A Comprehensive Guide To The Top 3D Printing Projects For 2023
A Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3D Printing Projects for 2023
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3D Printing Projects for 2023
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3D Printing Projects for 2023. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3D Printing Projects for 2023

The world of 3D printing continues to evolve at a rapid pace, offering an ever-expanding range of possibilities for both hobbyists and professionals. From intricate models to functional prototypes, the technology empowers individuals to create objects previously unimaginable. As we delve into 2023, several trends emerge, highlighting the most compelling and impactful 3D printing projects.
1. Functional Prototypes and Customizations:
3D printing has become an indispensable tool for engineers, designers, and product developers. The ability to rapidly create prototypes allows for iterative design processes, reducing development time and costs. This is particularly crucial in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, where precision and functionality are paramount.
Benefits:
- Accelerated Design Cycles: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping, facilitating quick iteration and refinement of designs.
- Cost Reduction: Prototyping with 3D printing eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds, reducing overall development costs.
- Enhanced Functionality: 3D printing allows for intricate designs and complex geometries, enabling the creation of highly functional prototypes.
- Customizations: 3D printing empowers the creation of customized prototypes tailored to specific needs and applications.
FAQs:
- What materials are best suited for functional prototypes? The choice of material depends on the specific application. ABS, PLA, nylon, and carbon fiber reinforced plastics are commonly used for their strength, durability, and heat resistance.
- How can I ensure the accuracy and functionality of my 3D printed prototypes? Calibration of the 3D printer and use of high-quality materials are crucial for achieving accurate and functional prototypes. Employing design software with simulation capabilities can further enhance the process.
Tips:
- Utilize CAD software: Leverage CAD software for precise design and model creation, ensuring accurate representation of the prototype.
- Optimize for 3D printing: Design with printability in mind, considering factors like overhangs, support structures, and material properties.
- Test and iterate: Conduct thorough testing of the prototype to identify any design flaws or areas for improvement.
2. Personalized and Customized Products:
The ability to create unique and personalized products is a significant advantage of 3D printing. From custom jewelry and home decor to personalized medical devices and prosthetics, the technology empowers individuals to design and manufacture objects tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
Benefits:
- Uniqueness and Individuality: 3D printing allows for the creation of truly unique products, reflecting personal style and preferences.
- Customization for Specific Needs: Products can be customized to fit individual requirements, providing optimal comfort and functionality.
- Enhanced Personalization: 3D printing enables the integration of personalized elements, such as names, dates, or logos, adding a unique touch to products.
- Mass Customization: 3D printing allows for the production of customized products on a larger scale, catering to diverse individual needs.
FAQs:
- What types of materials are suitable for creating personalized products? A wide range of materials can be used, including resins, metals, and ceramics, depending on the desired aesthetic and functional properties.
- How can I design and create personalized products using 3D printing? Various online platforms and design software tools are available to assist with designing and creating personalized products, offering templates, customization options, and 3D printing services.
Tips:
- Explore design software: Experiment with design software specifically tailored for 3D printing, allowing for intricate detailing and personalization.
- Utilize online platforms: Leverage online platforms that offer 3D printing services and design templates for personalized products.
- Consider material properties: Select materials that align with the intended use and aesthetics of the personalized product.
3. Educational and STEM Tools:
3D printing has emerged as a powerful tool for education, particularly in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) fields. The technology allows students to visualize and interact with complex concepts, fostering hands-on learning experiences and sparking creativity.
Benefits:
- Engaging Learning Experiences: 3D printing provides students with tangible, interactive models, enhancing their understanding of abstract concepts.
- Problem-Solving and Design Thinking: Students can design, print, and test their own creations, developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Project-Based Learning: 3D printing facilitates project-based learning, encouraging students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems.
- Increased Accessibility: 3D printing makes advanced technology accessible to students, providing opportunities for hands-on experimentation and exploration.
FAQs:
- What types of projects are suitable for 3D printing in education? A wide range of projects can be undertaken, from simple models to complex mechanical devices, allowing students to explore different disciplines.
- How can teachers integrate 3D printing into their curriculum? Teachers can incorporate 3D printing into existing lessons, designing projects that require students to utilize the technology and apply their knowledge.
Tips:
- Develop age-appropriate projects: Design projects that are engaging and challenging for students at different age levels.
- Provide adequate support: Offer clear instructions, tutorials, and technical support to ensure students can effectively utilize 3D printing technology.
- Encourage creativity and experimentation: Promote a culture of innovation and exploration, encouraging students to think outside the box and experiment with different designs.
4. Architectural Models and Design Visualization:
3D printing has revolutionized architectural design, allowing architects to create highly detailed and accurate models of buildings and structures. These models provide valuable tools for visualization, communication, and client presentations.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Visualization: 3D printed models provide a tangible representation of architectural designs, enabling better visualization and understanding.
- Improved Communication: Models facilitate clear communication between architects, clients, and stakeholders, reducing ambiguity and misunderstandings.
- Client Engagement: 3D printed models enhance client engagement, providing a more immersive and interactive experience.
- Design Iteration and Testing: Models allow for experimentation with different design elements and the identification of potential issues before construction.
FAQs:
- What materials are commonly used for architectural models? Materials like PLA, ABS, and resin are commonly used, offering a balance of strength, detail, and affordability.
- How can I create detailed architectural models using 3D printing? Specialized CAD software and 3D printing services are available, catering to the specific needs of architectural modeling.
Tips:
- Utilize professional-grade software: Employ specialized CAD software designed for architectural modeling, ensuring accuracy and detail.
- Consider scale and detail: Choose the appropriate scale and level of detail for the model, balancing accuracy with practicality.
- Enhance with paint and finishing: Apply paint, textures, and other finishing techniques to enhance the visual appeal and realism of the model.
5. Medical Devices and Prosthetics:
3D printing is playing an increasingly important role in the medical field, enabling the creation of custom medical devices, prosthetics, and implants. The technology offers a personalized approach to healthcare, providing patients with tailored solutions that meet their specific needs.
Benefits:
- Personalized Solutions: 3D printing allows for the creation of custom medical devices and prosthetics tailored to individual anatomy and requirements.
- Improved Functionality: Customized solutions enhance functionality and comfort, improving patients’ quality of life.
- Reduced Costs: 3D printing can reduce the cost of manufacturing medical devices, making them more accessible to patients.
- Faster Production: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and production, reducing wait times for patients in need of medical devices.
FAQs:
- What materials are used for 3D printed medical devices? Biocompatible materials like PEEK, nylon, and titanium are commonly used, ensuring safety and compatibility with the human body.
- How are 3D printed medical devices designed and manufactured? Specialized software and 3D printing techniques are employed, utilizing patient-specific data and advanced manufacturing processes.
Tips:
- Collaborate with medical professionals: Partner with medical professionals to ensure the design and functionality of 3D printed devices meet clinical standards.
- Utilize biocompatible materials: Choose materials that are safe, non-toxic, and compatible with the human body.
- Maintain strict quality control: Implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure the safety and effectiveness of 3D printed medical devices.
6. Home Decor and Furniture:
3D printing is transforming the way we design and create home decor and furniture. From intricate ornaments and decorative objects to functional furniture pieces, the technology enables the creation of unique and personalized items that add character and style to our living spaces.
Benefits:
- Unique and Personalized Designs: 3D printing allows for the creation of custom home decor and furniture pieces that reflect individual taste and preferences.
- Enhanced Functionality: 3D printed furniture can be designed with specific functionalities, such as integrated lighting, storage compartments, or adjustable features.
- Sustainable Production: 3D printing reduces waste and material consumption compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
- Affordable Customization: 3D printing makes custom home decor and furniture more accessible, allowing individuals to create unique pieces without breaking the bank.
FAQs:
- What materials are suitable for 3D printed home decor and furniture? Materials like PLA, ABS, wood filament, and resin are commonly used, offering a range of aesthetics and durability.
- How can I design and create my own home decor and furniture using 3D printing? Various online platforms and design software tools are available, offering templates, customization options, and 3D printing services.
Tips:
- Explore design resources: Utilize online platforms and design software that offer templates and resources for home decor and furniture.
- Consider material properties: Select materials that align with the intended use and aesthetic of the home decor or furniture piece.
- Experiment with finishes: Explore different finishing techniques, such as painting, sanding, or adding textures, to enhance the visual appeal.
7. Toys and Games:
3D printing has opened up a world of possibilities for toy and game design. The technology enables the creation of custom toys, game pieces, and even entire board games, fostering creativity and imagination in children and adults alike.
Benefits:
- Personalized Toys and Games: 3D printing allows for the creation of custom toys and games tailored to individual interests and preferences.
- Enhanced Play Experiences: 3D printed toys and games can be designed with unique features and functionalities, enhancing the play experience.
