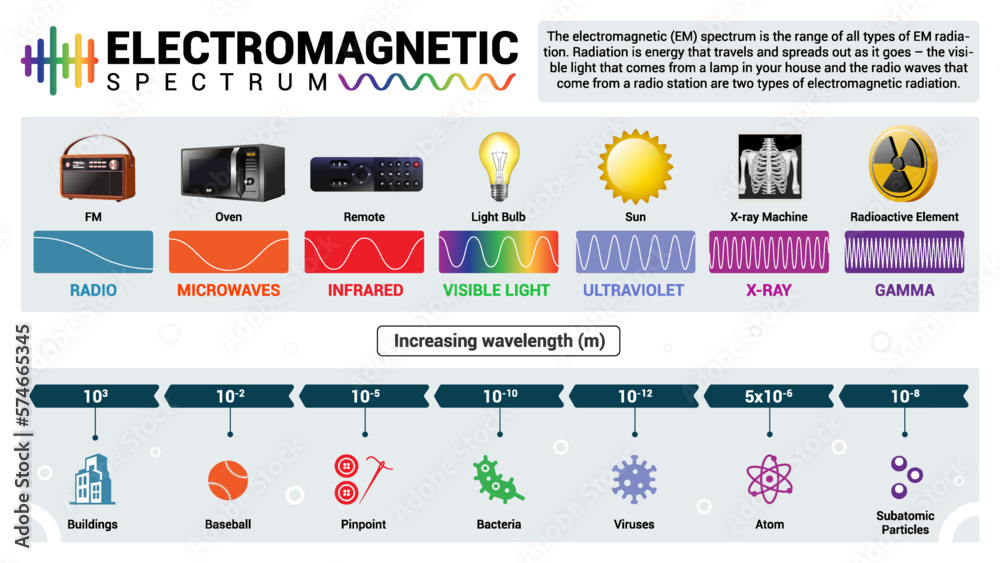
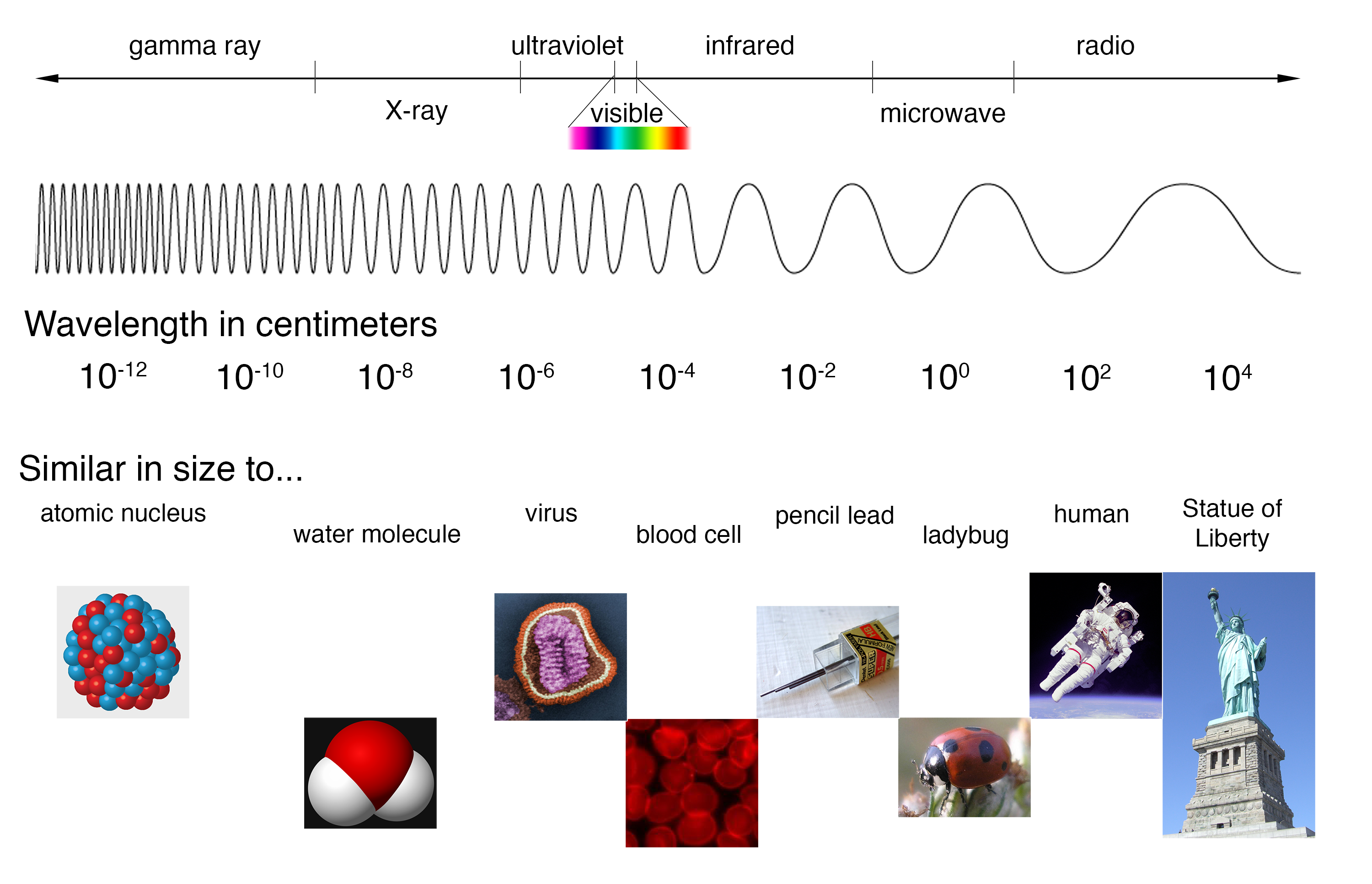
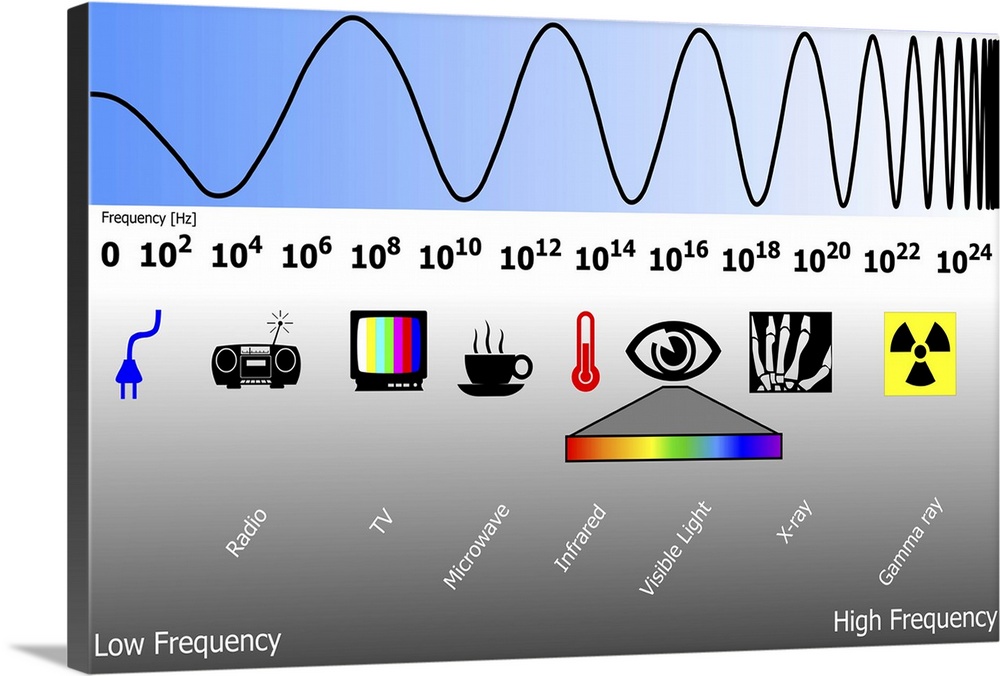
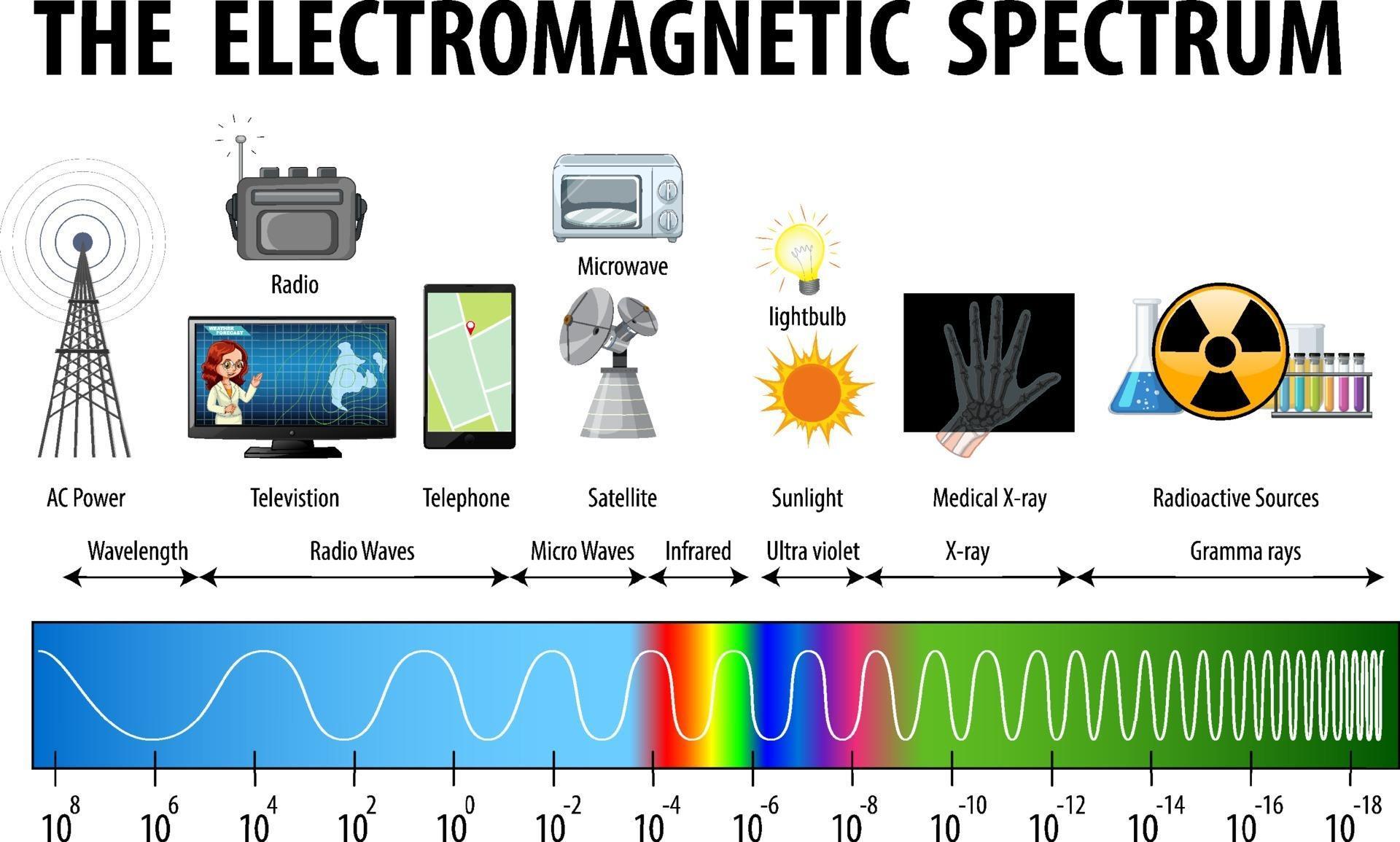
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is ordered by frequency, with the lowest frequencies at one end and the highest frequencies at the other. Each segment of this spectrum possesses distinct properties that dictate its applications.
-
Radio Waves: These waves, with frequencies ranging from 3 kHz to 300 GHz, are used for communication, broadcasting, and radar. Their long wavelengths allow them to travel long distances and penetrate obstacles.
-
