Navigating The Head Of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide
Navigating the Head of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Head of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Head of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Head of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide

The tax system in the United States employs various filing statuses, each designed to reflect an individual’s unique financial circumstances. One such status, "Head of Household," offers tax advantages to unmarried individuals who shoulder significant financial responsibility for a qualifying dependent. Understanding this filing status and its nuances is crucial for maximizing tax benefits and minimizing tax liability.
Defining Head of Household: The Criteria
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) defines "Head of Household" as a filing status available to unmarried taxpayers who meet the following criteria:
- Unmarried: The taxpayer must be unmarried as of the end of the tax year. This includes individuals who are legally separated, divorced, or widowed.
- Qualifying Dependent: The taxpayer must pay more than half the costs of keeping up a home for a qualifying child or dependent relative. This "qualifying child" must meet specific age and residency requirements, while a "qualifying relative" must meet income and relationship criteria.
- Home as Principal Residence: The taxpayer’s home must be the principal residence for the qualifying child or dependent relative for more than half the year.
- No Qualifying Dependent Claimed by Another: No other taxpayer can claim the qualifying child or dependent relative as a dependent.
Understanding the Benefits
The Head of Household filing status offers significant tax advantages compared to filing as "Single." These advantages manifest in:
- Lower Tax Brackets: The Head of Household tax brackets are more favorable than the Single brackets, meaning taxpayers pay less in federal income tax.
- Higher Standard Deduction: The standard deduction for Head of Household filers is greater than the Single standard deduction, further reducing taxable income.
- Larger Child Tax Credit: If the qualifying child meets specific age requirements, the Head of Household filer can claim a larger Child Tax Credit than a Single filer.
- Potential for Other Credits: Depending on the specific circumstances, Head of Household filers may be eligible for additional tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit.
Examples of Qualifying Dependents:
- Children: Unmarried children under the age of 19 (or 24 if they are a full-time student) who live with the taxpayer for more than half the year.
- Stepchildren: Stepchildren who meet the same age and residency requirements as biological children.
- Foster Children: Foster children who live with the taxpayer for more than half the year.
- Other Relatives: Unmarried children, grandchildren, siblings, or parents who live with the taxpayer for more than half the year and meet specific income and relationship requirements.
Navigating Complexities:
While the Head of Household filing status offers distinct advantages, understanding its complexities is vital. Certain situations can affect eligibility, such as:
- Joint Custody: If a divorced parent shares custody of a child, the parent claiming the child as a dependent on their tax return can choose the Head of Household status, regardless of who provides more financial support for the child.
- Military Deployment: If a qualifying child lives with a relative while a parent is deployed, the parent may still be eligible for Head of Household status if they meet the other requirements.
- Multiple Qualifying Dependents: If a taxpayer has multiple qualifying dependents, they can choose the Head of Household status even if they don’t provide more than half the support for all dependents.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: Can I claim Head of Household if I am legally separated but not divorced?
- A: Yes, if you meet the other requirements, you can claim Head of Household even if you are legally separated but not yet divorced.
-
Q: Can I claim Head of Household if my child lives with me only part of the year?
- A: No, your child must live with you for more than half the year to qualify as a dependent for Head of Household status.
-
Q: Can I claim Head of Household if my child is 25 years old and living with me?
- A: No, unless your child is a full-time student, they must be under 19 years old (or 24 if a full-time student) to qualify as a dependent for Head of Household status.
-
Q: Can I claim Head of Household if my child is in the military?
- A: Yes, if your child is in the military and meets the other requirements, you can claim Head of Household status.
Tips for Claiming Head of Household:
- Gather Documentation: Collect all relevant documents, including birth certificates, custody agreements, and tax forms, to support your claim.
- Consult a Tax Professional: If you have complex family circumstances or are unsure about your eligibility, consult a tax professional for guidance.
- File Early: File your tax return before the April deadline to ensure you receive any potential tax refunds.
Conclusion:
The Head of Household filing status offers significant tax advantages to unmarried individuals who provide financial support for a qualifying dependent. Understanding the criteria, benefits, and complexities of this status is essential for maximizing tax benefits and navigating the tax system effectively. By carefully assessing your individual circumstances and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can leverage the Head of Household filing status to your advantage.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Head of Household Filing Status: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide To Energy Efficiency
Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Related Articles: Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
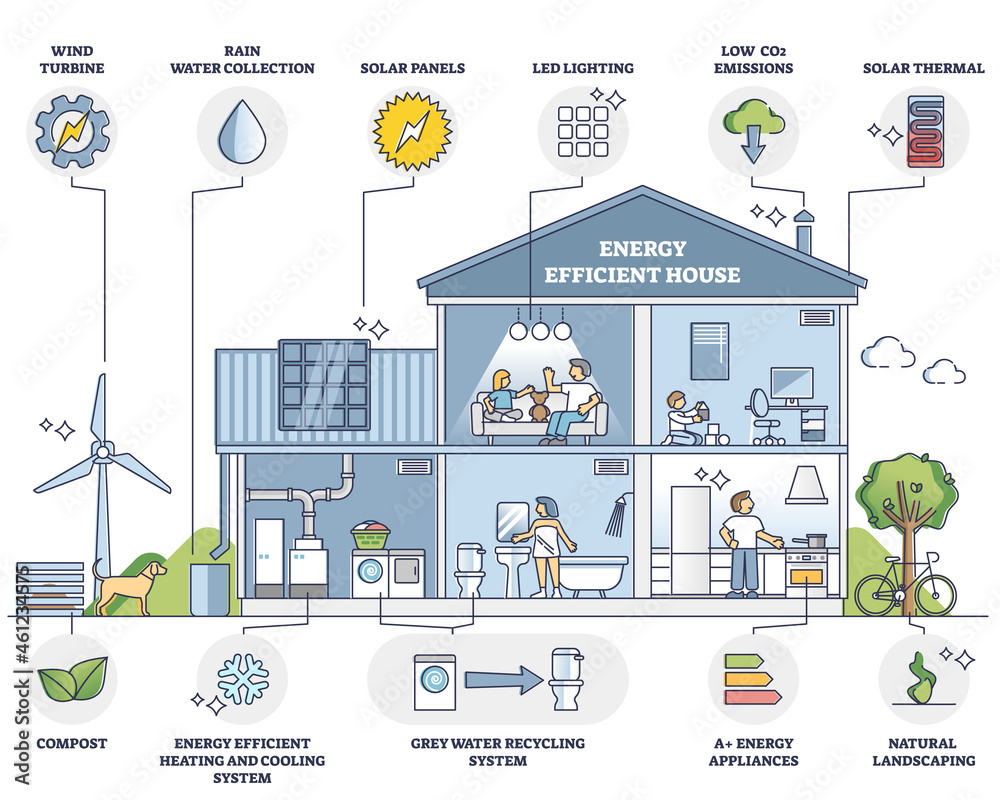
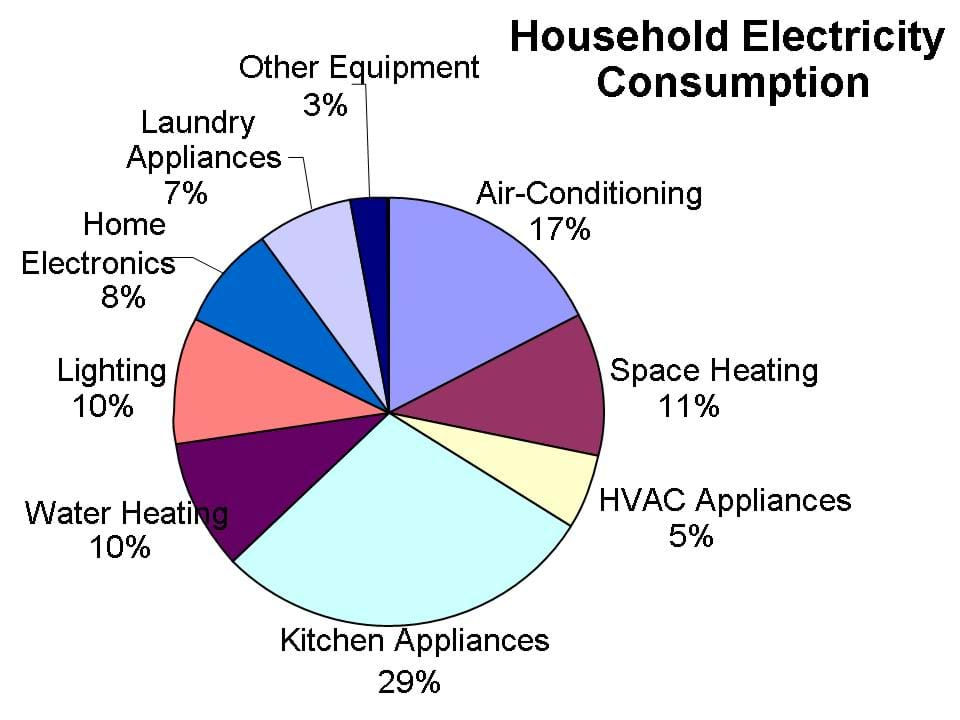
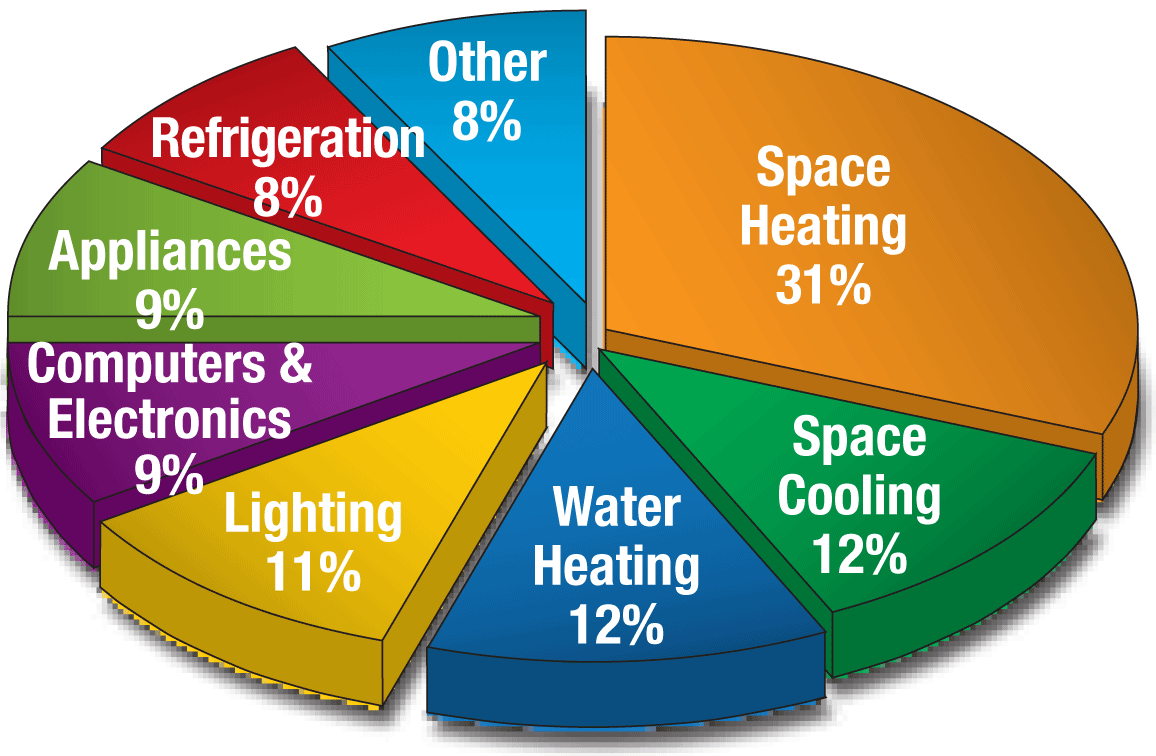
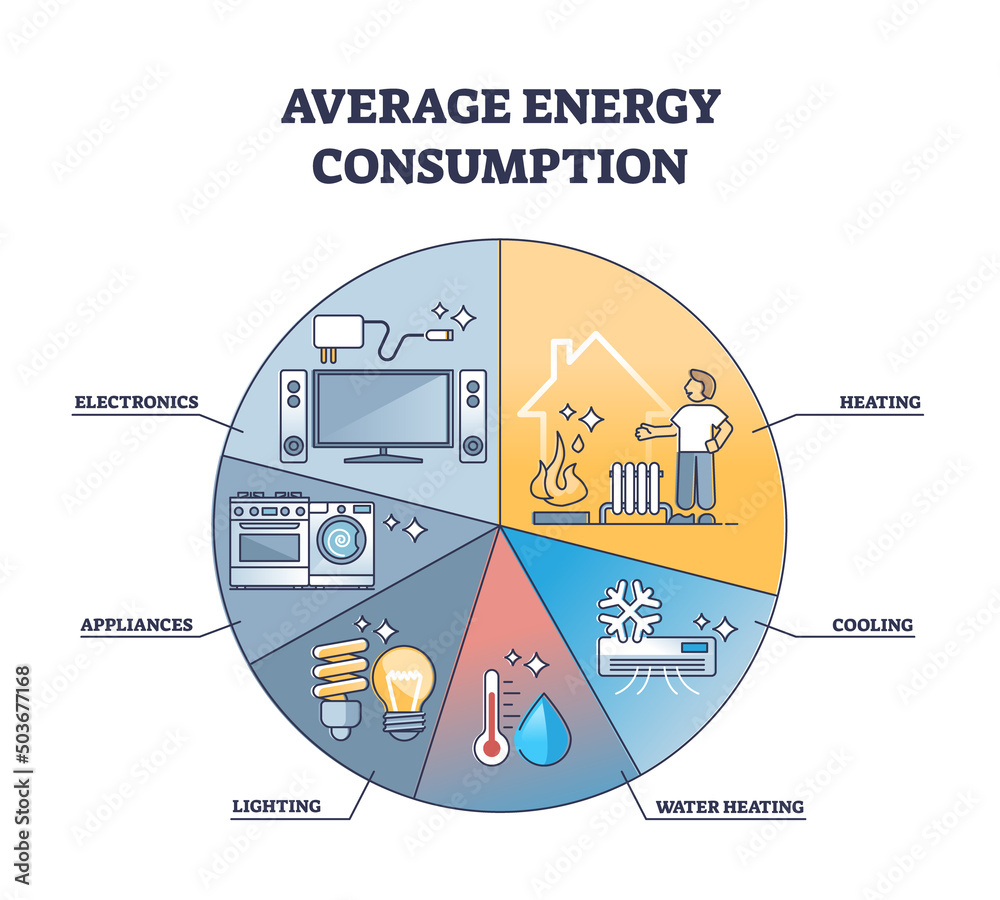
The average household consumes a significant amount of electricity daily, powering everything from lights and appliances to entertainment systems and heating/cooling. This energy consumption, measured in watts (W), is crucial to understand for several reasons. It directly impacts energy bills, environmental sustainability, and even the overall functionality of a home.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of typical household wattage use, exploring the various appliances and devices that contribute to overall energy consumption. It delves into the importance of understanding wattage, highlighting its significance in making informed decisions about energy efficiency and cost savings.
A Breakdown of Typical Household Wattage Use
Understanding the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices is essential for managing energy usage effectively. Here’s a breakdown of common household items and their typical wattage ranges:
1. Lighting
- Incandescent Bulbs: These traditional bulbs are known for their high wattage consumption, typically ranging from 40W to 100W.
- Halogen Bulbs: Similar to incandescent bulbs, halogen bulbs consume a slightly lower wattage, ranging from 20W to 75W.
- Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFLs): CFLs are significantly more energy-efficient than incandescent bulbs, consuming between 5W and 15W.
- Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs): LEDs are the most energy-efficient lighting option, consuming only 3W to 10W.
2. Appliances
