The Art and Science of Plant Growth: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Gardens
Related Articles: The Art and Science of Plant Growth: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Gardens
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Art and Science of Plant Growth: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Gardens. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art and Science of Plant Growth: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Gardens
![]()
The verdant tapestry of life that unfolds in gardens and landscapes is a testament to the intricate dance between nature and human intervention. Understanding the fundamental principles of plant growth empowers individuals to nurture thriving ecosystems, from miniature pots to sprawling fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the key factors influencing plant growth, offering insights into optimizing conditions for flourishing vegetation.
Light: The Engine of Photosynthesis
Sunlight, the lifeblood of plants, serves as the primary energy source for photosynthesis, the intricate process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. This energy fuels growth, enabling plants to produce essential nutrients and structural components. The quantity and quality of light influence plant growth in profound ways:
- Light Intensity: Plants require varying levels of light intensity to thrive. Sun-loving plants, such as sunflowers and tomatoes, flourish in full sun, while shade-tolerant plants, like ferns and hostas, prefer dappled light conditions. Understanding a plant’s light requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate location.
- Light Duration: The duration of light exposure, known as photoperiod, plays a significant role in plant development. Plants respond to changes in day length, triggering processes like flowering, fruiting, and dormancy. For example, some plants require long days to flower, while others need shorter days.
- Light Spectrum: Different wavelengths of light influence specific plant processes. Red and blue light are particularly important for photosynthesis, while far-red light influences stem elongation. Understanding these nuances allows for the use of specialized lighting systems, such as grow lights, to optimize plant growth in indoor environments.
Water: The Elixir of Life
Water is essential for plant life, acting as a solvent for nutrients, a medium for transport, and a vital component in numerous physiological processes. The availability and quality of water significantly influence plant growth:
- Water Availability: Adequate water supply is crucial for maintaining turgor pressure, the internal pressure that keeps plant cells plump and upright. Insufficient water leads to wilting, stunted growth, and even death.
- Water Quality: The quality of water can influence plant growth. High levels of salts, minerals, or contaminants can negatively impact plant health. Understanding the composition of water sources is essential for optimizing plant growth.
- Water Management: Proper watering techniques are essential for maintaining healthy plants. Overwatering can lead to root rot, while underwatering can result in wilting and stress. Understanding a plant’s specific water requirements and adjusting watering practices accordingly is crucial.
Nutrients: The Building Blocks of Growth
Plants require a diverse array of nutrients to thrive, each playing a specific role in supporting growth, development, and overall health. These nutrients are absorbed from the soil through the roots:
- Macronutrients: Macronutrients are required in relatively large quantities by plants. They include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S). Each macronutrient plays a vital role in plant growth and development. For instance, nitrogen is crucial for leaf growth, phosphorus is essential for root development and flowering, and potassium contributes to disease resistance.
- Micronutrients: Micronutrients are required in trace amounts but are equally important for plant health. They include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), boron (B), molybdenum (Mo), and chlorine (Cl). Micronutrients often act as cofactors in enzymatic reactions, supporting various metabolic processes within the plant.
- Nutrient Availability: The availability of nutrients in the soil can be influenced by factors such as soil pH, organic matter content, and microbial activity. Understanding these factors allows for targeted nutrient supplementation to address specific deficiencies and optimize plant growth.
Temperature: The Thermostat of Life
Temperature plays a crucial role in regulating plant growth, affecting physiological processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and nutrient uptake. Each plant species has an optimal temperature range for growth:
- Optimal Temperature Range: Plants have specific temperature ranges within which they thrive. Exceeding or falling below this range can lead to stress, reduced growth, and even death. Understanding a plant’s optimal temperature range is crucial for selecting the appropriate growing location or adjusting environmental conditions.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Sudden temperature fluctuations can be detrimental to plant growth. Plants require a stable temperature environment for optimal development. Temperature fluctuations can disrupt physiological processes, leading to stress and reduced growth.