- Educational Value: 3D printed toys and games can incorporate educational elements, teaching children about STEM concepts or history.
- Sustainable Production: 3D printing reduces waste and material consumption in the toy and game industry.
FAQs:
- What materials are safe for 3D printed toys? Materials like PLA, ABS, and non-toxic resins are generally considered safe for children’s toys.
- How can I design and create my own toys and games using 3D printing? Design software and online platforms offer templates, tools, and resources for creating custom toys and games.
Tips:
- Prioritize safety: Ensure the materials used for 3D printed toys are non-toxic and meet safety standards.
- Consider age appropriateness: Design toys and games that are suitable for the intended age group, considering factors like size, complexity, and safety.
- Embrace creativity: Encourage children to design their own toys and games, fostering their imagination and problem-solving skills.
Conclusion:
3D printing continues to transform various industries and aspects of our lives, offering endless possibilities for innovation and creativity. From functional prototypes to personalized products, educational tools, and artistic expressions, the technology empowers individuals and businesses to create objects that were previously unimaginable. As we move forward, 3D printing is poised to play an even greater role in shaping our future, pushing the boundaries of design, manufacturing, and human ingenuity.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Top 3D Printing Projects for 2023. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The World Of "N": An Exploration Of Objects, Concepts, And Phenomena
The World of "N": An Exploration of Objects, Concepts, and Phenomena
Related Articles: The World of "N": An Exploration of Objects, Concepts, and Phenomena
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The World of "N": An Exploration of Objects, Concepts, and Phenomena. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The World of "N": An Exploration of Objects, Concepts, and Phenomena

The letter "N" holds a prominent place in the English alphabet, serving as a starting point for a diverse array of words representing objects, concepts, and phenomena that shape our world. This exploration delves into the significance of these "N" words, highlighting their importance and benefits across various domains.
Nature’s Bounty: A Symphony of "N"
From the majestic Nile River, the lifeblood of ancient Egypt, to the towering Neverest, the world’s highest peak, nature’s wonders often begin with the letter "N". These natural marvels inspire awe, foster scientific inquiry, and provide essential resources for human sustenance.
Nutrients, for instance, are the building blocks of life, providing the energy and materials necessary for growth and development. Nitrogen, a crucial component of DNA and proteins, is a vital element for plant growth, underpinning agricultural productivity and food security. Natural resources, ranging from forests and minerals to water and air, sustain human civilization and require responsible management for long-term sustainability.
Navigating the World: Tools and Techniques Starting with "N"
Navigation, the art of finding one’s way, is crucial for exploration, transportation, and communication. Navigational tools, such as compasses, maps, and GPS systems, have revolutionized human mobility and facilitated global connectivity. Navigable waterways, from rivers and lakes to oceans, have historically served as vital trade routes, connecting civilizations and fostering cultural exchange.
Networks, both physical and digital, are essential for information sharing and collaboration. Network infrastructure, including roads, railways, and communication systems, enables the efficient movement of goods, people, and ideas. Networking, the process of building relationships and connections, is vital for personal and professional growth, fostering collaboration and innovation.
Nourishment and Sustenance: The Importance of "N" in Food and Drink
Nutrition plays a central role in human health and well-being. Nutritious foods, rich in vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients, support physical growth, cognitive function, and disease prevention. Nutraceuticals, food-derived substances with potential health benefits, offer promising avenues for disease management and overall well-being.
Nourishment extends beyond food to encompass the act of caring and supporting others. Nurturing relationships, characterized by empathy, compassion, and understanding, contribute to emotional well-being and foster strong social bonds. Nurturing environments, whether in homes, schools, or communities, provide a safe and supportive space for individuals to thrive.
Knowledge and Understanding: The "N" of Learning and Discovery
Numeracy, the ability to understand and use numbers, is a fundamental skill for navigating the complexities of modern life. Numbers, from simple counting to advanced mathematics, provide a framework for understanding the world around us. Numerical data, collected and analyzed through statistics, informs decision-making and drives progress in various fields.
Nomenclature, the system of naming things, provides a common language for communication and understanding. Nomenclature systems, from scientific classifications to legal terminology, facilitate the organization and dissemination of knowledge. Nomenclature is essential for clarity, precision, and effective communication in diverse fields, from science and technology to law and literature.
The "N" of Art and Creativity
Novelty, the quality of being new and original, is a hallmark of artistic expression. Novel works of art challenge conventions, push boundaries, and inspire new ways of seeing the world. New perspectives, emerging from the creative process, enrich our understanding of human experience and the complexities of life.
Narrative, the art of storytelling, is a fundamental human endeavor. Narratives, whether written, spoken, or visual, connect us to our past, shape our present, and inspire our future. Narrative forms, ranging from novels and plays to films and music, offer diverse avenues for exploring human emotions, experiences, and aspirations.
FAQs by "N"
Q: What are some examples of "N" words that represent natural phenomena?
A: Examples include Nature, Nights, Northern Lights, Natural Disasters, Natural Selection, Natural Resources, Nature Conservancy, and Natural Gas.
Q: How does "N" relate to the concept of knowledge and understanding?
A: Nomenclature, Numeracy, Natural Laws, Novelty, New Discoveries, New Insights, News, and National Geographic are examples of "N" words related to knowledge and understanding.
Q: What are some examples of "N" words related to art and creativity?
A: Examples include Novel, Narrative, Novelty, New Wave, New Media, New York Times, New Yorker, and New Music.
Tips by "N"
Tip 1: Nurture your curiosity by exploring new ideas and perspectives.
Tip 2: Nurture your relationships by fostering empathy, compassion, and understanding.
Tip 3: Nurture your creativity by embracing novelty and experimentation.
Tip 4: Nurture your environment by practicing sustainability and responsible resource management.
Tip 5: Nurture your health by consuming nutritious foods and engaging in regular physical activity.
Conclusion by "N"
The letter "N" serves as a starting point for a vast array of words that represent objects, concepts, and phenomena crucial to human existence. From the wonders of nature to the tools of navigation, from the importance of nourishment to the pursuit of knowledge, the world of "N" encompasses diverse aspects of our lives, highlighting their significance and benefits in shaping our understanding and experience of the world. By appreciating the richness and diversity of "N" words, we gain a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of our world and the vital role these elements play in shaping our lives.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The World of "N": An Exploration of Objects, Concepts, and Phenomena. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Exploring The Multi-Layered World Of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring the Multi-Layered World of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Exploring the Multi-Layered World of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Multi-Layered World of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Multi-Layered World of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide

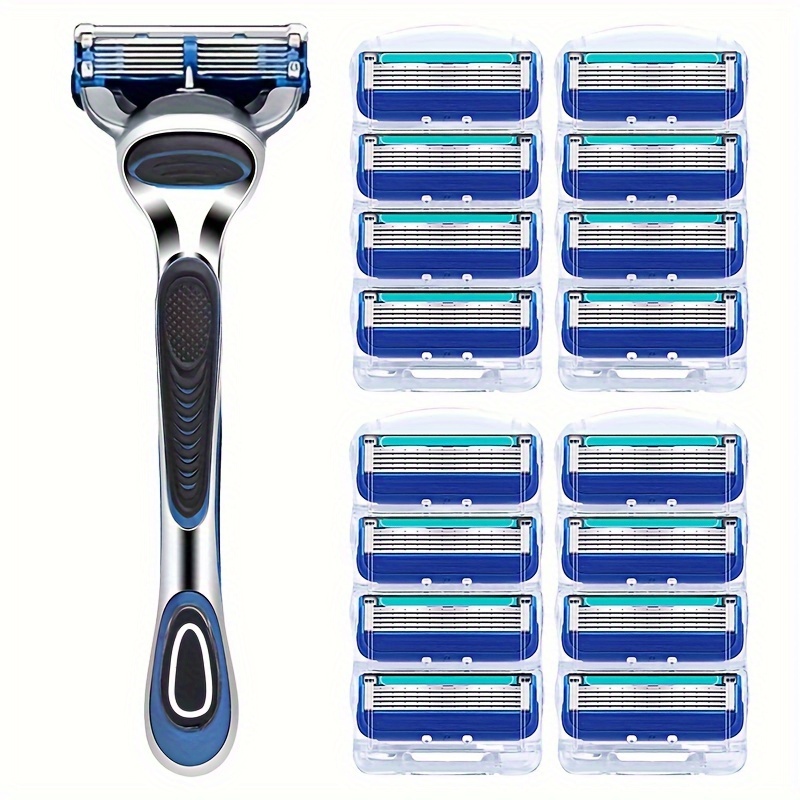
In the realm of personal care, razors are essential tools for maintaining a smooth and clean appearance. Temu, a popular online retailer, offers a diverse range of razors, including those with six layers. These razors, characterized by their multi-layered blades, promise a superior shaving experience with enhanced precision and comfort. This article delves into the world of Temu’s six-layer razors, exploring their construction, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Unveiling the Multi-Layered Design:
Temu’s six-layer razors are designed to provide a close and comfortable shave. The multiple layers of blades are strategically arranged to achieve specific functions:
- The First Layer: Typically the outermost layer, this blade serves as the initial cutting edge, removing bulk hair.