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators are among the highest energy consumers in a household, with wattage ranging from 100W to 200W. Energy-efficient models can reduce this consumption significantly.
- Freezers: Similar to refrigerators, freezers consume a considerable amount of energy, typically ranging from 100W to 200W.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers consume around 1200W to 1800W during operation.
- Washing Machines: Washing machines consume approximately 500W to 1500W depending on the load size and cycle.
- Dryers: Clothes dryers are significant energy consumers, with wattage ranging from 1500W to 5000W.
- Ovens: Electric ovens consume a substantial amount of energy, typically ranging from 2000W to 5000W.
- Microwaves: Microwaves are relatively energy-efficient, consuming around 700W to 1500W during operation.
- Coffee Makers: Coffee makers consume between 500W and 1000W depending on the size and features.
3. Electronics
- Televisions: Televisions consume a varying amount of wattage depending on screen size and technology. Older models can consume up to 200W, while newer LED TVs consume significantly less, around 50W to 100W.
- Computers: Desktop computers consume a considerable amount of energy, ranging from 100W to 500W. Laptops, on the other hand, consume much less, typically between 30W and 100W.
- Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles consume a significant amount of energy, ranging from 100W to 200W.
- Streaming Devices: Streaming devices like Roku and Chromecast consume relatively low wattage, typically around 5W to 15W.
4. Heating and Cooling
- Heating Systems: Heating systems are major energy consumers, with wattage ranging from 1000W to 5000W depending on the type and size of the system.
- Air Conditioners: Air conditioners consume a considerable amount of energy, typically ranging from 1000W to 5000W.
5. Other Devices
- Hair Dryers: Hair dryers consume a significant amount of energy, ranging from 1000W to 2000W.
- Vacuum Cleaners: Vacuum cleaners consume between 500W and 1500W depending on the type and features.
- Electric Kettles: Electric kettles consume around 1000W to 1500W during operation.
The Importance of Understanding Wattage
Understanding wattage consumption is crucial for several reasons:
1. Reducing Energy Bills: By being aware of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can make informed decisions about their energy usage. Choosing energy-efficient models and using appliances sparingly can significantly reduce energy bills.
2. Promoting Environmental Sustainability: Excessive energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. Reducing wattage consumption through energy efficiency measures is crucial for mitigating climate change.
3. Ensuring Safe and Efficient Operation: Understanding wattage consumption is essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation of electrical appliances. Overloading electrical circuits can lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
4. Optimizing Home Performance: By understanding the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can optimize their home’s energy performance. This can involve implementing energy-efficient upgrades, such as installing LED lighting or upgrading to energy-efficient appliances.
FAQs about Typical Household Wattage Use
1. What is the average wattage consumption of a typical household?
The average wattage consumption of a typical household varies significantly depending on factors such as the size of the home, the number of occupants, and their energy usage habits. However, it is estimated that the average household in the United States consumes around 10,000 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per year.
2. How can I calculate my household’s wattage consumption?
You can calculate your household’s wattage consumption by monitoring your energy bill and keeping track of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices. You can also use a wattmeter to measure the actual wattage consumption of specific appliances.
3. How can I reduce my household’s wattage consumption?
There are several ways to reduce your household’s wattage consumption:
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Opt for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate energy efficiency.
- Unplug Devices When Not in Use: Unplug devices like phone chargers, laptops, and televisions when not in use to prevent phantom load.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with CFLs or LEDs.
- Adjust Thermostat Settings: Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature and avoid unnecessary heating or cooling.
- Wash Clothes in Cold Water: Washing clothes in cold water can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Air Dry Clothes: Air drying clothes instead of using a dryer can save a considerable amount of energy.
- Use a Power Strip: Use a power strip for electronics and turn it off when not in use.
Tips for Reducing Household Wattage Consumption
- Prioritize Energy Efficiency: When purchasing new appliances, prioritize energy efficiency over initial cost.
- Implement a "Power Down" Routine: Make it a habit to turn off lights and appliances when leaving a room.
- Use Natural Light: Maximize natural light during the day by opening curtains and blinds.
- Insulate Your Home: Proper insulation can significantly reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling.
- Seal Air Leaks: Seal air leaks around windows and doors to prevent heat loss.
- Maintain Appliances Regularly: Regular maintenance can improve the efficiency of appliances.
- Consider Solar Energy: Explore the possibility of installing solar panels to generate renewable energy.
Conclusion
Understanding typical household wattage consumption is crucial for managing energy usage effectively. By being aware of the wattage consumption of different appliances and devices, homeowners can make informed decisions about their energy usage, reducing energy bills, promoting environmental sustainability, and ensuring safe and efficient operation of their home. Implementing energy efficiency measures can significantly reduce wattage consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future. By adopting these strategies, homeowners can make a positive impact on both their wallets and the environment.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Wattage Consumption: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
The Price Is Right: A Timeless Game Show For Kids And Adults Alike
The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike
Related Articles: The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike
- 3.1 The Foundation of the Game: Estimation and Critical Thinking
- 3.2 Beyond the Price Tag: The Social and Emotional Benefits
- 3.3 The Price is Right for Kids: Adapting the Game for Young Audiences
- 3.4 FAQs About The Price is Right Game for Kids
- 3.5 Tips for Playing The Price is Right with Kids
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike

The Price is Right, a beloved television game show that has entertained generations, is not just a source of amusement but also a valuable tool for learning and development, particularly for children. While the show’s format may appear simple, it subtly engages participants in a variety of cognitive and social skills, making it an enriching experience for young viewers.
The Foundation of the Game: Estimation and Critical Thinking
At its core, The Price is Right revolves around the ability to estimate and make informed judgments. Contestants are presented with everyday items, ranging from household appliances to luxurious vacations, and are tasked with determining their retail price. This process encourages participants to consider various factors influencing cost, such as brand, size, and quality.