- Temperature and Growth Stages: Different plant growth stages are affected by temperature in unique ways. For example, seed germination requires specific temperature ranges, while flowering and fruiting are influenced by temperature fluctuations. Understanding these temperature sensitivities allows for optimizing growth conditions for each stage of development.
Air: The Invisible Nutrient
While often overlooked, air plays a crucial role in plant growth, providing essential gases for respiration and photosynthesis:
- Carbon Dioxide: Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a vital component of photosynthesis, serving as the source of carbon for plant growth. Increased CO2 levels can stimulate photosynthesis and enhance growth, particularly in enclosed environments.
- Oxygen: Oxygen is essential for respiration, the process by which plants convert stored energy into usable energy. Adequate oxygen levels are crucial for root growth and overall plant health.
- Air Circulation: Good air circulation is essential for preventing fungal diseases, promoting healthy growth, and ensuring proper gas exchange. Stagnant air can lead to moisture buildup and fungal infections, hindering plant growth.
Soil: The Foundation of Life
Soil provides a physical support system for plants, anchoring roots and providing essential nutrients. The composition and characteristics of soil significantly influence plant growth:
- Soil Texture: Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay particles. Each particle size influences water retention, drainage, and aeration, all of which impact plant growth.
- Soil Structure: Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates. Good soil structure promotes aeration, drainage, and root growth. Compacted soils hinder root development and reduce water and nutrient availability.
- Soil pH: Soil pH refers to its acidity or alkalinity. Each plant species has an optimal pH range for growth. Extremes in pH can affect nutrient availability and lead to nutrient deficiencies.
- Organic Matter: Organic matter, consisting of decomposed plant and animal material, improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. It also promotes microbial activity, which is essential for healthy soil ecosystems.
Other Factors Influencing Plant Growth
Beyond the fundamental elements of light, water, nutrients, temperature, air, and soil, several other factors can influence plant growth:
- Plant Genetics: Plant genetics play a crucial role in determining growth characteristics, such as height, leaf shape, and disease resistance. Selecting appropriate plant varieties for specific growing conditions is essential for success.
- Plant Hormones: Plant hormones, also known as phytohormones, regulate various physiological processes, including growth, development, and stress response. Understanding the role of different hormones allows for targeted interventions to enhance growth or mitigate stress.
- Pests and Diseases: Pests and diseases can significantly impact plant health and growth. Implementing preventative measures, such as proper sanitation, pest control, and disease management, is essential for maintaining healthy plants.
- Environmental Stress: Environmental stressors, such as drought, salinity, extreme temperatures, and pollution, can negatively impact plant growth. Understanding these stressors and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies is crucial for maintaining healthy plants.
FAQs about Plant Growth
1. What is the best way to water plants?
The best watering method depends on the plant species and growing conditions. Generally, it is best to water deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot.
2. How often should I fertilize my plants?
Fertilization frequency depends on the plant species, soil type, and growth stage. Follow the instructions on fertilizer packaging and observe plant growth for signs of nutrient deficiencies. Avoid overfertilizing, which can damage roots and negatively impact plant health.
3. What is the best way to improve soil quality?
Improving soil quality involves incorporating organic matter, such as compost or manure, to enhance soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. Regularly amending the soil with organic matter promotes microbial activity and creates a healthy soil ecosystem.
4. How can I protect my plants from pests and diseases?
Preventative measures are essential for protecting plants from pests and diseases. This includes maintaining good sanitation practices, identifying and removing infected plants, using organic pest control methods, and promoting healthy plant growth through proper care.
5. What are some common signs of plant stress?
Common signs of plant stress include wilting, leaf discoloration, stunted growth, and premature leaf drop. Addressing the underlying cause of stress, such as lack of water, inadequate nutrients, or pest infestation, is crucial for restoring plant health.
Tips for Promoting Plant Growth
- Choose the right plants for your growing conditions: Consider factors such as light availability, soil type, and climate when selecting plants.
- Provide adequate water and nutrients: Water deeply and infrequently, and fertilize according to plant needs.