- The Second Layer: Designed to refine the initial cut, this blade helps reduce razor burn and irritation.
- The Third Layer: This layer focuses on precision, ensuring a close shave and reducing the need for multiple passes.
- The Fourth Layer: This layer further refines the shave, enhancing smoothness and reducing the risk of ingrown hairs.
- The Fifth Layer: This blade is primarily focused on providing a comfortable shaving experience, minimizing skin irritation.
- The Sixth Layer: The innermost layer acts as a final touch, ensuring a smooth and clean finish.
Benefits of Six-Layer Razors:
The multi-layered design of Temu’s razors offers several advantages over traditional razors:
- Enhanced Precision: The multiple blades allow for a closer and more precise shave, reducing the need for multiple passes.
- Reduced Skin Irritation: The layered design helps minimize razor burn and irritation, providing a more comfortable shaving experience.
- Improved Smoothness: The multiple blades work together to achieve a smoother and more even shave, resulting in a more polished appearance.
- Reduced Ingrown Hairs: The precision and smoothness offered by the multi-layered design can help prevent ingrown hairs.
- Durability: The robust construction of six-layer razors typically results in longer blade life, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Potential Drawbacks:
While six-layer razors offer numerous benefits, there are also potential drawbacks to consider:
- Cost: Temu’s six-layer razors may be more expensive than traditional razors, especially when considering the cost of replacement blades.
- Maintenance: The intricate design of multi-layered razors requires careful cleaning and maintenance to prevent clogging and ensure optimal performance.
- Sensitivity: Individuals with sensitive skin may experience increased irritation with multi-layered razors, as the multiple blades can increase friction.
FAQs
Q: Are six-layer razors suitable for all skin types?
A: While six-layer razors offer benefits for many individuals, those with sensitive skin may experience increased irritation. It is recommended to test a small area of skin before using a multi-layered razor on the entire body.
Q: How often should I replace the blades on a six-layer razor?
A: The blade life of a six-layer razor varies depending on usage and individual hair growth patterns. However, it is generally recommended to replace the blades every 5-7 shaves for optimal performance and hygiene.
Q: Are six-layer razors better than traditional razors?
A: There is no definitive answer to this question, as individual preferences and skin types vary. Six-layer razors offer enhanced precision, comfort, and durability, but they may be more expensive and require more maintenance.
Tips
- Prepare Your Skin: Before shaving, it is crucial to soften the hair and prepare the skin. This can be achieved by applying a warm washcloth or using a shaving cream or gel.
- Shave with the Grain: For a smoother and less irritating shave, shave in the direction of hair growth.
- Avoid Excessive Pressure: Applying excessive pressure can increase the risk of razor burn and irritation.
- Rinse Regularly: Rinse the blades frequently to remove hair and shaving cream buildup, ensuring a clean and efficient shave.
- Moisturize After Shaving: Applying a moisturizer after shaving helps soothe the skin and prevent dryness.
Conclusion
Temu’s six-layer razors offer a unique and innovative approach to shaving, promising enhanced precision, comfort, and durability. While they may be more expensive than traditional razors and require careful maintenance, their multi-layered design provides a close and smooth shave, reducing the need for multiple passes and minimizing skin irritation. Ultimately, the decision of whether to invest in a six-layer razor depends on individual preferences, skin type, and budget. By carefully considering the benefits and drawbacks, individuals can make an informed choice that best suits their shaving needs.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Multi-Layered World of Temu’s Household Razors: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Navigating The Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Vocabulary
Navigating the Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Vocabulary
Related Articles: Navigating the Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Vocabulary
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Vocabulary. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Vocabulary

The space we call home is a complex ecosystem of objects and spaces, each serving a specific purpose and contributing to our daily lives. Understanding the vocabulary associated with this environment is crucial for effective communication, navigating daily tasks, and appreciating the nuances of our domestic sphere. This guide delves into the diverse vocabulary associated with things at home, exploring its importance and providing a comprehensive overview of key categories and terms.
The Foundations of Home: Structures and Spaces
The physical structure of a dwelling forms the foundation for its internal organization. Understanding the terminology associated with these structures is essential for comprehending the overall layout and functionality of a home:
-
Rooms: The basic units of a home, each serving a distinct purpose. Common rooms include:
- Living Room: The primary social space, often featuring comfortable seating, entertainment systems, and decorative elements.
- Kitchen: The heart of the home, where food is prepared and meals are often enjoyed.
- Bedroom: A private space for sleeping, relaxation, and personal belongings.
- Bathroom: A space dedicated to hygiene and personal care, typically equipped with a toilet, sink, and shower or bathtub.
- Dining Room: A formal space for dining, often separate from the kitchen.
- Study: A dedicated space for work, reading, or other intellectual pursuits.
- Basement: A lower level of the house, often used for storage, utilities, or recreational activities.
- Attic: The uppermost level of the house, typically used for storage or conversion into living space.
- Walls: The vertical structures that enclose rooms and define their boundaries.
- Ceiling: The uppermost surface of a room, often concealing electrical wiring and other utilities.
- Floor: The horizontal surface that forms the base of a room, typically made of wood, tile, or carpet.
- Windows: Openings in walls that allow light and ventilation.
- Doors: Openings in walls that provide access to and from rooms.
- Stairs: Structures that connect different levels of a home.
- Roof: The uppermost structure of a home, protecting the interior from the elements.
Furnishing the Home: Essential Objects and Their Roles
Once the physical structure is established, the interior is furnished with objects that serve various purposes and contribute to the home’s functionality and aesthetic appeal.
-
Furniture: The large, movable objects that define the layout and functionality of rooms. Common furniture types include:
- Sofas and Chairs: Provide seating for relaxation and socializing.
- Tables: Surfaces for dining, working, or displaying objects.
- Beds: Provide sleeping surfaces and storage for bedding.
- Desks: Provide work surfaces for writing, computing, or studying.
- Cabinets and Dressers: Provide storage for clothes, dishes, or other household items.
- Shelves: Provide storage for books, decorative objects, or other items.
-
Appliances: Electrical devices that perform specific tasks, enhancing the functionality of the home. Common appliances include:
- Refrigerator: Stores food at a cool temperature to preserve freshness.
- Stove: Used for cooking food.
- Oven: Used for baking and roasting food.
- Dishwasher: Cleans dishes automatically.
- Washing Machine and Dryer: Used for cleaning and drying laundry.
- Microwave: Heats food quickly and efficiently.
- Television: Provides entertainment through video and audio.
- Computer: Used for communication, information access, and entertainment.
-
Decorative Objects: Items that enhance the aesthetic appeal of a home, reflecting personal taste and style. These can include:
- Paintings: Artwork that adds visual interest and personality to a room.
- Photographs: Personal images that evoke memories and create a sense of home.
- Sculptures: Three-dimensional art objects that add visual texture and depth.
- Vases: Decorative containers for displaying flowers or other plants.
- Rugs: Floor coverings that add warmth, comfort, and visual interest.
- Curtains and Blinds: Window coverings that provide privacy, light control, and decorative accents.
Maintaining the Home: Tools and Supplies for Everyday Tasks
Keeping a home clean, organized, and functional requires a variety of tools and supplies:
-
Cleaning Supplies: Products used for cleaning surfaces, floors, and appliances. These include:
- Detergents: Cleaning agents for dishes, laundry, and general surfaces.
- Disinfectants: Agents that kill bacteria and viruses.
- Sprays and Cleaners: Specialized products for cleaning specific surfaces, such as glass, wood, or metal.
- Brooms, Mops, and Vacuums: Tools for cleaning floors and carpets.
- Sponges, Rags, and Brushes: Tools for cleaning various surfaces.
-
Maintenance Tools: Tools used for minor repairs and upkeep of the home. These include:
- Screwdrivers, Hammers, and Wrenches: Tools for tightening, loosening, and assembling objects.
- Measuring Tape: Used for measuring distances and dimensions.
- Level: Used to ensure surfaces are horizontal or vertical.
- Pliers: Used for gripping and manipulating objects.
- Safety Glasses and Gloves: Protective gear for working with tools and cleaning supplies.
-
Storage Solutions: Containers and organizers used for storing and organizing household items. These include:
- Boxes and Bins: Containers for storing a variety of items.
- Drawers and Shelves: Storage solutions for organizing clothes, books, and other items.