The game’s design emphasizes critical thinking, pushing contestants to analyze available information and make informed decisions. The ability to accurately estimate prices requires observation, comparison, and a nuanced understanding of market dynamics. These skills are not only valuable in the context of the game but also applicable to real-life scenarios involving budgeting, shopping, and financial literacy.
Beyond the Price Tag: The Social and Emotional Benefits
Beyond its focus on estimation and critical thinking, The Price is Right fosters social and emotional development. The show’s format encourages teamwork and collaboration, as contestants often work together to determine the correct price. This collaborative environment promotes communication, negotiation, and the ability to reach consensus.
Furthermore, the game’s competitive nature instills valuable lessons about sportsmanship and handling both success and failure. Contestants learn to navigate the pressure of competition, celebrate their victories, and gracefully accept defeat. This exposure to the dynamics of competition contributes to emotional maturity and resilience.
The Price is Right for Kids: Adapting the Game for Young Audiences
While The Price is Right is primarily targeted at adults, its underlying principles can be effectively adapted for children. Numerous variations of the game exist, specifically designed for younger audiences, offering a fun and engaging way to introduce essential life skills.
Simplified Versions:
- Guess the Price of Toys: This simplified version utilizes familiar toys and everyday items, making it easier for young children to estimate prices.
- Grocery Store Challenge: By using grocery store flyers, children can practice identifying and comparing prices of common food items.
- Family Budget Game: This activity involves allocating a predetermined budget for a family grocery shopping trip, encouraging children to make responsible spending decisions.
Interactive Learning Activities:
- Price Comparison Charts: Children can create charts comparing the prices of different brands or versions of the same product, fostering analytical and comparison skills.
- Shopping Scavenger Hunts: This engaging activity encourages children to search for specific items within a designated budget, promoting decision-making and problem-solving skills.
- Price Tag Puzzles: Children can create puzzles with price tags, requiring them to identify the correct price for each item.
FAQs About The Price is Right Game for Kids
1. How can I make The Price is Right game more educational for my child?
- Incorporate real-world examples: Use items from your home or grocery store to make the game more relatable.
- Discuss the factors influencing price: Encourage your child to consider brand, size, quality, and other relevant factors.
- Connect the game to real-life situations: Discuss how estimating prices can be helpful when shopping, budgeting, or making financial decisions.
2. What are the age-appropriate variations of The Price is Right for kids?
- Toddlers and preschoolers: Focus on simple games involving familiar items and basic price concepts.
- Elementary school children: Introduce more complex games involving comparison, budgeting, and basic financial literacy concepts.
- Older children: Utilize more sophisticated versions that require advanced analytical and problem-solving skills.
3. Can The Price is Right be used to teach children about different cultures?
- Explore global products: Use items from different countries to introduce children to diverse cultures and their associated pricing structures.
- Discuss currency exchange rates: Explain how prices vary based on currency exchange rates, providing a valuable lesson in global economics.
Tips for Playing The Price is Right with Kids
- Keep it fun and engaging: The goal is to make learning enjoyable, so avoid excessive pressure or competition.
- Adapt the game to your child’s age and abilities: Start with simple variations and gradually introduce more complex concepts.
- Use real-world scenarios: Connect the game to everyday life to make the learning more relevant and meaningful.
- Encourage discussion and reflection: Ask your child to explain their reasoning behind their price estimates.
- Celebrate their successes: Acknowledge their efforts and achievements to foster confidence and motivation.
Conclusion
The Price is Right, though primarily known for its entertainment value, offers a valuable platform for learning and development, particularly for children. By engaging in estimation, critical thinking, and collaborative problem-solving, children can acquire essential skills that extend beyond the game itself. Its adaptability and versatility make it a valuable tool for parents, educators, and anyone looking to engage children in a fun and educational experience. The Price is Right, therefore, stands as a testament to the power of play-based learning, demonstrating that acquiring knowledge can be both entertaining and enriching.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Price is Right: A Timeless Game Show for Kids and Adults Alike. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
A Comprehensive Exploration Of Things Beginning With "H"
A Comprehensive Exploration of Things Beginning with "H"
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Things Beginning with "H"
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Things Beginning with "H". Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Things Beginning with "H"

The letter "H" occupies a prominent position in the English alphabet, marking the beginning of countless words that encompass a vast spectrum of concepts, objects, and experiences. This exploration delves into the significance and benefits of these "H" words, uncovering their multifaceted roles in our lives and the world around us.
Harnessing the Power of "H": A Journey Through Words and Concepts
Health: The foundation of well-being, health encompasses both physical and mental states. It is a fundamental human need, essential for living a fulfilling life. Maintaining good health requires a holistic approach, encompassing factors such as diet, exercise, stress management, and regular medical checkups. The pursuit of health extends beyond individual well-being, influencing societal progress and economic productivity.
Happiness: A state of contentment and joy, happiness is a sought-after human experience. While its definition varies across cultures and individuals, it often involves feelings of fulfillment, purpose, and connection. Research suggests that happiness can be cultivated through practices such as gratitude, mindfulness, and acts of kindness.
History: The study of past events, history provides invaluable insights into the present and informs our understanding of the future. It encompasses the evolution of societies, cultures, and civilizations, revealing the complexities of human experience and the interconnectedness of events. By learning from the past, we can gain valuable perspectives on current challenges and opportunities.
Hope: A feeling of optimism and anticipation, hope is a powerful force that sustains individuals and societies in times of adversity. It fuels aspirations, motivates action, and fosters resilience. Hope is a fundamental human emotion that enables us to envision a brighter future and persevere through challenges.
Honesty: A fundamental ethical principle, honesty involves truthfulness, integrity, and transparency in communication and actions. It fosters trust, builds strong relationships, and contributes to a just and equitable society. Honesty is essential for personal growth, professional success, and a healthy social environment.
Humility: A quality of modesty and self-awareness, humility involves recognizing one’s limitations and acknowledging the contributions of others. It fosters empathy, reduces arrogance, and promotes collaborative efforts. Humility is a virtue that enables individuals to learn, grow, and contribute meaningfully to society.
Harmony: A state of balance and concord, harmony exists when different elements coexist in a balanced and complementary way. It can be observed in nature, music, relationships, and social systems. Harmony fosters peace, stability, and a sense of well-being.
Humor: A form of communication that elicits laughter and amusement, humor can be a powerful tool for connecting with others, relieving stress, and promoting positive emotions. It can also be a means of social commentary and cultural critique.
Hospitality: The act of welcoming and providing care for guests, hospitality is a hallmark of graciousness and generosity. It can range from simple gestures of kindness to elaborate acts of service. Hospitality fosters a sense of community, strengthens relationships, and promotes cultural exchange.
Hydration: The process of maintaining adequate fluid levels in the body, hydration is essential for various bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and waste removal. Adequate hydration is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Hierarchy: A system of ranking or organization based on levels of authority or importance, hierarchies exist in various aspects of life, including social structures, organizations, and ecosystems. Hierarchies can be beneficial for creating order and efficiency, but they can also contribute to inequality and social divisions.
Home: A place of refuge, comfort, and belonging, home is a fundamental human need. It provides a sense of security, identity, and connection. Home can encompass a physical dwelling, a community, or a state of mind.
Heroism: The act of displaying courage, selflessness, and extraordinary bravery in the face of danger or adversity, heroism inspires others and serves as a model for ethical behavior. Heroes often emerge in times of crisis, demonstrating the best of human nature.
Habit: A learned behavior that is performed repeatedly and automatically, habits can be both positive and negative. They can contribute to personal growth and success, but they can also lead to unhealthy patterns and addictions.
Hardship: A period of difficulty, suffering, or adversity, hardship can be a source of resilience and personal growth. It can challenge individuals to adapt, overcome obstacles, and develop inner strength.
Help: The act of providing assistance or support, help is essential for human connection and social well-being. It can encompass various forms, from simple acts of kindness to formal interventions. Help is a fundamental aspect of human nature, reflecting our capacity for compassion and empathy.
Heritage: The traditions, customs, and values passed down from previous generations, heritage shapes our identities and connects us to our past. It encompasses cultural practices, historical events, and family legacies. Heritage is a source of pride, inspiration, and continuity.
Healing: The process of restoring health and well-being, healing can encompass physical, emotional, and spiritual aspects. It involves the body’s natural capacity for repair and renewal, as well as external interventions such as medical treatment and therapy.
Happiness: A state of contentment and joy, happiness is a sought-after human experience. While its definition varies across cultures and individuals, it often involves feelings of fulfillment, purpose, and connection. Research suggests that happiness can be cultivated through practices such as gratitude, mindfulness, and acts of kindness.
Humanity: The state of being human, encompassing our shared characteristics, experiences, and potential. It encompasses our capacity for love, compassion, creativity, and resilience. Humanity is a source of wonder, inspiration, and hope for the future.
FAQs: Exploring "H" Words Through Questions
Q: What are some common health concerns?
A: Common health concerns vary based on age, lifestyle, and genetic factors. Some prevalent concerns include heart disease, cancer, diabetes, mental health disorders, and infectious diseases.
Q: How can I cultivate happiness in my life?
A: Cultivating happiness involves a combination of factors, including:
- Practicing gratitude: Appreciating the good things in your life can shift your focus toward positivity.
- Mindfulness: Paying attention to the present moment without judgment can reduce stress and enhance well-being.
- Connecting with others: Strong social relationships contribute significantly to happiness.
- Pursuing meaningful activities: Engaging in activities that align with your values and interests can foster a sense of purpose.
Q: What are some important historical events?
A: Important historical events are those that have significantly shaped the course of human history. Examples include the invention of the printing press, the Renaissance, the Industrial Revolution, the World Wars, and the rise of the internet.
Q: How can I develop a sense of hope?
A: Cultivating hope involves:
- Focusing on positive possibilities: Envisioning a brighter future can fuel motivation and resilience.
- Surrounding yourself with supportive people: Positive relationships can provide encouragement and inspiration.
- Engaging in meaningful activities: Making a difference in the world can create a sense of purpose and hope.
Q: What are some tips for being more honest?
A: Practicing honesty involves:
- Being truthful in your words and actions: Avoid lying, cheating, or deceiving others.
- Taking responsibility for your mistakes: Acknowledge your errors and strive to learn from them.
- Being transparent in your communication: Clearly express your thoughts and feelings without hiding information.
Q: How can I cultivate humility?
A: Developing humility involves:
- Recognizing your limitations: Acknowledge that you don’t know everything and are capable of making mistakes.
- Appreciating the contributions of others: Give credit where credit is due and acknowledge the talents and efforts of others.
- Being open to learning and growth: Embrace opportunities to expand your knowledge and perspectives.
Q: What are some examples of harmony in nature?
A: Harmony in nature can be observed in various ways:
- The balance of ecosystems: Different species coexisting in a balanced and interconnected way.
- The rhythms of the seasons: Nature’s cyclical patterns of growth, decay, and renewal.
- The beauty of natural landscapes: The harmonious interplay of colors, textures, and forms.