- Maintain good soil health: Amend soil with organic matter and test pH levels regularly.
- Protect plants from pests and diseases: Implement preventative measures and address issues promptly.
- Monitor plant growth and adjust care accordingly: Observe plants for signs of stress or nutrient deficiencies and adjust care practices as needed.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate interplay of factors influencing plant growth empowers individuals to cultivate thriving gardens and landscapes. By providing optimal conditions for light, water, nutrients, temperature, air, and soil, and by implementing sound horticultural practices, individuals can nurture vibrant plant life, enriching their surroundings with the beauty and bounty of nature. A deep understanding of plant growth principles fosters a sense of stewardship, enabling individuals to contribute to the preservation of our planet’s green tapestry.
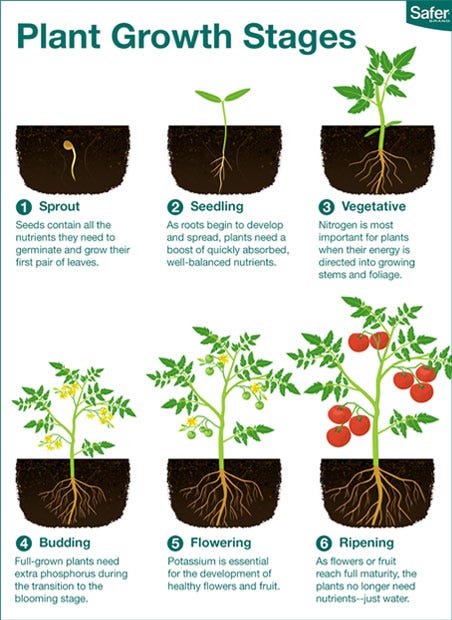
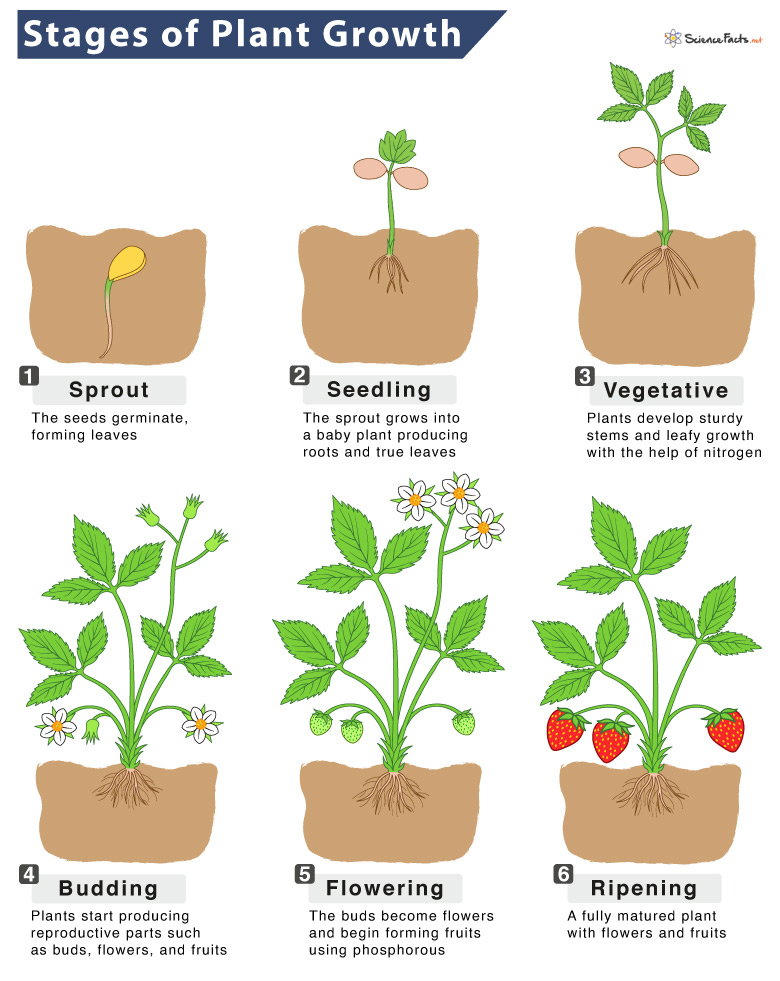
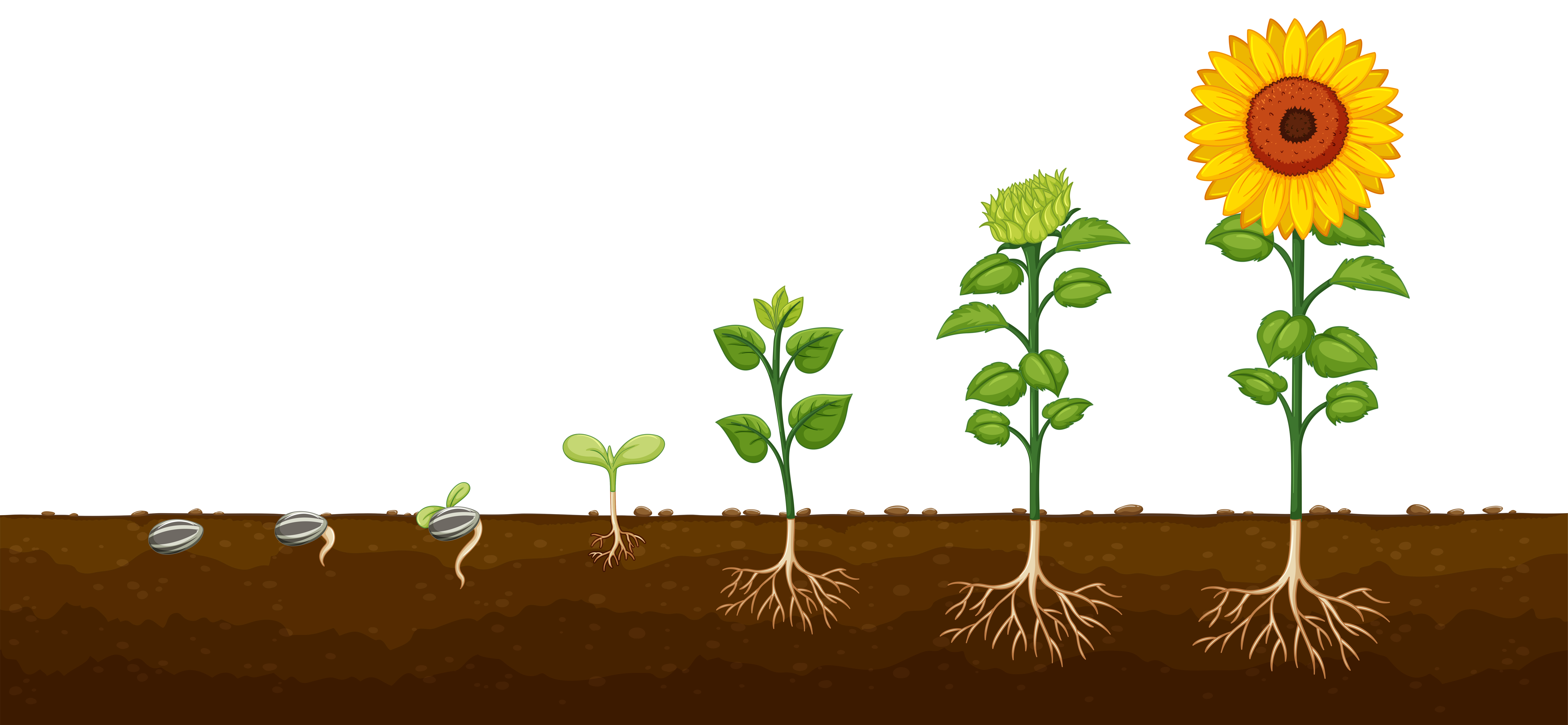
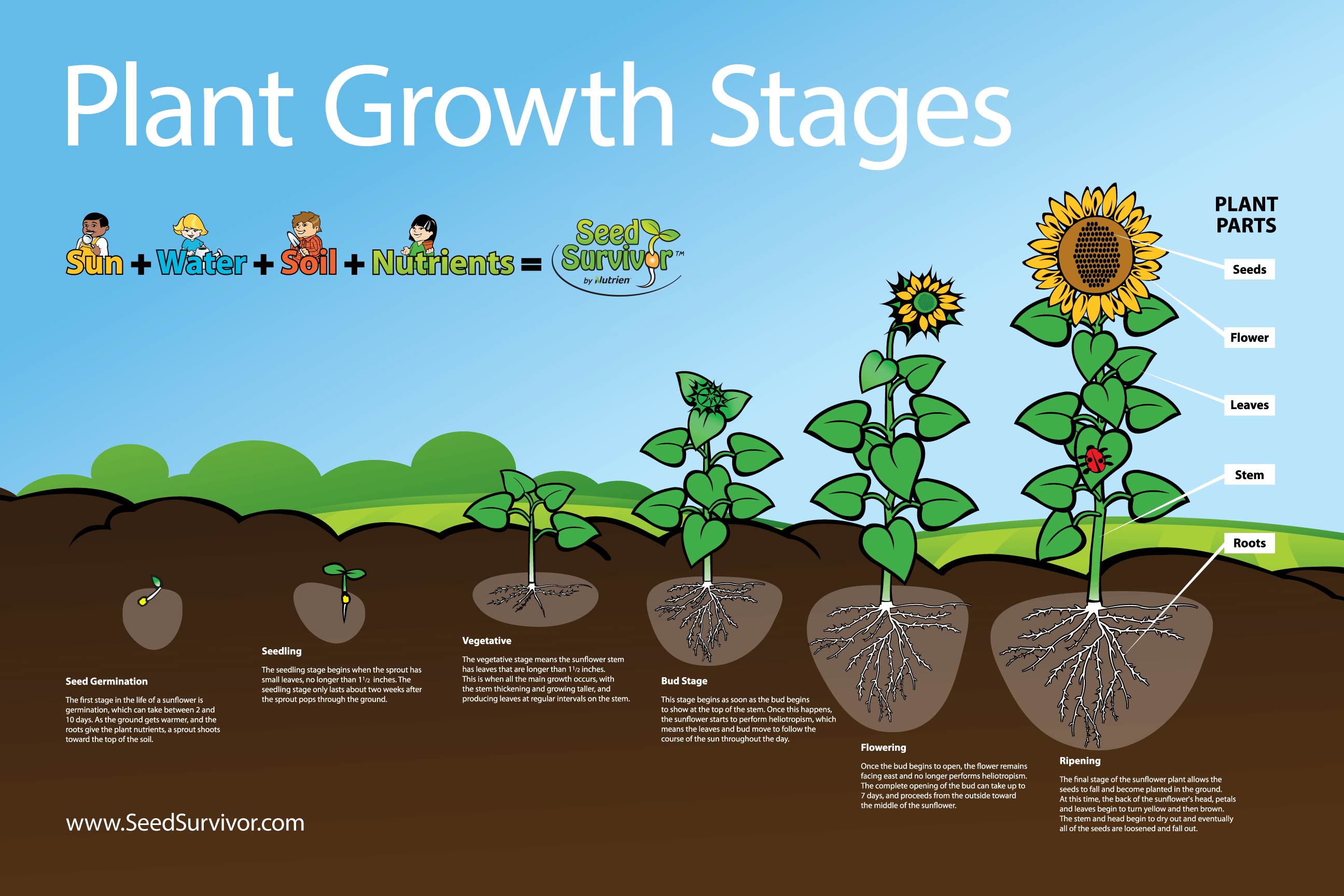
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art and Science of Plant Growth: A Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Gardens. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!