- Hangers: Used for hanging clothes and other items.
- Labels: Used for identifying and organizing storage containers.
Beyond the Basics: Specialized Vocabulary for Specific Areas
While the aforementioned terms provide a general overview of household vocabulary, specific areas within the home have their own unique terminology:
-
Kitchen:
- Countertops: Horizontal surfaces for food preparation and cooking.
- Sink: Used for washing dishes and food preparation.
- Stovetop: The cooking surface of a stove.
- Oven: Used for baking and roasting food.
- Dishwasher: Cleans dishes automatically.
- Refrigerator: Stores food at a cool temperature to preserve freshness.
- Microwave: Heats food quickly and efficiently.
- Pantry: A storage space for food and kitchen supplies.
-
Bathroom:
- Toilet: Used for waste disposal.
- Sink: Used for washing hands and face.
- Shower: A device for showering.
- Bathtub: A container for bathing.
- Mirror: Used for reflection and personal grooming.
- Towel Rack: Used for drying towels.
- Medicine Cabinet: A cabinet for storing medications and toiletries.
-
Bedroom:
- Bed: Provides a sleeping surface.
- Nightstand: A small table next to the bed for holding personal items.
- Dresser: Provides storage for clothes and other personal belongings.
- Wardrobe: A freestanding closet for storing clothes.
- Closet: A built-in storage space for clothes and other items.
- Curtains or Blinds: Window coverings that provide privacy and light control.
-
Living Room:
- Sofa: A large, comfortable seat for relaxation and socializing.
- Armchair: A comfortable chair with armrests.
- Coffee Table: A low table in front of the sofa for holding drinks and snacks.
- Television: Provides entertainment through video and audio.
- Bookshelf: A shelf for storing books.
- Fireplace: A hearth for burning wood or gas for warmth and ambiance.
- Rugs: Floor coverings that add warmth, comfort, and visual interest.
FAQs on Household Vocabulary
Q: What are some common words used to describe the layout of a home?
A: Common terms include "one-story," "two-story," "split-level," "ranch," "colonial," "condo," "apartment," "duplex," "townhouse," and "loft." These terms describe the overall structure and configuration of a dwelling.
Q: What are some words used to describe the style of a home?
A: Common style descriptors include "modern," "contemporary," "traditional," "victorian," "colonial," "farmhouse," "mid-century," "rustic," and "industrial." These terms reflect the architectural and design elements of a dwelling.
Q: What are some words used to describe the condition of a home?
A: Common condition descriptors include "new," "renovated," "updated," "maintained," "move-in ready," "needs work," "fixer-upper," "foreclosure," and "distressed." These terms provide insight into the overall state of a dwelling.
Q: What are some words used to describe the features of a home?
A: Common feature descriptors include "garage," "driveway," "yard," "porch," "balcony," "deck," "pool," "fireplace," "central air," "finished basement," "walk-in closet," and "stainless steel appliances." These terms highlight specific amenities and features of a dwelling.
Tips for Expanding Your Household Vocabulary
- Read Home Improvement Magazines and Websites: These resources often feature articles and guides that use a wide range of household vocabulary.
- Watch Home Improvement Shows: Television shows and streaming services offer a wealth of information about home construction, design, and maintenance, exposing viewers to a diverse range of vocabulary.
- Visit Home Improvement Stores: Browsing through aisles and observing product labels and descriptions can expand your knowledge of household items and their associated terminology.
- Pay Attention to Everyday Language: Listen for household vocabulary used in conversations, news reports, and everyday life.
- Use a Dictionary or Thesaurus: When encountering unfamiliar terms, consult a dictionary or thesaurus to understand their meaning and usage.
Conclusion
The vocabulary associated with things at home is essential for navigating our daily lives, communicating effectively, and appreciating the intricacies of our domestic spaces. By expanding our knowledge of these terms, we gain a deeper understanding of the objects, structures, and functions that contribute to the comfort, functionality, and beauty of our homes. This comprehensive guide provides a foundation for understanding the diverse vocabulary associated with our living environments, empowering us to communicate more effectively and navigate the complexities of homeownership with greater confidence.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Familiar: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Vocabulary. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
A Comprehensive Look At Objects Measuring Five Inches
A Comprehensive Look at Objects Measuring Five Inches
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Objects Measuring Five Inches
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Objects Measuring Five Inches. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Objects Measuring Five Inches

The measurement of five inches, seemingly unremarkable on its own, holds a surprisingly diverse range of applications across various fields. This length, roughly the size of a human hand, can be found in objects as commonplace as a smartphone to as specialized as a medical instrument.
The Everyday Five Inches:
The world around us is filled with objects that measure five inches in length. Everyday items such as smartphones, credit cards, and standard-sized pens all fall within this measurement. These objects, often taken for granted, play crucial roles in our daily lives, facilitating communication, financial transactions, and note-taking.
-
Smartphones: The ubiquitous smartphone, measuring approximately five inches in length, has revolutionized communication, information access, and entertainment. Its compact size allows for comfortable handheld use and portability, while its screen size offers a balance between visual clarity and ease of handling.
-
Credit Cards: Credit cards, measuring five inches in length, have become an integral part of modern financial systems. Their standardized dimensions ensure compatibility with card readers and facilitate secure transactions.
-
Pens: Pens, a common writing tool, typically measure five inches in length. This length provides a comfortable grip and allows for precise control during writing.
Five Inches in the World of Technology:
The five-inch measurement extends beyond everyday objects, finding its way into the realm of technology. Components such as memory sticks and hard drives, often measuring five inches, play a vital role in storing and retrieving digital information.
-
Memory Sticks: Memory sticks, measuring five inches in length, provide portable storage for digital files. Their compact size and high storage capacity make them ideal for transferring data between devices.
-
Hard Drives: Hard drives, a crucial component of computers, often measure five inches in length. These devices provide large storage capacity for operating systems, applications, and user data.
Five Inches in the Medical Field:
The five-inch length also finds application in the medical field, where precision and accuracy are paramount. Medical instruments such as surgical blades and catheters often measure five inches, allowing for precise procedures and minimally invasive interventions.
-
Surgical Blades: Surgical blades, used for precise incisions during surgery, typically measure five inches in length. This length provides sufficient reach and control for delicate procedures.
-
Catheters: Catheters, used for various medical procedures, often measure five inches in length. Their size and flexibility allow for insertion into different body cavities for diagnosis and treatment.
Five Inches in the Culinary World:
Even in the culinary world, five inches plays a role. Cooking utensils such as spatulas and ladles, often measuring five inches, facilitate efficient food preparation and serving.
-
Spatulas: Spatulas, used for flipping and scraping food, typically measure five inches in length. Their size and flexibility allow for efficient cooking and serving.
-
Ladles: Ladles, used for serving liquids, often measure five inches in length. Their size and shape allow for precise portioning and comfortable handling.
Five Inches in the Arts and Crafts:
In the realm of arts and crafts, five inches can be found in various tools and materials. Paintbrushes, knitting needles, and sculpting tools often measure five inches, facilitating creative expression and meticulous craftsmanship.
-
Paintbrushes: Paintbrushes, used for applying paint to surfaces, typically measure five inches in length. This length provides a balance between control and reach for different brushstrokes.
-
Knitting Needles: Knitting needles, used for creating knitted fabrics, often measure five inches in length. This length allows for comfortable knitting and a variety of stitch patterns.
-
Sculpting Tools: Sculpting tools, used for shaping and molding clay or other materials, often measure five inches in length. This length provides sufficient leverage and precision for intricate details.
Five Inches in the World of Sports:
Even in the world of sports, five inches can be found in equipment and accessories. Golf clubs, baseball bats, and badminton rackets often measure five inches in specific parts, contributing to the performance and functionality of these tools.
-
Golf Clubs: Golf clubs, used for striking the golf ball, have specific lengths for different clubs, with some measuring five inches in certain parts. These dimensions contribute to the club’s swing weight and overall performance.
-
Baseball Bats: Baseball bats, used for hitting the baseball, have a specific length that influences the player’s swing and ability to hit the ball. Some parts of the bat may measure five inches, contributing to its overall balance and power.
-
Badminton Racquets: Badminton rackets, used for hitting the shuttlecock, have a specific length that affects the player’s reach and control. Certain parts of the racket may measure five inches, contributing to its overall balance and performance.
FAQs about Objects Measuring Five Inches:
Q: What are some common objects that measure five inches in length?
A: Some common objects that measure five inches in length include smartphones, credit cards, pens, memory sticks, hard drives, surgical blades, catheters, spatulas, ladles, paintbrushes, knitting needles, sculpting tools, golf clubs, baseball bats, and badminton rackets.
Q: Why is the five-inch measurement significant in different fields?