Q: How can I use humor to improve my relationships?
A: Humor can enhance relationships by:
- Breaking the ice: Easing tension and creating a more comfortable atmosphere.
- Expressing affection: Sharing laughter and lighthearted moments strengthens bonds.
- Providing a shared experience: Connecting with others through laughter and amusement.
Q: What are some tips for being a good host?
A: Practicing hospitality involves:
- Making your guests feel welcome: Offer warm greetings, offer refreshments, and make them feel comfortable.
- Being attentive to their needs: Anticipate their needs and provide assistance when necessary.
- Creating a positive and enjoyable atmosphere: Engage in conversation, provide entertainment, and ensure a pleasant experience.
Q: What are some signs of dehydration?
A: Signs of dehydration include:
- Thirst: A primary indicator of fluid loss.
- Dry mouth: Reduced saliva production.
- Fatigue: Reduced energy levels due to impaired bodily functions.
- Headache: Caused by dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Dark urine: Concentrated urine due to fluid depletion.
Q: What are some examples of hierarchies in society?
A: Hierarchies in society can be observed in:
- Social classes: Distributions of wealth, power, and status.
- Organizational structures: Levels of authority and responsibility within institutions.
- Political systems: Distributions of power and decision-making authority.
Q: How can I create a sense of home?
A: Creating a sense of home involves:
- Personalizing your space: Decorating your surroundings with items that reflect your personality and interests.
- Building relationships with your community: Connecting with your neighbors and participating in local events.
- Cultivating a sense of belonging: Finding a place where you feel accepted, supported, and valued.
Q: What are some examples of heroism in everyday life?
A: Heroism can be found in everyday acts of courage and selflessness, such as:
- Helping someone in need: Offering assistance to a stranger in distress.
- Standing up for what is right: Speaking out against injustice or discrimination.
- Making a difference in your community: Volunteering your time and resources to support others.
Q: How can I break a bad habit?
A: Breaking a bad habit involves:
- Identifying the trigger: Understanding what prompts the behavior.
- Developing a plan: Creating strategies to avoid the trigger or replace the habit with a positive behavior.
- Seeking support: Enlisting the help of friends, family, or a therapist.
Q: How can I overcome hardship?
A: Overcoming hardship involves:
- Maintaining a positive attitude: Focusing on hope and resilience.
- Seeking support: Leaning on friends, family, or professionals for guidance and encouragement.
- Learning from the experience: Identifying lessons learned and applying them to future challenges.
Q: How can I be more helpful to others?
A: Being helpful involves:
- Offering assistance without being asked: Observing needs and taking initiative.
- Being a good listener: Providing a supportive and non-judgmental ear.
- Making a difference in your community: Volunteering your time and resources to support others.
Q: What are some ways to preserve my heritage?
A: Preserving heritage involves:
- Sharing your traditions with others: Educating younger generations about your culture and history.
- Supporting cultural institutions: Contributing to museums, libraries, and other organizations that preserve cultural heritage.
- Documenting your family history: Collecting stories, photographs, and other materials that preserve your family legacy.
Q: What are some examples of healing practices?
A: Healing practices encompass:
- Medical interventions: Surgery, medication, and other treatments.
- Therapy: Counseling, psychotherapy, and other forms of mental health support.
- Complementary and alternative medicine: Acupuncture, massage, and other holistic approaches.
Q: What are some tips for promoting human connection?
A: Promoting human connection involves:
- Engaging in face-to-face interactions: Spending time with loved ones and building relationships in person.
- Being present in conversations: Actively listening and showing genuine interest in others.
- Practicing empathy and compassion: Understanding and responding to the emotions of others.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of "H" Words
The words that begin with "H" encompass a vast array of concepts and experiences that are integral to human existence. They represent our fundamental needs, aspirations, values, and challenges. From the pursuit of health and happiness to the cultivation of honesty and humility, these "H" words guide us toward a more fulfilling and meaningful life. They remind us of our shared humanity, our capacity for growth, and the importance of making a positive impact on the world around us. By understanding and embracing the significance of these "H" words, we can navigate the complexities of life with greater awareness, purpose, and compassion.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Things Beginning with "H". We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
The Enduring Appeal Of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
The Enduring Appeal of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Enduring Appeal of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Enduring Appeal of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Enduring Appeal of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide
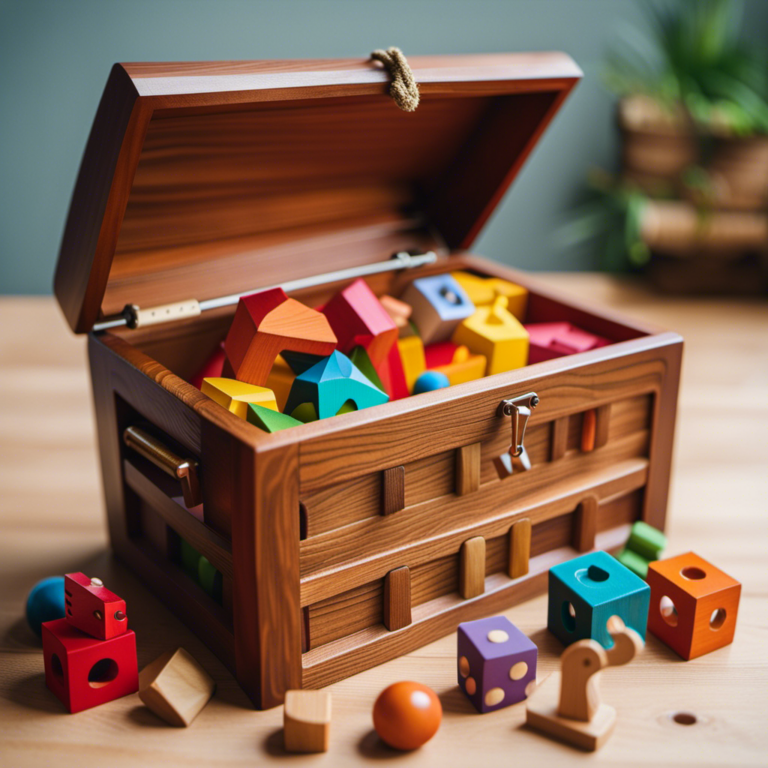

The world of toys is a vibrant and ever-evolving landscape. While the allure of brand-new, shiny toys is undeniable, there’s a growing appreciation for the value and benefits of pre-loved playthings. Used toys offer a unique blend of affordability, sustainability, and nostalgia, making them a compelling choice for parents, collectors, and children alike.
The Allure of Used Toys
1. Affordability: The financial benefits of purchasing used toys are undeniable. The cost of toys, particularly those with advanced features or popular brands, can be significant. Buying pre-owned allows families to access a wider range of toys without straining their budgets. This is particularly crucial in times of economic uncertainty.
2. Sustainability: In an era of growing environmental awareness, the purchase of used toys aligns perfectly with sustainable practices. By giving toys a second life, we reduce the demand for new production, minimizing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing, packaging, and transportation. This promotes a circular economy and reduces waste.
3. Nostalgia and Sentimental Value: Used toys often carry a sense of nostalgia, evoking memories of childhood and simpler times. For collectors, the hunt for vintage or rare toys can be a rewarding experience, connecting them to a bygone era. The sentimental value of these toys can be immense, making them cherished heirlooms passed down through generations.
4. Diversity and Uniqueness: The world of used toys offers an unparalleled diversity of options. From classic wooden toys to vintage action figures, the selection is vast and often unique. This allows children to explore a broader range of play experiences and develop their imaginations in diverse ways.
5. Educational Value: Used toys, especially those from earlier eras, often embody classic play patterns that encourage creativity, problem-solving, and social interaction. These toys, free from the bells and whistles of modern technology, encourage children to use their imaginations and develop essential skills.
Navigating the Used Toy Market
1. Online Marketplaces: Platforms like eBay, Etsy, and Facebook Marketplace offer a vast selection of used toys. These platforms allow for easy browsing, comparison, and purchase, often with detailed descriptions and photographs. However, it’s essential to exercise caution, verifying seller legitimacy and product condition.
2. Consignment Shops and Thrift Stores: Local consignment shops and thrift stores are excellent sources for used toys. These shops often offer curated selections and knowledgeable staff who can assist with finding the perfect toy. The benefit of these physical locations is the ability to inspect items firsthand before purchase.
3. Garage Sales and Estate Sales: These events offer a treasure trove of used toys at bargain prices. However, it’s important to be prepared for a more unpredictable selection and potentially limited availability.
4. Toy Libraries and Swap Groups: Some communities offer toy libraries, where members can borrow toys for a set period. Toy swap groups provide platforms for families to exchange toys, fostering a sense of community and reducing waste.
5. Online Auction Sites: Platforms like eBay and specialized auction sites allow for bidding on used toys, often resulting in competitive pricing. This option can be advantageous for finding rare or highly sought-after items.
Important Considerations
- Safety: Thoroughly inspect used toys for any signs of damage, wear, or missing parts. Ensure the toy is age-appropriate and meets safety standards.
- Cleanliness: Clean used toys thoroughly before allowing children to play with them. This involves washing, disinfecting, and removing any potential allergens.
- Condition: Be realistic about the condition of used toys. While some may be in excellent condition, others may show signs of wear and tear.
- Authenticity: When purchasing vintage or collectible toys, research the authenticity of the item to avoid purchasing fakes or replicas.
FAQs about Used Toys
1. Are used toys safe for children?
Used toys can be safe for children if they are thoroughly inspected and cleaned. Look for signs of damage, missing parts, or sharp edges. Ensure the toy is age-appropriate and meets safety standards.
2. How can I tell if a used toy is authentic?
Research the toy’s history, manufacturer, and distinguishing features. Look for signs of authenticity, such as original packaging, markings, or documentation.
3. What are the best ways to clean used toys?
Wash toys with mild soap and water. Disinfect toys using a diluted bleach solution or a commercial toy disinfectant. Avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive cleaners.
4. How do I dispose of old or broken toys?
Recycle or donate toys that are still in good condition. Broken or unusable toys can be disposed of according to local guidelines.
5. What are the benefits of buying used toys?
Used toys offer affordability, sustainability, nostalgia, diversity, and educational value. They are a responsible and often rewarding alternative to brand-new toys.
Tips for Buying and Selling Used Toys
1. Research and Preparation: Research the market value of toys before buying or selling. Take clear and detailed photos of toys for sale.
2. Fair Pricing: Set realistic prices for used toys, considering their condition, age, and popularity. Offer discounts for multiple purchases or for toys in less than perfect condition.
3. Honest Descriptions: Be honest and transparent about the condition of used toys. Highlight any flaws or imperfections.
4. Packaging and Shipping: Package used toys securely for shipping to prevent damage during transit. Use appropriate packaging materials and provide tracking information.
5. Communication: Respond promptly to inquiries and provide clear and concise information about toys. Be respectful and patient with buyers and sellers.
