The Closed Loop: Exploring the Potential of Tray-to-Tray Recycling
Related Articles: The Closed Loop: Exploring the Potential of Tray-to-Tray Recycling
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Closed Loop: Exploring the Potential of Tray-to-Tray Recycling. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Closed Loop: Exploring the Potential of Tray-to-Tray Recycling
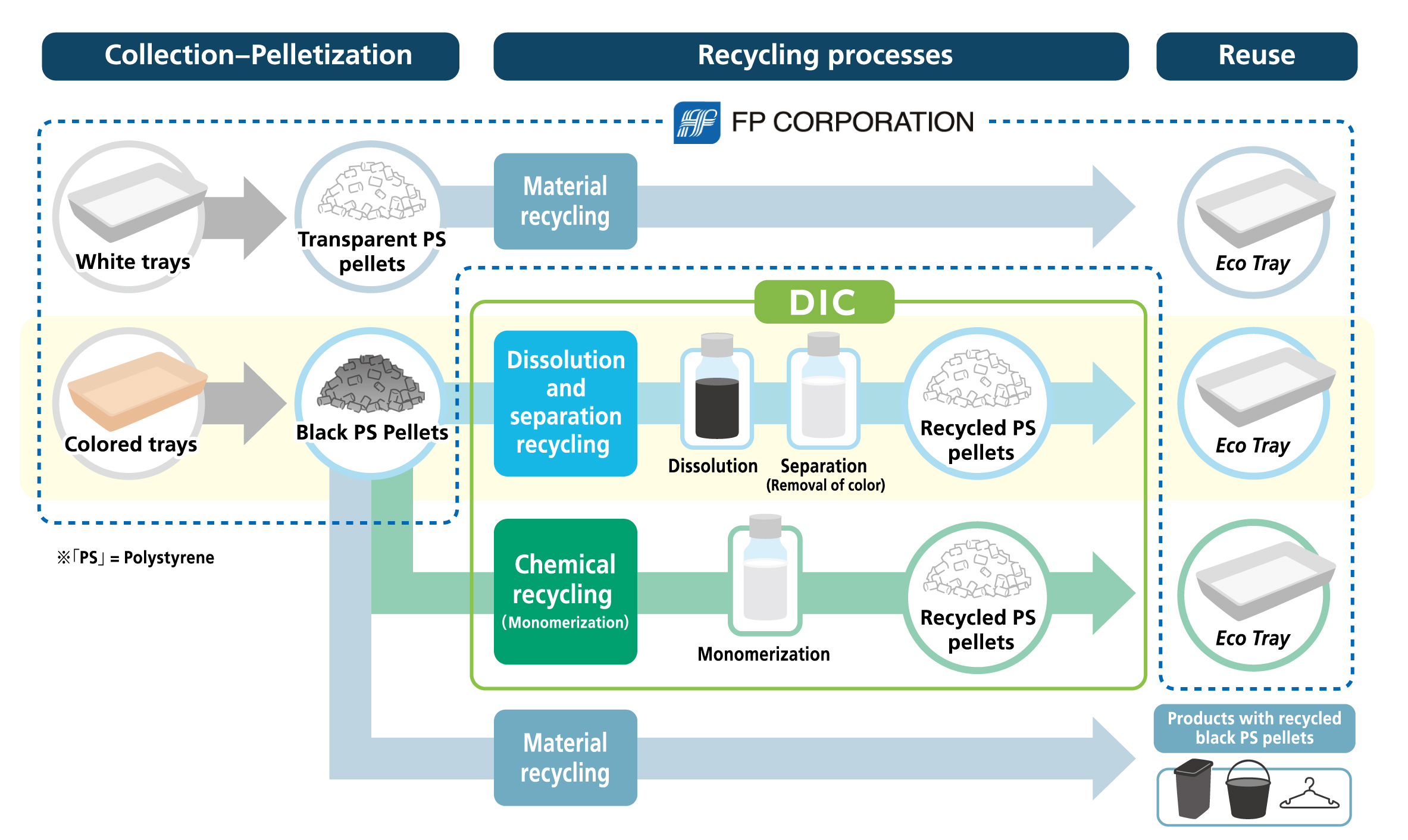
The global plastic waste crisis demands innovative solutions. One such solution, gaining momentum in the recycling industry, is tray-to-tray recycling. This process, also known as closed-loop recycling, focuses on transforming used plastic trays back into new, functional trays, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
Understanding Tray-to-Tray Recycling
The concept of tray-to-tray recycling revolves around a circular economy model. Unlike traditional recycling methods that often downcycle plastic into lower-grade products, this process aims to retain the quality and functionality of the original material.
Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
-
Collection and Sorting: Used plastic trays are collected from various sources, such as grocery stores, restaurants, and households. They are then sorted based on their material composition, ensuring only compatible plastics are processed together.
-
Cleaning and Preparation: The collected trays undergo a rigorous cleaning process to remove any contaminants, residues, or foreign objects. This step ensures the purity and quality of the recycled material.
-
Grinding and Extrusion: The cleaned trays are ground into small flakes or pellets. These flakes are then melted and extruded through a die to form new plastic strands.
-
Molding and Manufacturing: The extruded strands are further processed through molding techniques to create new, functional plastic trays. These trays can be used in various applications, including food packaging, retail displays, and industrial purposes.
The Advantages of Tray-to-Tray Recycling
This innovative approach offers several benefits, making it a valuable strategy for tackling plastic waste:
-
Resource Conservation: By reclaiming and repurposing existing plastic, tray-to-tray recycling reduces the demand for virgin materials, conserving finite natural resources.
-
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Producing virgin plastic requires significant energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Recycling plastic trays significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with plastic production.
-
Enhanced Sustainability: This process promotes a circular economy, minimizing waste and maximizing resource utilization. It aligns with sustainable development goals and contributes to a more environmentally responsible future.
-
Improved Material Quality: Unlike downcycling, tray-to-tray recycling maintains the quality of the recycled material, ensuring it can be used repeatedly without compromising its performance.
-
Economic Benefits: Investing in tray-to-tray recycling infrastructure can create new jobs and stimulate local economies. It also reduces reliance on imported materials, fostering economic independence.
Challenges and Considerations
While tray-to-tray recycling holds immense promise, several challenges need to be addressed:
-
Technological Advancements: Developing efficient and cost-effective technologies for sorting, cleaning, and processing different types of plastic trays is crucial for widespread adoption.
-
Material Compatibility: Not all plastic trays are compatible with tray-to-tray recycling. Ensuring the use of recyclable materials and developing methods to separate mixed plastics are essential.
-
Consumer Awareness: Raising awareness among consumers about the importance of properly disposing of plastic trays and supporting tray-to-tray recycling programs is crucial for success.
-
Infrastructure Development: Investing in collection, sorting, and processing infrastructure is vital to support the growth of tray-to-tray recycling initiatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What types of plastic trays are suitable for tray-to-tray recycling?
A: Currently, the most common recyclable plastic trays are made from polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE). However, advancements are being made to recycle other types of plastic trays, such as polystyrene (PS).
Q: How can I identify recyclable plastic trays?
A: Look for the recycling symbol (often a triangle with a number inside) on the bottom of the tray. The numbers 1 (PET), 2 (HDPE), 4 (LDPE), and 5 (PP) generally indicate recyclable materials.
Q: What are the limitations of tray-to-tray recycling?
A: Current technologies may not be able to recycle all types of plastic trays effectively. Additionally, contamination from food residues or other materials can hinder the recycling process.
Q: How can I contribute to tray-to-tray recycling?
A: Properly dispose of plastic trays in designated recycling bins. Support businesses and initiatives that prioritize tray-to-tray recycling. Advocate for policies that encourage and incentivize this practice.
Tips for Effective Tray-to-Tray Recycling
- Empty and rinse: Thoroughly empty and rinse plastic trays to remove food residues and other contaminants.
- Avoid mixing materials: Separate plastic trays from other recyclable materials, such as paper or metal.
- Check for recycling symbols: Ensure the plastic trays you are recycling carry the appropriate recycling symbols.
- Support local initiatives: Engage with local recycling programs and initiatives that promote tray-to-tray recycling.
Conclusion
Tray-to-tray recycling represents a significant step towards a more sustainable future. By closing the loop and transforming used plastic trays into new products, this process conserves resources, reduces waste, and minimizes environmental impact. While challenges remain, continued research, technological innovation, and collaboration among stakeholders are crucial to overcome these obstacles and unlock the full potential of tray-to-tray recycling. By embracing this approach, we can move towards a circular economy where plastic waste is no longer a burden but a valuable resource, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Closed Loop: Exploring the Potential of Tray-to-Tray Recycling. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!