A: The five-inch measurement is significant in different fields due to its practicality and functionality. It provides a balance between size, portability, control, and reach, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Q: Are there any specific benefits to objects measuring five inches?
A: Yes, objects measuring five inches often offer specific benefits such as ease of use, portability, precision, and control. These benefits contribute to their effectiveness in various fields.
Tips for Working with Objects Measuring Five Inches:
-
Consider the purpose: Before working with an object measuring five inches, it is essential to understand its purpose and intended use. This will help in choosing the appropriate tool or material.
-
Ensure proper handling: Objects measuring five inches may require specific handling techniques to ensure safety and prevent damage. Refer to instructions or guidelines for proper use.
-
Maintain cleanliness: Regular cleaning and maintenance are crucial for objects measuring five inches, especially those used in medical or culinary settings. This helps prevent contamination and ensures optimal performance.
Conclusion:
The five-inch measurement, while seemingly insignificant, plays a crucial role in various aspects of our lives. From everyday objects to specialized tools, the five-inch length offers a balance of size, portability, control, and functionality, making it a significant measurement in numerous fields. Understanding the importance of this length allows us to appreciate the diverse applications of five-inch objects and their contributions to our daily lives.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Objects Measuring Five Inches. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The Evolution Of Precision: Exploring The World Of Stylus For Touchscreen Computers
The Evolution of Precision: Exploring the World of Stylus for Touchscreen Computers
Related Articles: The Evolution of Precision: Exploring the World of Stylus for Touchscreen Computers
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Evolution of Precision: Exploring the World of Stylus for Touchscreen Computers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Evolution of Precision: Exploring the World of Stylus for Touchscreen Computers

The advent of touchscreen computers ushered in a new era of human-computer interaction, making technology more accessible and intuitive. Yet, for tasks requiring precision, accuracy, and intricate control, a simple fingertip often falls short. Enter the stylus, a tool that bridges the gap between the digital and the physical, empowering users with heightened control and finesse.
A History of Precision: From Early Beginnings to Modern Innovations
The concept of a stylus predates the digital age, tracing its roots back to ancient writing tools. The earliest iterations were rudimentary instruments used for inscription on clay tablets and papyrus. However, the modern stylus, as we know it today, evolved alongside the development of touchscreen technology.
Early touchscreens, primarily used in industrial applications, relied on resistive technology, where pressure applied to the screen registered an input. Styluses designed for these screens were typically constructed from hard plastic or rubber, offering limited sensitivity and accuracy.
The advent of capacitive touchscreens, now ubiquitous in smartphones, tablets, and laptops, ushered in a new era of stylus technology. These screens respond to the electrical field generated by a conductive object, allowing for greater accuracy and responsiveness. This paved the way for more sophisticated styluses, incorporating features like pressure sensitivity, tilt recognition, and even programmable buttons.
Navigating the Stylus Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide
The modern stylus market offers a diverse range of options, each tailored to specific needs and preferences. Understanding the key features and functionalities of different styluses can help users make an informed choice.
1. Tip Technology: The Foundation of Precision
The tip of a stylus is the point of contact with the touchscreen, directly influencing accuracy and responsiveness.
- Rubber Tips: These are common in basic styluses, offering a smooth, frictionless experience. However, they lack pressure sensitivity and can be prone to wear and tear.
- Fiber Tips: These tips are made from a fine, flexible fiber, providing a more natural writing experience with improved accuracy and pressure sensitivity.
- Disc Tips: These tips feature a small, circular disc, designed for a more precise and controlled input, particularly for drawing and sketching.
- Active Tips: Active tips incorporate specialized technology, such as electromagnetic resonance or optical sensors, for enhanced precision and responsiveness. These are typically found in high-end styluses designed for professional applications.
2. Pressure Sensitivity: Translating Force into Digital Expression
Pressure sensitivity allows the stylus to register varying levels of force applied to the screen, translating this input into nuanced variations in line thickness, brush strokes, and other artistic effects.
- Passive Pressure Sensitivity: This is achieved through the stylus’s tip material and design, responding to the pressure applied to the touchscreen.
- Active Pressure Sensitivity: This relies on internal sensors within the stylus, providing a more precise and sophisticated level of pressure detection.
3. Tilt Recognition: Adding Depth and Dimension
Tilt recognition enables the stylus to detect the angle at which it is held relative to the screen. This allows for more natural and expressive drawing and sketching, as the thickness and direction of lines can be manipulated based on the tilt angle.
4. Programmable Buttons: Expanding Functionality
Some styluses incorporate programmable buttons, providing users with customizable shortcuts and functionalities. These buttons can be programmed to perform actions like erasing, switching tools, or invoking specific commands within applications.
5. Battery Life and Connectivity: Considerations for Active Styluses
Active styluses, which rely on internal sensors and wireless connectivity, require a power source, typically a battery. The battery life and charging method vary depending on the model, with some offering several hours of continuous use on a single charge. Connectivity options include Bluetooth, USB-C, and proprietary protocols.
6. Compatibility: Ensuring Seamless Integration
Before purchasing a stylus, it is crucial to ensure compatibility with your touchscreen device. Some styluses are designed for specific brands or models, while others offer broader compatibility. It is important to check the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility information.
The Benefits of Embracing the Stylus: Unlocking New Possibilities
The stylus transcends its role as a mere input device, offering a range of benefits that enhance user experience and unlock new creative possibilities.
1. Precision and Accuracy: For Tasks Requiring Finesse
The stylus provides a level of precision and accuracy that is often unattainable with a fingertip. This is particularly valuable for tasks requiring meticulous control, such as:
- Digital Drawing and Sketching: Styluses enable artists to create intricate details, nuanced shading, and expressive brushstrokes.
- Note-Taking and Annotation: Styluses allow for precise writing and annotation, replicating the feel of traditional pen and paper.
- Technical Design and Engineering: Styluses facilitate the creation of detailed diagrams, schematics, and blueprints.
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: Styluses are used in medical applications for precise annotations and manipulations of images.
2. Enhanced Productivity and Efficiency: Streamlining Workflows
The stylus’s precision and functionality can significantly enhance productivity in various work environments:
- Digital Signature Verification: Styluses provide a secure and convenient method for signing documents electronically.
- Data Entry and Form Filling: Styluses offer a more efficient and accurate way to input data into digital forms.
- Interactive Presentations: Styluses allow presenters to interact with presentations directly, annotating slides and highlighting key points.
3. Increased Accessibility and Inclusivity: Bridging Gaps and Expanding Opportunities
Styluses can provide a more accessible and inclusive user experience for individuals with disabilities:
- Motor Impairment: Styluses offer a more comfortable and precise input method for individuals with limited dexterity.
- Visual Impairment: Styluses with tactile feedback can provide a more intuitive way to navigate touchscreens for individuals with visual impairments.
4. Expanding Creative Horizons: Unlocking Artistic Potential
The stylus has become an indispensable tool for artists and designers, empowering them to express their creativity in new and innovative ways:
- Digital Painting and Illustration: Styluses offer a range of brush types, pressure sensitivity, and tilt recognition, allowing artists to explore a wide range of artistic styles.
- Graphic Design and Layout: Styluses provide a precise and intuitive way to manipulate objects, create vector graphics, and design layouts.
- Animation and Motion Graphics: Styluses enable animators to create smooth and expressive movements, bringing characters and objects to life.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Stylus for Touchscreen Computers
1. What is the difference between an active and a passive stylus?
- Passive Styluses: These rely on the touchscreen’s capacitive technology to register input. They do not require a battery or wireless connection.
- Active Styluses: These incorporate internal sensors and wireless connectivity, providing enhanced accuracy, pressure sensitivity, and other advanced features. They typically require a battery and may have specific compatibility requirements.
2. How do I choose the right stylus for my needs?
Consider the following factors:
- Your intended use: If you are primarily using the stylus for note-taking, a basic passive stylus might suffice. For artistic applications, an active stylus with pressure sensitivity and tilt recognition is recommended.
- Your budget: Stylus prices vary significantly, from affordable basic models to high-end professional styluses.
- Compatibility with your device: Ensure that the stylus is compatible with your touchscreen computer.
3. Can I use any stylus on any touchscreen device?
No, not all styluses are compatible with all touchscreen devices. Some styluses are designed for specific brands or models, while others offer broader compatibility. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for compatibility information.
4. How do I calibrate my stylus?
Calibration ensures that the stylus’s input is accurately registered on the touchscreen. Calibration instructions may vary depending on the stylus and device. Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for specific instructions.
5. How do I clean my stylus?
Clean the stylus regularly to maintain its performance and hygiene. Use a soft, damp cloth to wipe away dirt and debris from the tip and body of the stylus. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
Tips for Optimal Stylus Usage:
- Practice: Familiarity with the stylus’s functionality is crucial for optimal performance. Practice using the stylus for various tasks to develop a natural feel and improve accuracy.