Conclusion
The purchase of used toys represents a responsible and rewarding approach to play. It fosters a sense of community, promotes sustainability, and provides children with access to a diverse range of play experiences. By embracing the world of pre-loved playthings, we can cultivate a more conscious and sustainable approach to toy consumption, ensuring that the joy of play continues to resonate through generations.
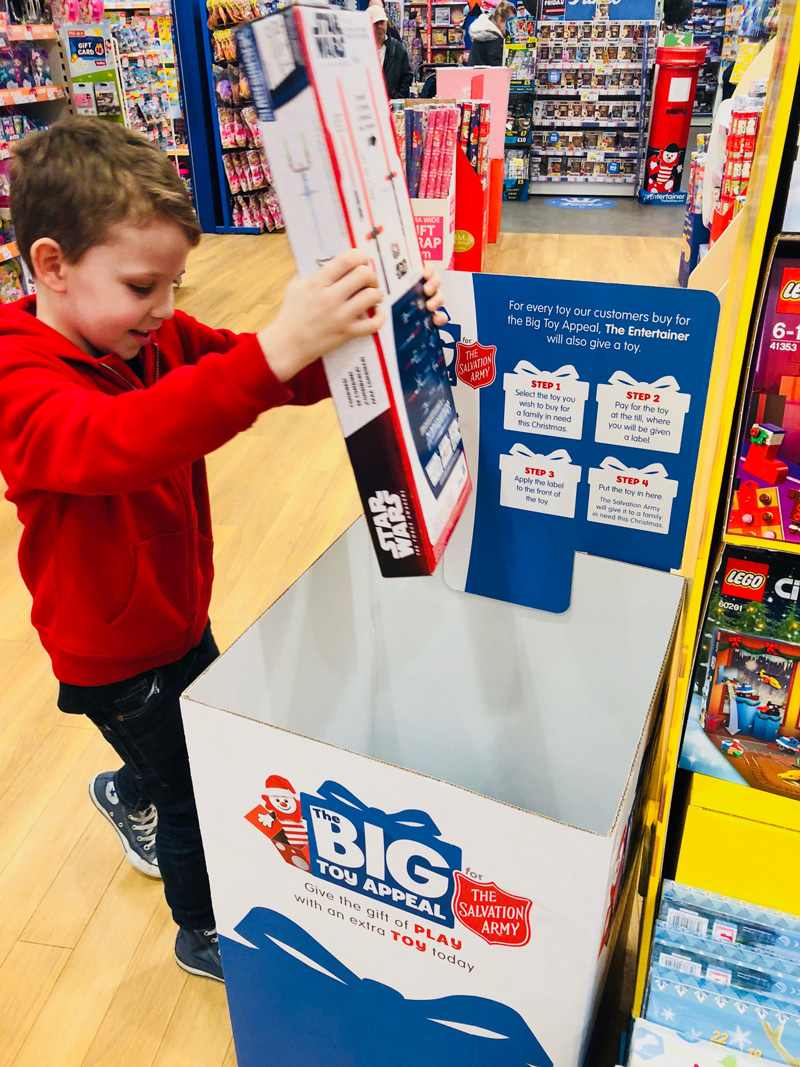








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Enduring Appeal of Used Toys: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring The Significance Of A Single Letter
The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring the Significance of a Single Letter
Related Articles: The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring the Significance of a Single Letter
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring the Significance of a Single Letter. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring the Significance of a Single Letter

The letter "u" occupies a seemingly unremarkable position in the English alphabet. Yet, its presence in our language and beyond is far from insignificant. From the fundamental building blocks of communication to the intricate workings of the natural world, the letter "u" holds a surprising depth and breadth of significance.
Unlocking the Power of "U" in Language
The letter "u" plays a crucial role in shaping the sounds and meanings of words. Its versatility allows it to represent a variety of vowel sounds, from the short "u" in "cup" to the long "u" in "flute." This adaptability enriches the phonetic landscape of the English language, adding nuance and complexity to our spoken and written communication.
Furthermore, the "u" serves as a crucial component in numerous prefixes and suffixes, effectively modifying the meaning and grammatical function of words. Prefixes like "un-" (undo, unhappy) and "ultra-" (ultramodern, ultra-violet) add layers of negation, intensity, or extremity to existing terms. Similarly, suffixes like "-ous" (famous, dangerous) and "-ful" (beautiful, hopeful) denote qualities, states, or tendencies. These linguistic additions, often incorporating the letter "u," allow us to express a wide range of concepts and ideas with greater precision and expressiveness.
Beyond its role in individual words, the letter "u" forms an integral part of numerous common phrases and idioms. Phrases like "under the weather" (feeling unwell) and "up in the air" (uncertain) convey specific meanings and emotions, enriching our linguistic repertoire. Idioms like "under the thumb" (being controlled) and "up for grabs" (available) offer concise and vivid ways to express complex situations and opportunities. These linguistic structures, often incorporating the letter "u," contribute to the richness and dynamism of the English language.
Unveiling the "U" in Science and Technology
The letter "u" also finds a prominent place in the world of science and technology. In physics, the "u" symbol represents the initial velocity of an object, a fundamental concept in understanding motion and its dynamics. In chemistry, "u" signifies the atomic mass unit, a standardized measure used to express the mass of atoms and molecules. These scientific applications of the letter "u" highlight its crucial role in quantifying and understanding the physical world.
The "u" also features prominently in the realm of computer science and programming. In many programming languages, "u" is used to denote unsigned integers, a data type used to represent positive whole numbers. This application reflects the letter "u"s association with numerical values and its importance in the digital world.
Unmasking the "U" in Nature and the Universe
The letter "u" also appears in numerous natural phenomena and cosmic entities. The "U" in "ultraviolet" refers to a specific range of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than visible light. Ultraviolet radiation plays a critical role in various biological processes, including vitamin D synthesis and the regulation of circadian rhythms.
In astronomy, "U" designates the "ultraviolet" band of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is used to study stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. By analyzing the ultraviolet light emitted by these objects, astronomers can gain insights into their composition, temperature, and evolution.
Understanding the "U" in Art and Culture
The letter "u" also holds a significant place in the realm of art and culture. In music, "u" often represents the "upper" voice in a musical composition, particularly in vocal ensembles. This association reflects the letter "u"s connection to elevation and prominence.
In visual arts, the "u" shape can be found in numerous artistic motifs and designs. From the graceful curves of art nouveau to the abstract forms of modern art, the "u" shape serves as a versatile element for creating visual interest and conveying specific emotions.
Unraveling the "U" in Everyday Life
The letter "u" permeates our everyday lives in countless ways. We encounter it in countless words, from the mundane ("use") to the profound ("universe"). It appears in countless names, places, and objects, from "Ursula" to "Utrecht" to "umbrella."
The ubiquitous nature of the letter "u" serves as a reminder of its fundamental role in shaping our world. It contributes to our understanding of the universe, our ability to communicate, and our appreciation for the beauty and complexity of life.
FAQs by Things with the Letter "U"
Q: What is the significance of the "U" in "universe"?
A: The "U" in "universe" represents the vastness and interconnectedness of all existing matter and energy. It signifies the totality of all things, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest galaxies.
Q: How does the "U" in "ultraviolet" impact our lives?
A: Ultraviolet radiation, denoted by the "U," plays a crucial role in regulating our biological processes. It is essential for vitamin D synthesis, which strengthens our bones and immune system. However, excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation can be harmful, leading to sunburn and skin cancer.
Q: What is the importance of the "U" in "understanding"?
A: The "U" in "understanding" signifies the process of grasping the meaning or nature of something. It represents the act of acquiring knowledge and insight, which is essential for navigating the world around us.
Q: How does the "U" in "up" impact our perception of space?
A: The "U" in "up" represents a direction opposite to gravity, signifying a sense of elevation and ascent. This concept plays a crucial role in our perception of space and our understanding of gravity’s influence on our movements.
Tips by Things with the Letter "U"
Tip from "Universe": Embrace the vastness and interconnectedness of all things. Recognize that you are part of a larger whole and strive to understand your place within it.
Tip from "Ultraviolet": Be mindful of the power of sunlight and its impact on your health. Protect yourself from excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation, but also embrace its benefits for vitamin D synthesis.
Tip from "Understanding": Seek knowledge and strive to understand the world around you. Engage with different perspectives and challenge your own assumptions to broaden your understanding.
Tip from "Up": Aim high and strive for excellence in your endeavors. Don’t be afraid to reach for your dreams and push your limits.
Conclusion by Things with the Letter "U"
The letter "u" may appear simple and unassuming, but its impact on our world is profound. It plays a vital role in shaping our language, understanding our universe, and navigating our daily lives. From the smallest subatomic particles to the grandest cosmic structures, the "u" serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of all things and the power of a single letter to shape our perception of the world. By recognizing the significance of the letter "u," we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of language, science, and the universe itself.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ubiquitous "U": Exploring the Significance of a Single Letter. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
The Essential Pantry: A Guide To Stocking Your Kitchen For Culinary Success And Peace Of Mind
The Essential Pantry: A Guide to Stocking Your Kitchen for Culinary Success and Peace of Mind
Related Articles: The Essential Pantry: A Guide to Stocking Your Kitchen for Culinary Success and Peace of Mind
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Essential Pantry: A Guide to Stocking Your Kitchen for Culinary Success and Peace of Mind. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Pantry: A Guide to Stocking Your Kitchen for Culinary Success and Peace of Mind

A well-stocked pantry is the cornerstone of any kitchen, providing the foundation for culinary creativity and ensuring preparedness for unexpected events. It is a treasure trove of ingredients, staples, and culinary essentials, offering both convenience and peace of mind. This guide explores the crucial components of a well-stocked pantry, outlining the benefits of each category and providing practical advice for selection and storage.
Grains and Legumes: The Foundation of Flavor and Nutrition
Grains and legumes form the bedrock of a well-stocked pantry, providing sustenance, versatility, and affordability.
- Rice: A versatile staple, rice comes in countless varieties, each with its unique texture and flavor profile. White rice, brown rice, basmati rice, jasmine rice, and wild rice are all excellent additions to a pantry.
- Pasta: From classic spaghetti to intricate shapes like farfalle and penne, pasta offers endless culinary possibilities. Choose a variety of shapes and sizes to accommodate different dishes.
- Quinoa: A complete protein source, quinoa is a nutritious and versatile grain that can be used in salads, soups, and as a base for bowls.
- Oats: A hearty and versatile grain, oats are perfect for breakfast porridge, baked goods, and savory dishes. Choose rolled oats, steel-cut oats, or quick-cooking oats based on desired texture and cooking time.
- Beans: Dried beans are a budget-friendly source of protein and fiber. Stock a variety of beans, including black beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, chickpeas, and lentils.