Microwaves: Occupying the frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz, microwaves are utilized for communication, heating, and imaging. Their shorter wavelengths make them suitable for high-bandwidth data transmission and precise heating applications.
-
Infrared Radiation: With frequencies ranging from 300 GHz to 430 THz, infrared radiation is associated with heat and is used in thermal imaging, remote sensing, and optical communication.
-
Visible Light: The narrow band of the spectrum that our eyes perceive, visible light spans frequencies from 430 THz to 750 THz. It is crucial for human vision and plays a vital role in photography, lighting, and optical technologies.
-
Ultraviolet Radiation: Frequencies between 750 THz and 30 PHz characterize ultraviolet radiation. It is associated with the sun’s energy and has applications in sterilization, phototherapy, and fluorescent lighting.
-
X-rays: With frequencies ranging from 30 PHz to 30 EHz, X-rays have high energy and can penetrate matter, making them invaluable for medical imaging, material analysis, and security screening.
-
Gamma Rays: The highest frequency end of the spectrum, gamma rays possess the highest energy and are used in medical treatment, industrial applications, and astrophysics.
Harnessing the Power of EM Waves
The versatility of EM waves stems from their ability to interact with matter in unique ways, depending on their frequency. This interaction forms the foundation of numerous technologies that have revolutionized various sectors.