- Proper Grip: Hold the stylus comfortably and securely, ensuring that the tip is properly aligned with the touchscreen.
- Screen Protection: Use a screen protector to prevent scratches and damage to your touchscreen.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the stylus regularly to maintain its performance and hygiene.
- Experiment with Settings: Explore the stylus’s settings and adjust them to your preferences, such as pressure sensitivity, line thickness, and brush types.
Conclusion: The Stylus as a Catalyst for Innovation and Creativity
The stylus has evolved from a simple writing tool to a sophisticated instrument that empowers users with enhanced precision, control, and creative expression. Its integration into touchscreen computers has revolutionized human-computer interaction, unlocking new possibilities for creativity, productivity, and accessibility. As technology continues to advance, the stylus will undoubtedly play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of digital experiences, empowering users to interact with technology in more intuitive, expressive, and personalized ways.

![MEKO Universal Stylus,[2 in 1 Precision Series] Disc Stylus Touch Screen Pens for All Capacitive](https://images-na.ssl-images-amazon.com/images/I/41vJOw1k1rL.jpg)





![MEKO Universal Stylus,[2 in 1 Precision Series] Disc Stylus Touch Screen Pens for All Capacitive](https://i5.walmartimages.com/asr/528e414e-980d-419d-9f5a-db5ae7bf713f.d77e38c1543d7669339b4fcdd1b56f65.jpeg?odnWidth=612u0026odnHeight=612u0026odnBg=ffffff)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Evolution of Precision: Exploring the World of Stylus for Touchscreen Computers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of Weight Loss
- 3.2 Strategies for Effective Weight Loss
- 3.3 Debunking Common Weight Loss Myths
- 3.4 The Importance of Sustainability
- 3.5 FAQs about Weight Loss
- 3.6 Tips for Successful Weight Loss
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide

Weight loss is a common goal, often driven by a desire to improve health, enhance physical appearance, or boost confidence. While achieving rapid weight loss may seem appealing, it is crucial to prioritize sustainable, healthy methods that promote long-term well-being. This article will delve into the intricacies of weight loss, exploring effective strategies and debunking common misconceptions.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when the body burns more calories than it consumes. This calorie deficit can be achieved through a combination of dietary modifications and increased physical activity.
Dietary Modifications:
- Calorie Reduction: Reducing calorie intake is fundamental to weight loss. This can be achieved by consuming fewer portions, opting for lower-calorie foods, and limiting processed foods and sugary beverages.
- Nutrient-Dense Foods: Focusing on nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains, provides essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber while keeping calorie intake in check.
- Portion Control: Mindful portioning helps regulate calorie intake. Using smaller plates, measuring food, and paying attention to hunger cues can be beneficial.
- Hydration: Drinking sufficient water can aid in satiety, reducing overall calorie consumption.
- Balanced Macronutrients: A balanced intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is crucial for optimal health and sustained weight loss.
Physical Activity:
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Activities like running, swimming, cycling, and brisk walking increase heart rate and calorie expenditure.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass increases metabolism, leading to higher calorie burn even at rest.
- Regular Movement: Incorporating regular movement into daily routines, such as taking the stairs or walking during breaks, can contribute to overall calorie expenditure.
Strategies for Effective Weight Loss
- Setting Realistic Goals: Aiming for a gradual, sustainable weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week is more achievable and promotes long-term success.
- Creating a Calorie Deficit: Tracking calorie intake and expenditure through apps or food diaries helps maintain a calorie deficit.
- Mindful Eating: Paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and enjoying meals can prevent overeating.
- Seeking Professional Guidance: Consulting with a registered dietitian or a certified personal trainer can provide personalized plans and support.
- Building a Support System: Enlisting friends, family, or support groups can provide motivation and accountability.
- Addressing Emotional Eating: Identifying triggers for emotional eating and developing coping mechanisms can promote healthy eating habits.
Debunking Common Weight Loss Myths
- Rapid Weight Loss: While some weight loss programs promise quick results, these often involve unsustainable methods and can lead to health complications.
- "Miracle" Diets: Fad diets often lack scientific evidence and can be detrimental to long-term health.
- Skipping Meals: Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and disrupt metabolism.
- Starvation Diets: Restricting calories drastically can lead to nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and metabolic slowdown.
- Spot Reduction: Targeting specific areas for fat loss is not possible. Overall calorie deficit is crucial for fat reduction.
The Importance of Sustainability
Sustainable weight loss focuses on creating healthy habits that can be maintained over time. This approach prioritizes balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and a positive mindset.
- Long-Term Health Benefits: Sustainable weight loss reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
- Improved Quality of Life: Losing weight gradually can lead to increased energy levels, improved sleep, and enhanced self-esteem.
- Preventing Weight Regain: By establishing healthy habits, individuals can avoid regaining lost weight and maintain a healthy weight long-term.
FAQs about Weight Loss
Q: What is a safe rate of weight loss?
A: A safe and sustainable rate of weight loss is generally considered to be 1-2 pounds per week.
Q: What are some healthy snacks for weight loss?
A: Some healthy snack options include fruits, vegetables, nuts, yogurt, and hard-boiled eggs.
Q: How much exercise is recommended for weight loss?
A: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities at least twice a week.
Q: Can I lose weight without exercise?
A: While dietary changes alone can lead to weight loss, exercise is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, boosting metabolism, and improving overall health.
Q: What are some common weight loss plateaus and how to overcome them?
A: Weight loss plateaus can occur due to various factors, including metabolic adaptation, decreased calorie intake, and insufficient physical activity. To overcome plateaus, consider increasing exercise intensity, adjusting calorie intake, or seeking professional guidance.
Q: Is weight loss surgery a viable option?
A: Weight loss surgery is a viable option for individuals with severe obesity who have not achieved significant weight loss through other methods. It is important to consult with a qualified surgeon and healthcare professionals to determine if surgery is appropriate.
Tips for Successful Weight Loss
- Start Small: Begin with small, achievable changes to your diet and exercise routine, gradually increasing the intensity and duration.
- Focus on Whole Foods: Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains.
- Read Food Labels: Become familiar with serving sizes and calorie content of foods.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can lead to weight gain. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
- Be Patient and Persistent: Weight loss takes time and effort. Don’t get discouraged by setbacks; focus on making progress towards your goals.
Conclusion
Achieving sustainable weight loss is a journey that requires commitment, patience, and a holistic approach. It is crucial to prioritize health and well-being over rapid weight loss. By understanding the fundamentals of weight loss, adopting effective strategies, and debunking common myths, individuals can embark on a journey towards a healthier and happier life. Remember, it’s not about perfection but about progress. Embrace sustainable habits, celebrate successes, and seek support when needed.






![4 Steps To Sustainable Weight Loss [Infographic]](https://www.positivehealthwellness.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Steps-to-Sustainable-Weight-Loss.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Achieving Sustainable Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
A Comprehensive Guide To Substances Poisonous To Cats: Understanding The Risks And Safeguarding Your Feline Companion
A Comprehensive Guide to Substances Poisonous to Cats: Understanding the Risks and Safeguarding Your Feline Companion
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Substances Poisonous to Cats: Understanding the Risks and Safeguarding Your Feline Companion
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Substances Poisonous to Cats: Understanding the Risks and Safeguarding Your Feline Companion. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Substances Poisonous to Cats: Understanding the Risks and Safeguarding Your Feline Companion

Cats, with their curious nature and independent spirit, often explore their environment with a playful inquisitiveness. This natural instinct, however, can inadvertently lead them to encounter substances that pose a serious threat to their health. Recognizing the potential dangers and understanding the effects of common household toxins on cats is crucial for any cat owner. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of the substances that can be poisonous to cats, emphasizing the importance of preventative measures and prompt action in case of accidental ingestion.
Common Household Substances Poisonous to Cats:
1. Human Medications:
Cats are particularly sensitive to medications formulated for humans, even in small doses. The following categories of medications are especially dangerous:
- Pain Relievers: Acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), and aspirin are all highly toxic to cats. Even a small amount can lead to liver failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, and kidney damage.
- Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and paroxetine (Paxil) can cause tremors, seizures, and behavioral changes in cats.
- Antihistamines: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and cetirizine (Zyrtec) can cause drowsiness, lethargy, and even coma in cats.
- Cough and Cold Medications: Decongestants containing pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine can cause hyperactivity, tremors, and seizures in cats.
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, such as penicillin and tetracycline, can cause gastrointestinal upset and allergic reactions in cats.
2. Household Cleaning Products:
Many common household cleaning products contain chemicals that can be toxic to cats, especially if ingested or absorbed through the skin.