- Flour: All-purpose flour is a pantry essential for baking, while whole wheat flour offers a healthier alternative. Consider specialty flours like almond flour, coconut flour, and rice flour for gluten-free options.
Canned Goods: Convenience and Longevity
Canned goods offer long shelf life and convenience, providing quick and easy meal solutions.
- Tomatoes: Canned diced tomatoes, crushed tomatoes, and tomato paste are essential ingredients for sauces, soups, and stews.
- Beans: Canned beans offer a convenient alternative to dried beans, providing a quick and easy source of protein and fiber.
- Tuna and Salmon: Canned fish is a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Choose varieties packed in water or oil for healthier options.
- Soup and Broth: Canned soup and broth provide a quick and easy base for meals, offering both flavor and nutritional value.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Canned fruits and vegetables offer a convenient way to enjoy seasonal produce year-round. Choose varieties packed in juice or water for healthier options.
Spices and Seasonings: The Essence of Flavor
Spices and seasonings are the heart of flavor, adding depth and complexity to dishes.
- Salt and Pepper: Essential for basic seasoning, choose high-quality salt and freshly ground peppercorns.
- Herbs: Dried herbs like oregano, basil, thyme, and rosemary are versatile additions to a pantry.
- Spices: Explore a variety of spices like cumin, coriander, turmeric, paprika, and chili powder to enhance your culinary repertoire.
- Flavor Enhancers: Soy sauce, fish sauce, Worcestershire sauce, and vinegar are essential flavor enhancers that can elevate dishes.
Nuts and Seeds: Healthy Snacks and Flavorful Additions
Nuts and seeds are nutrient-rich snacks and versatile ingredients.
- Almonds, Walnuts, Cashews: These nuts offer healthy fats, protein, and fiber.
- Sunflower Seeds, Pumpkin Seeds: These seeds are rich in antioxidants and offer a crunchy texture.
- Peanut Butter: A pantry staple, peanut butter provides protein and healthy fats. Choose natural peanut butter without added sugar or oil.
Oils and Vinegars: Culinary Essentials
Oils and vinegars are essential for cooking, dressing salads, and creating marinades.
- Olive Oil: A versatile oil for cooking, baking, and salad dressings. Choose extra virgin olive oil for its superior flavor and nutritional benefits.
- Vegetable Oil: A neutral-flavored oil suitable for high-heat cooking.
- Vinegar: Choose a variety of vinegars, including balsamic vinegar, apple cider vinegar, and white wine vinegar, for different flavor profiles.
Sweeteners and Baking Essentials:
Sweeteners and baking essentials are necessary for baking and creating sweet treats.
- Sugar: Granulated sugar is essential for baking and sweetening drinks.
- Honey: A natural sweetener with a unique flavor profile.
- Maple Syrup: Another natural sweetener with a distinct taste.
- Baking Powder and Baking Soda: Essential leavening agents for cakes, cookies, and bread.
- Vanilla Extract: A fragrant and versatile flavoring agent.
Other Essential Pantry Items:
- Pasta Sauce: Choose a variety of pasta sauces to create quick and easy meals.
- Broth Cubes: A convenient way to add flavor to soups, stews, and sauces.
- Cereal: Choose a variety of cereals for breakfast or snacks.
- Snacks: Stock healthy snacks like dried fruit, nuts, and granola bars for quick and easy options.
- Chocolate: Dark chocolate or unsweetened cocoa powder can be used in baking or as a healthy snack.
FAQs
Q: How long can I store items in my pantry?
A: The shelf life of pantry items varies depending on the product. Most items have a "best by" date, which indicates the optimal time for consumption. However, many pantry staples can be stored for extended periods if properly stored in a cool, dark, and dry environment.
Q: How can I prevent pantry pests?
A: To prevent pantry pests, store all food in airtight containers, clean spills promptly, and regularly inspect your pantry for signs of infestation.
Q: How often should I rotate my pantry stock?
A: It is recommended to rotate your pantry stock regularly to ensure freshness and prevent spoilage. Check expiration dates and use older items before newer ones.
Tips for Stocking Your Pantry:
- Plan Ahead: Take inventory of your pantry staples and create a shopping list based on your needs.
- Buy in Bulk: Purchase items in bulk to save money and reduce the frequency of grocery shopping.
- Prioritize Quality: Choose high-quality ingredients that will enhance your cooking and provide nutritional value.
- Organize Your Pantry: Use shelves, bins, and labels to organize your pantry and make it easy to find what you need.
- Store Properly: Store items in airtight containers to prevent spoilage and infestation.
Conclusion
A well-stocked pantry is a culinary treasure trove, offering convenience, flexibility, and peace of mind. By stocking your pantry with essential ingredients, staples, and culinary essentials, you can create delicious and nutritious meals while ensuring preparedness for unexpected events. Remember to prioritize quality, organize your pantry effectively, and rotate your stock regularly to maintain freshness and prevent waste. With a well-stocked pantry, you can embark on culinary adventures and enjoy the satisfaction of creating delicious and nourishing meals from the comfort of your own home.
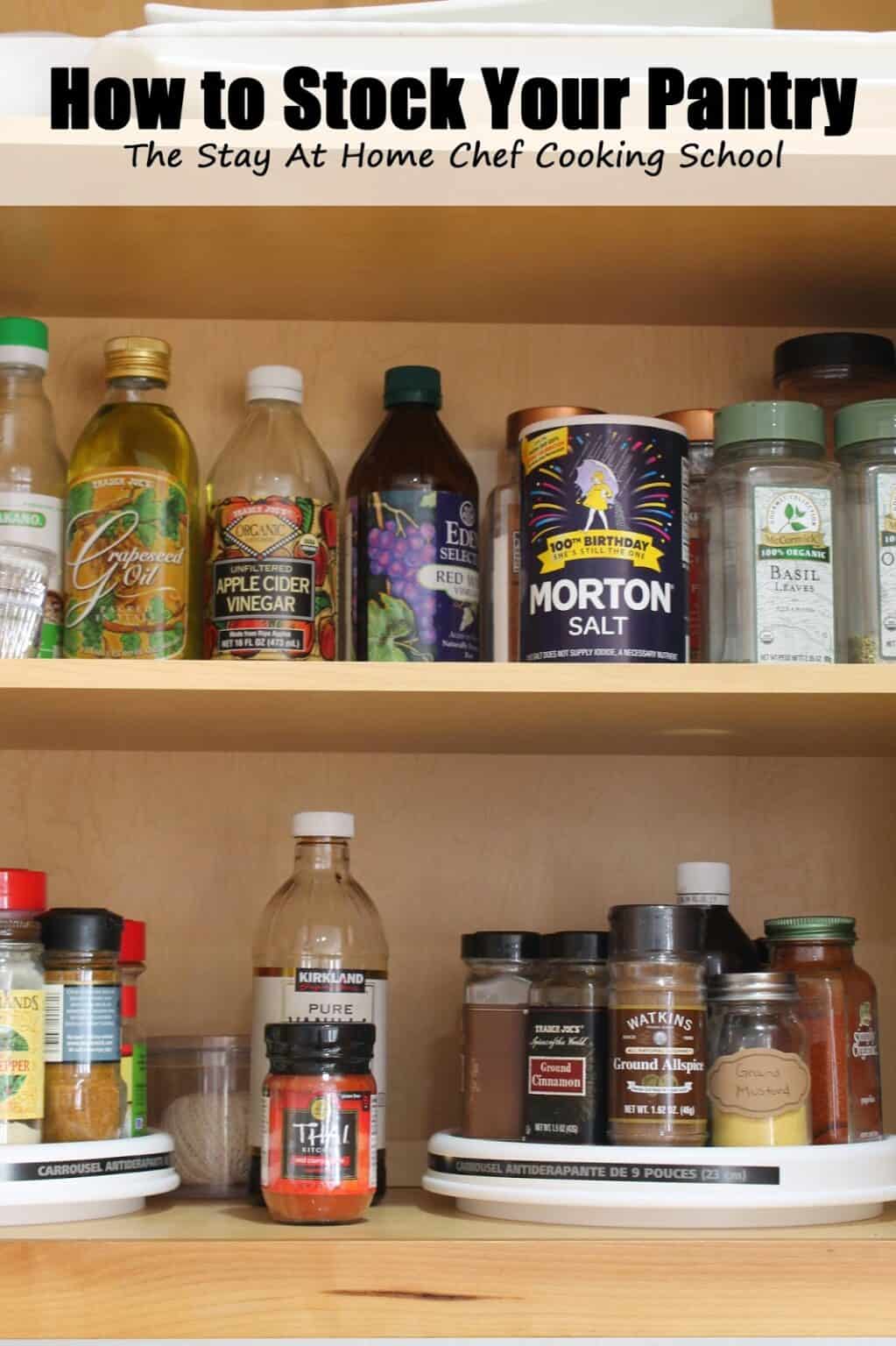
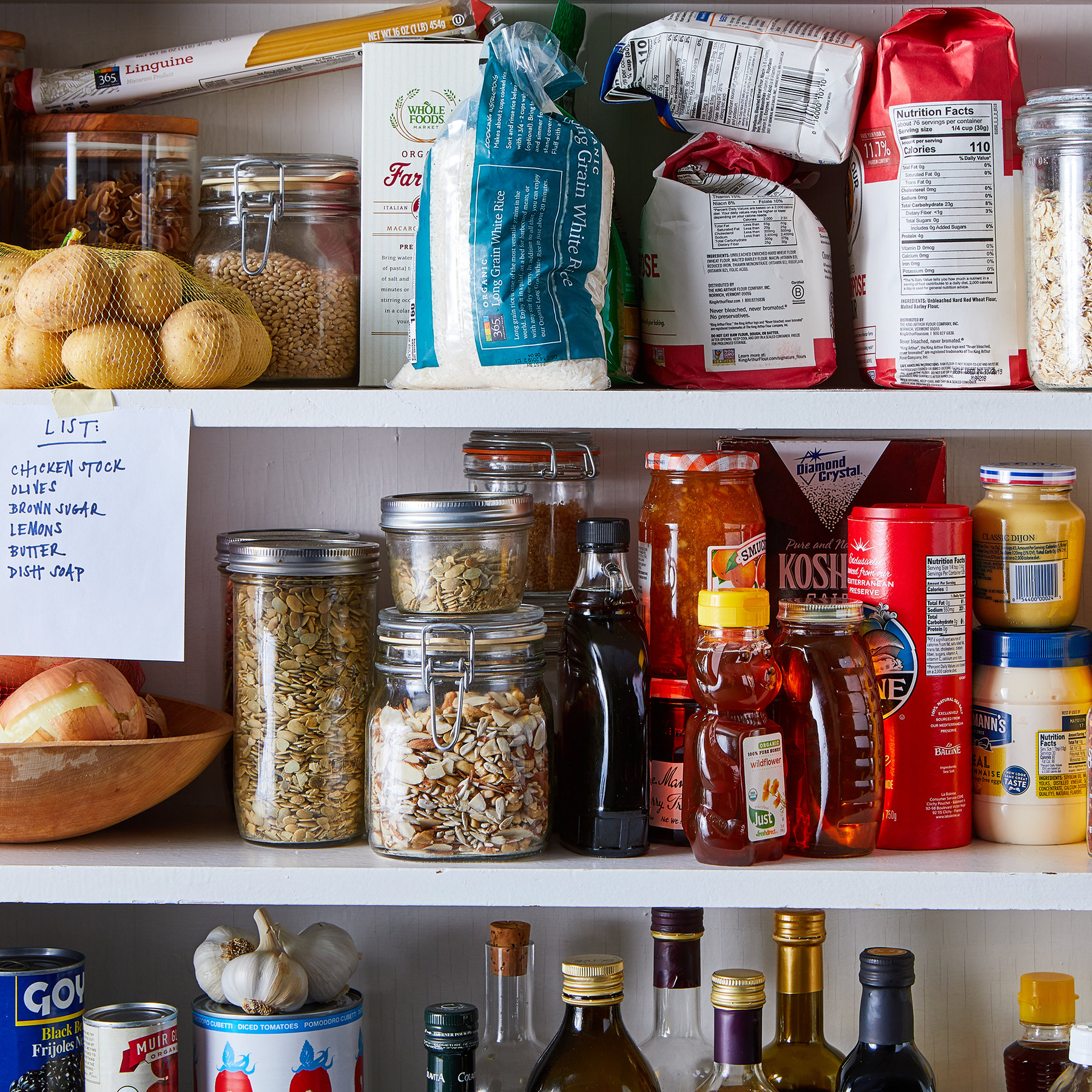








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Pantry: A Guide to Stocking Your Kitchen for Culinary Success and Peace of Mind. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The Kilogram: A Universal Measure Of Mass
The Kilogram: A Universal Measure of Mass
Related Articles: The Kilogram: A Universal Measure of Mass
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Kilogram: A Universal Measure of Mass. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Kilogram: A Universal Measure of Mass

The kilogram (kg), a fundamental unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), serves as a universal language for quantifying the amount of matter in objects and substances. Its significance extends beyond mere measurement, playing a crucial role in scientific research, engineering, commerce, and everyday life. This article delves into the diverse applications of the kilogram, exploring its importance across various domains and highlighting the benefits it brings to our understanding of the physical world.