Communication and Information Technology:
-
Radio and Television Broadcasting: Radio waves are the backbone of wireless communication, enabling the transmission of audio and video signals over vast distances. AM and FM radio, satellite television, and terrestrial broadcasting all rely on radio waves.
-
Cellular Networks: Mobile phone communication relies heavily on microwaves, which can travel through the atmosphere and penetrate buildings, allowing users to stay connected in various environments.
-
Wi-Fi and Bluetooth: These wireless technologies utilize radio waves in the microwave frequency range to provide high-speed data transfer and seamless connectivity for devices.
-
Satellite Communication: Satellites use microwaves to transmit data, voice, and television signals across the globe, connecting remote areas and facilitating global communication.
Healthcare and Medical Applications:
-
Medical Imaging: X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans utilize EM waves to create detailed images of the human body, aiding in diagnosis and treatment.
-
Radiotherapy: Gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells, offering a non-invasive treatment option.
-
Lasers in Surgery: Lasers, which emit highly focused beams of light, are used in a variety of surgical procedures, enabling precise incisions, tissue ablation, and coagulation.
Industrial and Manufacturing Applications:
-
Microwave Heating: Microwaves are used in ovens to heat food by exciting water molecules, and they also find applications in industrial processes like drying and curing.
-
Metal Detection: Metal detectors utilize radio waves to identify the presence of metals, commonly used in security screening and industrial applications.
-
Remote Sensing: Infrared radiation is used in remote sensing to monitor the Earth’s surface, providing valuable data for agriculture, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
Scientific Research and Exploration:
-
Astronomy: Radio telescopes detect radio waves emitted from celestial objects, providing insights into the universe’s structure, composition, and evolution.
-
Spectroscopy: Different types of EM waves are used in spectroscopy to analyze the chemical composition of materials, aiding in scientific research and industrial quality control.
-
Particle Physics: High-energy gamma rays are used in particle accelerators to probe the fundamental constituents of matter, advancing our understanding of the universe’s building blocks.
Beyond the Familiar:
The applications of EM waves extend far beyond these examples. They are employed in various fields, including:
-
Lighting: Visible light is used for illumination, from incandescent bulbs to LED lights, shaping our visual environment.
-
Optical Communication: Fiber optic cables transmit information using light pulses, enabling high-speed data transfer over long distances.
-
Security Systems: Infrared sensors are used in security systems to detect movement and trigger alarms, enhancing safety and security.
-
Environmental Monitoring: EM waves are used to monitor air quality, water pollution, and soil conditions, providing vital data for environmental management.
FAQs about Technologies Using EM Waves
1. What are the potential risks associated with EM waves?
While EM waves are essential for numerous technologies, exposure to high levels of certain frequencies can pose health risks. Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can cause sunburn and skin cancer, while high-energy gamma rays can damage cells and tissues. However, most technologies using EM waves operate at levels deemed safe for human health.
2. How are EM waves regulated?
International and national regulatory bodies set limits on the levels of EM waves that are considered safe for human exposure. These limits vary depending on the frequency and type of EM radiation.
3. What are the future trends in EM wave technology?
Research and development continue to push the boundaries of EM wave technology. Advancements in materials science, antenna design, and computational modeling are leading to the development of new and more efficient applications, including:
-
5G and Beyond: Next-generation cellular networks are expected to utilize higher frequency bands of the EM spectrum, enabling faster data speeds and lower latency.
-
Terahertz Technology: Research into terahertz radiation is exploring its potential for high-resolution imaging, non-destructive testing, and secure communication.
-
Light-Based Computing: Scientists are exploring the use of light to process information, potentially revolutionizing computing speed and efficiency.
Tips for Understanding and Appreciating EM Waves
-
Explore the Spectrum: Familiarize yourself with the different types of EM waves and their properties. This will enhance your understanding of the technologies that rely on them.
-
Seek Out Educational Resources: Many websites, books, and documentaries provide detailed information about EM waves and their applications.
-
Engage in Hands-On Activities: Participate in science experiments or demonstrations that explore the properties of EM waves, such as building a simple radio or observing light refraction.
-
Stay Informed about Technological Advancements: Keep up with the latest developments in EM wave technology, as new applications and innovations are constantly emerging.
Conclusion
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and powerful resource, a canvas on which human ingenuity paints a vibrant tapestry of technological advancements. From communication and healthcare to manufacturing and scientific exploration, EM waves are woven into the fabric of our modern world. Understanding their properties and appreciating their diverse applications is crucial for comprehending the technologies that shape our lives and the potential for future innovations. As we continue to explore the possibilities of EM waves, we can anticipate a future where these invisible forces continue to drive progress and shape the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Canvas for Innovation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!