- Bleach: Ingestion of bleach can cause severe burns to the mouth, throat, and stomach, leading to vomiting, diarrhea, and even death.
- Dishwashing Detergent: Similar to bleach, dishwashing detergent can cause severe irritation and damage to the digestive system.
- Air Fresheners: Certain air fresheners contain essential oils that can be toxic to cats, especially citrus oils like lemon and orange.
- Furniture Polish: Many furniture polishes contain petroleum distillates that can cause respiratory distress, lethargy, and even coma in cats.
3. Pesticides and Insecticides:
Pesticides and insecticides, both indoor and outdoor, can be extremely dangerous to cats.
- Rat Poison: Rodenticide containing anticoagulants can cause internal bleeding, anemia, and death in cats.
- Insect Repellents: Many insect repellents, including those containing DEET, permethrin, and pyrethrins, can be toxic to cats, causing neurological symptoms, skin irritation, and respiratory distress.
- Slug and Snail Bait: Metaldehyde, a common ingredient in slug and snail bait, can cause seizures, tremors, and even death in cats.
4. Plants:
While many houseplants are harmless, some can be toxic to cats.
- Lilies: All parts of lilies, including the pollen, are highly toxic to cats, causing kidney failure and death.
- Tulips and Daffodils: These bulbs contain lycorine, a toxic substance that can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and drooling in cats.
- Sago Palms: All parts of sago palms are toxic to cats, causing liver failure and death.
- Pothos: This common houseplant can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and oral irritation in cats.
5. Food and Beverages:
Certain foods and beverages commonly consumed by humans can be harmful to cats.
- Chocolate: Theobromine, a compound found in chocolate, is toxic to cats, causing vomiting, diarrhea, hyperactivity, and even death.
- Grapes and Raisins: These fruits can cause kidney failure in cats.
- Onions and Garlic: These vegetables contain thiosulphate compounds that can damage red blood cells in cats.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can cause severe intoxication, respiratory distress, and even death in cats.
6. Other Toxic Substances:
- Anti-freeze: Ethylene glycol, the main ingredient in antifreeze, is highly toxic to cats, causing kidney failure and death.
- Batteries: The contents of batteries, particularly those containing lithium, can cause severe burns and poisoning in cats.
- Glue and Adhesives: Some glues and adhesives contain chemicals that can be toxic to cats, causing irritation, vomiting, and respiratory distress.
Symptoms of Poisoning in Cats:
Recognizing the signs of poisoning in cats is crucial for prompt veterinary care. Common symptoms include:
- Gastrointestinal distress: Vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, drooling
- Neurological symptoms: Tremors, seizures, lethargy, disorientation, incoordination
- Respiratory distress: Difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing
- Cardiovascular problems: Rapid heart rate, weakness, collapse
- Skin irritation: Redness, itching, inflammation
- Behavioral changes: Anxiety, aggression, depression
First Aid and Prevention:
- Immediate Veterinary Care: If you suspect your cat has ingested a toxic substance, contact your veterinarian or the ASPCA Animal Poison Control Center (APCC) immediately.
- Identify the Substance: If possible, try to identify the substance your cat ingested to provide the veterinarian with crucial information.
- Do Not Induce Vomiting: Unless instructed by a veterinarian, do not induce vomiting as it can worsen the situation.
- Preventative Measures: Keep all potentially toxic substances out of reach of your cat. Secure medications in child-proof containers, store cleaning products in locked cabinets, and choose pet-friendly plants.
FAQs by Substances Poisonous to Cats:
Q: Is it safe for cats to eat human food?
A: While some human foods can be shared with cats in moderation, many are toxic. It’s best to consult with your veterinarian about safe food options for your cat.
Q: What should I do if my cat chews on a plant?
A: If you suspect your cat has ingested a toxic plant, contact your veterinarian immediately. Keep a list of potentially toxic plants in your home and ensure they are out of reach of your cat.
Q: Are all lilies toxic to cats?
A: Yes, all types of lilies are highly toxic to cats, including Easter lilies, tiger lilies, and daylilies. Even a small amount of pollen or water from a vase containing lilies can cause severe kidney failure in cats.
Q: What is the best way to store medications to prevent cats from accessing them?
A: Store medications in child-proof containers, preferably in a locked cabinet or drawer. Keep medications out of reach of curious paws and ensure they are never left unattended on countertops or tables.
Q: Is it safe to use essential oils around cats?
A: While some essential oils are considered safe for cats, others can be toxic. Consult with your veterinarian before using any essential oils around your cat.
Tips by Substances Poisonous to Cats:
- Regularly check your home for potential hazards. Identify and remove any substances that could be toxic to your cat, such as cleaning products, medications, and plants.
- Keep medications and cleaning supplies locked away. Use child-proof containers and store these items in cabinets or drawers that your cat cannot access.
- Choose pet-friendly plants. Opt for plants that are non-toxic to cats or place potentially toxic plants in areas your cat cannot reach.
- Be mindful of what you bring into your home. Read product labels carefully and be aware of any potential hazards to your cat.
- Educate yourself about common household toxins. Familiarize yourself with the symptoms of poisoning and the appropriate first aid measures.
Conclusion by Substances Poisonous to Cats:
Cats are curious creatures who often explore their surroundings with a playful spirit. However, this curiosity can lead them to encounter substances that pose a significant risk to their health. Understanding the potential dangers of common household toxins and taking preventative measures is crucial for safeguarding your feline companion. By being vigilant and proactive, you can create a safe and healthy environment for your cat to thrive.
Remember, prompt action is essential in case of suspected poisoning. Contact your veterinarian or the ASPCA Animal Poison Control Center immediately. With knowledge, vigilance, and swift action, you can protect your beloved cat from the dangers of poisonous substances.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Substances Poisonous to Cats: Understanding the Risks and Safeguarding Your Feline Companion. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
The Importance Of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide To Materials And Practices
The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Related Articles: The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices
Recycling, the process of converting waste materials into reusable objects, is a crucial aspect of environmental sustainability. It plays a vital role in conserving natural resources, reducing pollution, and mitigating the impact of our consumption on the planet. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of the materials that should be recycled, the benefits of recycling, and the best practices for maximizing its effectiveness.
Materials that Should be Recycled
The materials that can and should be recycled vary depending on local regulations and the availability of recycling facilities. However, some common materials are consistently recyclable and contribute significantly to environmental protection. These include:
Paper and Cardboard:
- Types: Newspapers, magazines, office paper, cardboard boxes, paper bags, junk mail, and paperboard packaging.
- Benefits: Recycling paper reduces the need to harvest trees, thereby protecting forests and reducing carbon emissions. It also conserves water and energy used in paper production.
- Tips: Flatten cardboard boxes to save space and remove plastic windows or tape before recycling. Ensure paper is clean and free of food residue.
Plastic:
- Types: Plastic bottles (PET), milk jugs (HDPE), grocery bags (LDPE), food containers (PP), and other recyclable plastic items.
- Benefits: Recycling plastic reduces the amount of plastic waste that ends up in landfills, where it can take hundreds of years to decompose. It also conserves oil resources used in plastic production.
- Tips: Rinse plastic containers thoroughly to remove food residue and ensure they are empty. Check local recycling guidelines for specific plastic types accepted in your area.
Aluminum and Steel Cans:
- Types: Aluminum beverage cans, steel food cans, and other metal containers.
- Benefits: Recycling aluminum and steel cans saves energy and reduces the need for mining new resources. It also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- Tips: Rinse cans thoroughly to remove food residue and crush them to save space. Ensure cans are free of any non-recyclable materials like plastic lids.
Glass:
- Types: Glass bottles and jars, including clear, green, and brown glass.
- Benefits: Recycling glass saves energy and reduces the need for raw materials in glass production. It also reduces the amount of glass waste that ends up in landfills.
- Tips: Rinse glass containers thoroughly and remove any non-recyclable materials like metal lids. Separate glass by color if instructed by local guidelines.
Electronic Waste (E-Waste):
- Types: Computers, laptops, smartphones, televisions, printers, and other electronic devices.
- Benefits: Recycling e-waste prevents harmful substances like lead and mercury from contaminating landfills and the environment. It also recovers valuable materials for reuse.
- Tips: Dispose of e-waste responsibly through designated collection points or recycling programs. Avoid throwing e-waste in regular trash.
Other Recyclable Materials:
- Textiles: Old clothing, bedding, towels, and other fabric items.
- Batteries: Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries.
- Batteries: Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries.
- Construction and Demolition Debris: Wood, concrete, metal, and other materials from construction and renovation projects.