A Journey Through the Kilogram’s Applications:
1. Scientific Research:
The kilogram is the cornerstone of scientific research, enabling precise measurements that underpin fundamental discoveries. In physics, it allows for the accurate determination of forces, energy, and momentum, crucial for understanding the laws governing the universe. Chemistry relies on the kilogram to quantify the mass of reactants and products in chemical reactions, facilitating the development of new materials and processes. Biology utilizes the kilogram to measure the mass of organisms, cells, and molecules, providing insights into life’s intricate mechanisms.
2. Engineering and Technology:
Engineering relies heavily on the kilogram for designing and building structures, machines, and systems. Civil engineers use it to calculate the load-bearing capacity of bridges and buildings, ensuring their safety and stability. Mechanical engineers utilize the kilogram to design engines, vehicles, and other machinery, optimizing their performance and efficiency. Aerospace engineers employ the kilogram to determine the mass of rockets, satellites, and spacecraft, crucial for navigating the vastness of space.
3. Commerce and Trade:
The kilogram plays a vital role in commerce and trade, ensuring fairness and transparency in transactions involving goods and commodities. It standardizes the measurement of products, facilitating accurate pricing, weighing, and distribution. From groceries to industrial materials, the kilogram provides a common language for buyers and sellers, enabling efficient exchange of goods across borders.
4. Food and Nutrition:
The kilogram is fundamental to understanding and managing our food intake. Nutrition labels on food products utilize the kilogram to indicate the mass of ingredients, serving sizes, and nutritional content. This information empowers consumers to make informed choices about their diet, promoting healthy eating habits and overall well-being.
5. Health and Medicine:
The kilogram is crucial in healthcare and medicine, enabling accurate diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of patients. Doctors use it to measure body mass index (BMI), a key indicator of health, and to prescribe appropriate dosages of medications based on a patient’s weight. The kilogram also plays a role in the development and administration of vaccines and other medical treatments, ensuring their effectiveness and safety.
FAQs about the Kilogram:
Q1: What is the history of the kilogram?
A: The kilogram’s history dates back to the late 18th century, when the French Academy of Sciences defined it as the mass of one cubic decimeter of water at its maximum density. However, this definition proved impractical, leading to the creation of a physical prototype – the International Prototype Kilogram (IPK) – in 1889. The IPK, a cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy, served as the standard for the kilogram for over a century.
Q2: Why is the kilogram important for scientific research?
A: The kilogram is essential for scientific research because it provides a consistent and reliable unit for measuring mass, enabling accurate and repeatable experiments. This allows scientists to compare results across different studies, leading to a deeper understanding of the natural world.
Q3: How is the kilogram used in everyday life?
A: The kilogram is used in everyday life for tasks such as grocery shopping, cooking, and weighing oneself. It helps us quantify the amount of food we consume, the ingredients we use in recipes, and our own body weight, influencing our daily decisions and activities.
Q4: What are the benefits of using the kilogram?
A: The kilogram offers several benefits, including:
- Standardization: It provides a universal unit of mass, ensuring consistency in measurements across different countries and industries.
- Accuracy: It allows for precise measurements, crucial for scientific research, engineering, and commerce.
- Efficiency: It simplifies transactions and communication, facilitating trade and economic growth.
- Safety: It ensures the safety of structures, machines, and products, safeguarding human life and property.
Tips for Using the Kilogram:
- Understand the difference between mass and weight: Mass is a fundamental property of matter, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. The kilogram measures mass, not weight.
- Use appropriate tools for measuring mass: Choose scales or balances calibrated in kilograms for accurate measurements.
- Be aware of the limitations of the kilogram: The kilogram is not a perfect measure, as it is subject to variations due to factors like temperature and humidity.
- Stay updated on the latest developments in the kilogram: The kilogram is constantly being refined and redefined, so it is important to stay informed about the latest standards and practices.
Conclusion:
The kilogram, a fundamental unit of mass, plays a crucial role in our understanding and interaction with the physical world. Its diverse applications in science, engineering, commerce, and everyday life highlight its significance as a universal language for quantifying matter. From the intricate workings of atoms to the vastness of the universe, the kilogram serves as a powerful tool for exploring and harnessing the wonders of nature. By understanding and utilizing the kilogram effectively, we can continue to advance knowledge, innovate, and improve our lives.