Benefits of Recycling
Recycling offers a multitude of benefits, both environmental and economic, making it a crucial practice for a sustainable future:
Environmental Benefits:
- Conservation of Natural Resources: Recycling conserves valuable natural resources like trees, minerals, and fossil fuels, which are used in the production of new materials.
- Pollution Reduction: Recycling reduces pollution from manufacturing new products, including air, water, and land pollution.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Recycling helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing and waste disposal.
- Landfill Space Reduction: Recycling reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, extending their lifespan and minimizing environmental impacts.
Economic Benefits:
- Job Creation: Recycling creates jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing industries.
- Resource Recovery: Recycling recovers valuable materials from waste, reducing the need for new resources and saving costs.
- Energy Savings: Recycling saves energy compared to manufacturing new products from raw materials.
- Economic Growth: Recycling contributes to a circular economy, where resources are used more efficiently and waste is minimized, promoting sustainable economic growth.
Best Practices for Recycling
To maximize the effectiveness of recycling efforts, it is essential to follow best practices:
- Check Local Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with local recycling guidelines and regulations, as they vary by region.
- Clean and Empty Containers: Rinse and empty containers to remove food residue and other contaminants.
- Separate Materials: Separate different materials for recycling, such as paper, plastic, glass, and metal.
- Avoid Contamination: Do not mix recyclable materials with non-recyclable items.
- Use Recycling Bins: Use designated recycling bins or containers for recyclable materials.
- Support Recycling Programs: Participate in local recycling programs and initiatives to promote recycling.
- Reduce Waste Generation: Reduce waste generation in the first place by using reusable items and purchasing products with minimal packaging.
FAQs on Recycling
Q: What happens to recycled materials?
A: Recycled materials are collected, sorted, and processed into new products. Paper is recycled into new paper products, plastic is recycled into new plastic items, glass is recycled into new glass containers, and metals are recycled into new metal products.
Q: Why is it important to recycle properly?
A: Improper recycling can contaminate recyclable materials, making them unusable. It is essential to follow guidelines and ensure that only recyclable materials are placed in recycling bins.
Q: Can I recycle everything?
A: Not all materials are recyclable. Some items, such as plastic bags, food wrappers, and certain types of plastic, may not be accepted in local recycling programs.
Q: What are some challenges to recycling?
A: Challenges to recycling include the cost of collection and processing, the need for advanced sorting technologies, and the lack of public awareness and participation.
Conclusion
Recycling is an essential practice for environmental protection and sustainable development. By understanding the materials that should be recycled, the benefits of recycling, and the best practices for maximizing its effectiveness, we can collectively contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. Recycling is not just about throwing away waste; it is about transforming waste into valuable resources, reducing our environmental footprint, and creating a more sustainable world for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Importance of Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials and Practices. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The Art Of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide To Sustainable Living
The Art of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Living
Related Articles: The Art of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Living
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Art of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Living. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Art of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Living

In an era marked by escalating environmental concerns, the concept of reuse has taken center stage as a powerful tool for sustainable living. This practice, far from being a mere trend, represents a fundamental shift in our relationship with materials and resources, encouraging us to view discarded items not as waste but as potential raw materials for new purposes.
The act of reusing is not simply about extending the lifespan of an object. It encompasses a broader philosophy of resource conservation, reducing the demand for virgin materials and minimizing the environmental impact associated with their extraction, processing, and disposal. This approach offers a myriad of benefits, ranging from reducing landfill waste and conserving natural resources to fostering creativity and promoting a sense of community.
A Universe of Reusable Materials
The scope of reusable materials is vast, spanning across diverse categories, each offering unique opportunities for creative repurposing.
1. Everyday Household Items:
- Glass Jars and Bottles: These versatile containers find countless applications beyond their initial use. They can be transformed into storage jars for pantry staples, decorative vases for fresh flowers, or even DIY candle holders.
- Plastic Containers: While plastic often carries a negative connotation due to its environmental impact, many plastic containers can be reused for a variety of purposes. Food-grade containers can be used to store leftovers, pack lunches, or organize small items.
- Paper and Cardboard: These materials are readily reusable for crafting projects, gift wrapping, or even as packing materials. Old newspapers can be used for lining birdcages or as a protective layer for delicate items during storage.
- Textiles: Old clothing, towels, and linens can be given new life as cleaning rags, sewing projects, or even as stuffing for cushions and pillows.
2. Building Materials:
- Wood: Reclaimed wood, salvaged from old buildings or demolition projects, offers a unique aesthetic appeal and a sustainable alternative to newly harvested wood. It can be used for furniture, flooring, wall paneling, or even as decorative elements in home décor.
- Bricks and Stones: These materials are incredibly durable and can be reused in various construction projects, from building walls and pathways to creating decorative features in gardens.
- Metal: Scrap metal, including pipes, sheets, and wire, can be repurposed for various projects, from constructing outdoor furniture to creating artistic sculptures.
3. Electronics:
- Batteries: While batteries are often considered disposable, some types, such as rechargeable batteries, can be reused multiple times. This reduces the need for new batteries and minimizes the environmental impact associated with battery production and disposal.
- Computer Hardware: Old computer components, such as hard drives, RAM, and motherboards, can be reused in DIY projects or donated to educational institutions or community organizations.
- Mobile Devices: Old smartphones and tablets can be repurposed for various purposes, including using them as dedicated music players, e-readers, or even as security cameras.
4. Packaging Materials:
- Boxes and Bubble Wrap: These materials are ideal for packing fragile items or storing belongings. They can be reused multiple times before being recycled.
- Plastic Bags: Reusable grocery bags are a great alternative to disposable plastic bags. They can also be used for storing small items or as trash bags for smaller bins.
5. Furniture and Appliances:
- Furniture: Old furniture can be refinished, reupholstered, or even transformed into entirely new pieces. This practice not only extends the lifespan of furniture but also adds a unique character to any space.
- Appliances: While some appliances might require professional repair, others can be easily fixed or repurposed for different uses. For example, an old refrigerator can be converted into a beverage cooler or a storage unit.
The Benefits of Reusing
The practice of reusing offers a multitude of benefits, both for individuals and the environment:
1. Environmental Conservation:
- Reduced Landfill Waste: Reusing items significantly reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, thereby mitigating the environmental impact of landfill operations, including greenhouse gas emissions and pollution.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: By reusing materials, we lessen the demand for new resources, such as timber, minerals, and fossil fuels, which are often extracted from the environment with significant environmental consequences.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Manufacturing new products requires a considerable amount of energy. Reusing existing materials reduces the need for new production, leading to lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Economic Advantages:
- Cost Savings: Reusing items can save money compared to purchasing new ones. This is particularly relevant for items like furniture, appliances, and building materials.
- Stimulation of Local Economies: The reuse sector often involves local businesses and artisans, supporting local economies and creating job opportunities.
3. Social and Cultural Impact:
- Community Building: Reusing initiatives often involve community participation, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and collaboration.
- Creativity and Innovation: Reusing encourages creative thinking and problem-solving, leading to unique and innovative solutions for repurposing materials.
- Preservation of History and Culture: Reusing historical or antique objects helps preserve cultural heritage and connects us to the past.
FAQs about Reusing
Q: What are some common misconceptions about reusing?
A: One common misconception is that reusing is only for people who are "eco-conscious" or "crafty." However, reusing is a practical and accessible practice for everyone. Another misconception is that reusing is messy or time-consuming. While some projects might require effort, many reusing activities are simple and straightforward.
Q: How can I start reusing?
A: Start by identifying areas in your life where you can incorporate reuse. Consider your everyday routines, from cooking and cleaning to hobbies and home improvement. Look for opportunities to repurpose items you already own or to source reusable materials from local thrift stores or online marketplaces.
Q: What are some challenges associated with reusing?
A: One challenge is the availability of reusable materials. Not all items are readily available for reuse, and sourcing specific materials can be time-consuming. Another challenge is the potential for contamination or safety concerns when reusing certain materials, especially those that have been in contact with hazardous substances.
Q: What are some tips for successful reusing?
A:
- Clean and Sanitize: Thoroughly clean and sanitize reusable items before using them for food storage, personal care, or other sensitive applications.
- Inspect for Damage: Check reusable items for damage or defects before using them. If an item is beyond repair, consider recycling it or donating it to a recycling facility.
- Store Properly: Store reusable items in a clean and dry environment to prevent damage or contamination.
- Be Creative: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different ways to reuse items. There are endless possibilities for creative repurposing.
Conclusion
The act of reusing is not simply a matter of environmental responsibility; it is a transformative approach to living that embraces resourcefulness, creativity, and a deep connection to the natural world. By embracing reuse, we contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future, leaving a positive legacy for generations to come. As we continue to navigate the challenges of a changing planet, the practice of reusing will play an increasingly vital role in shaping a more sustainable and equitable future for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art of Reusing: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Living. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!