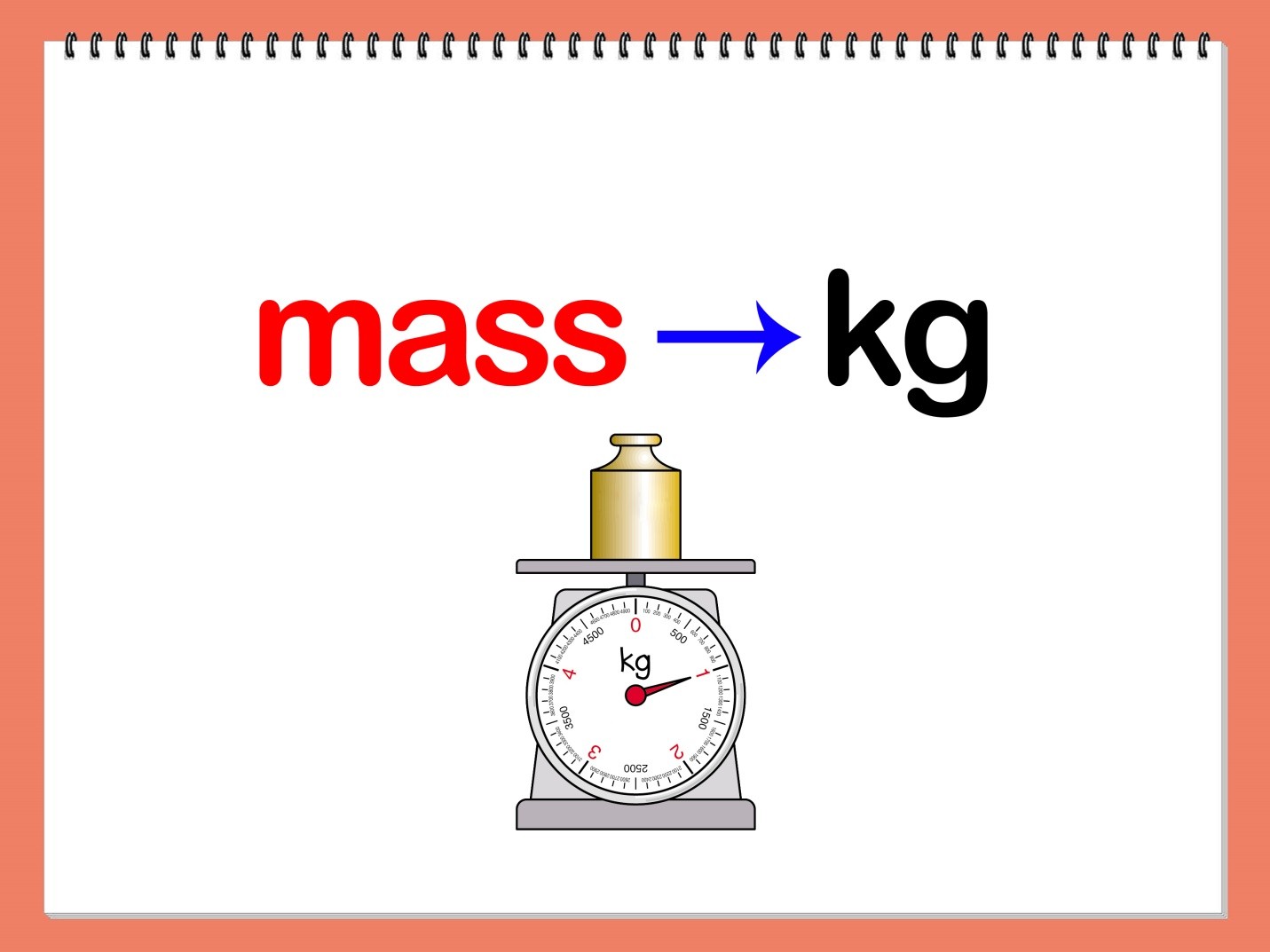

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Kilogram: A Universal Measure of Mass. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
Understanding The Power Of High PH: Exploring The World Of Alkaline Substances
Understanding the Power of High pH: Exploring the World of Alkaline Substances
Related Articles: Understanding the Power of High pH: Exploring the World of Alkaline Substances
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power of High pH: Exploring the World of Alkaline Substances. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power of High pH: Exploring the World of Alkaline Substances

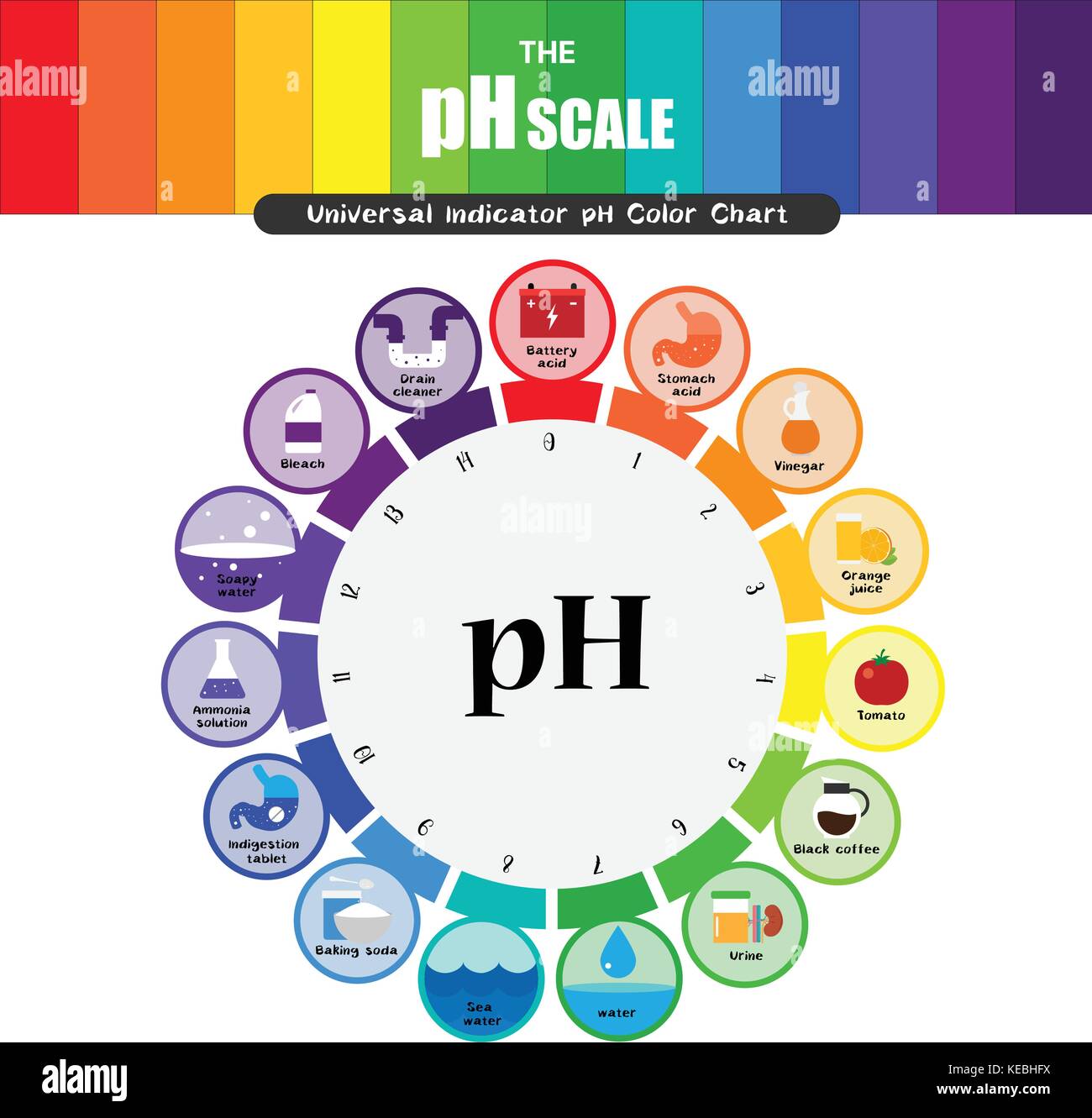
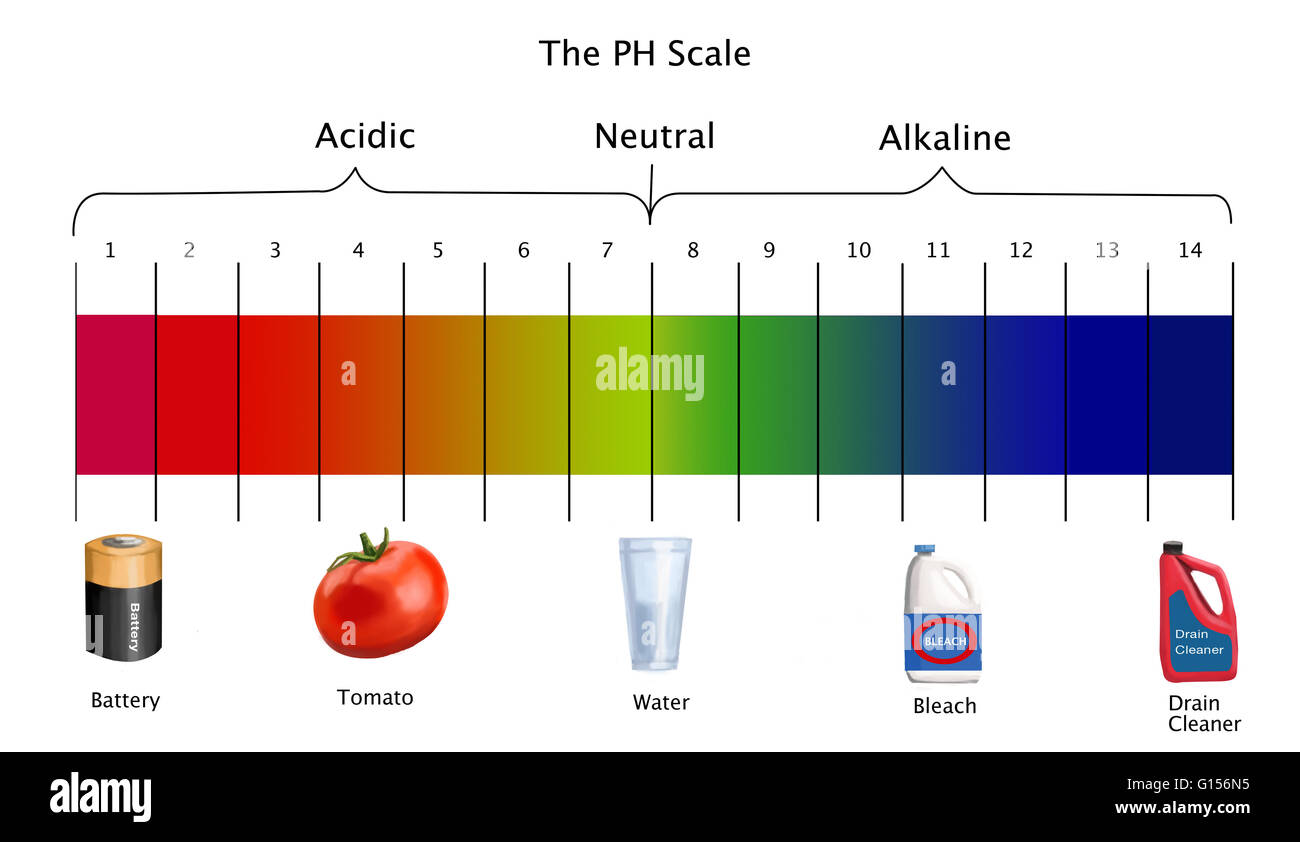
The pH scale, a numerical representation of acidity and alkalinity, ranges from 0 to 14. Substances with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those above 7 are alkaline, also known as basic. The higher the pH value, the more alkaline a substance is. Understanding the properties of high pH substances is crucial for various applications, from industrial processes to maintaining human health.
The Chemistry of High pH
High pH substances are characterized by a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) compared to hydrogen ions (H+). This imbalance in ion concentration leads to the alkaline nature of these substances. The presence of hydroxide ions is responsible for the characteristic properties of high pH substances, such as their ability to neutralize acids, their slippery feel, and their potential to corrode certain materials.
Examples of High pH Substances
Many substances commonly encountered in our daily lives exhibit high pH values. These include:
- Household cleaners: Products like ammonia-based cleaners, bleach, and drain cleaners are highly alkaline. Their high pH allows them to effectively dissolve grease, grime, and other organic matter, making them useful for cleaning purposes.
- Soaps and detergents: The alkaline nature of soaps and detergents helps break down dirt and grime, making them effective cleaning agents.
- Antacids: These medications contain alkaline substances like calcium carbonate or magnesium hydroxide, which neutralize excess stomach acid, providing relief from heartburn and indigestion.
- Cement and concrete: The high pH of these materials is essential for their hardening process, creating strong and durable structures.
- Seawater: The average pH of seawater is around 8.1, making it slightly alkaline. This alkalinity is crucial for maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
- Baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate): A common household staple, baking soda has a pH of around 8.3, making it a mild alkaline substance. It is used in baking, cleaning, and as an antacid.
- Lye (Sodium hydroxide): A highly corrosive alkaline substance with a pH of 14. It is used in various industrial processes, such as soap making and paper production.
Importance and Benefits of High pH
High pH substances play a significant role in various industries and aspects of our lives. Their importance stems from their unique properties:
- Cleaning and sanitation: The ability of high pH substances to dissolve organic matter makes them essential for cleaning and sanitation. They are used in household cleaning products, industrial cleaning processes, and even in water treatment plants to remove impurities.
- Industrial processes: High pH substances are crucial in several industrial processes, including manufacturing, chemical processing, and construction. Their ability to react with acids, their strong alkalinity, and their ability to dissolve certain materials make them valuable in various applications.
- Health and medicine: Alkaline substances play a role in maintaining health and treating medical conditions. Antacids are used to neutralize excess stomach acid, while alkaline mineral waters are believed to have various health benefits.
- Environmental applications: High pH substances are used in environmental remediation, such as neutralizing acidic soil and water. They also play a role in wastewater treatment, helping to remove harmful pollutants.
Risks Associated with High pH
While high pH substances offer numerous benefits, they also pose certain risks:
- Skin and eye irritation: High pH substances can irritate the skin and eyes, causing redness, burning, and even chemical burns. Therefore, it is crucial to handle these substances with caution, wearing appropriate protective gear.
- Corrosion: High pH substances can corrode metals and other materials, leading to damage and deterioration. This is particularly important to consider in industrial settings where these substances are used.
- Environmental damage: The release of highly alkaline substances into the environment can disrupt ecosystems and harm aquatic life. Proper disposal and handling of these substances are crucial to minimize environmental impact.
FAQs about High pH Substances
Q: What is the difference between acidic and alkaline substances?
A: Acidic substances have a pH below 7, while alkaline substances have a pH above 7. Acidic substances release hydrogen ions (H+), while alkaline substances release hydroxide ions (OH-).
Q: What are the common uses of high pH substances?
A: High pH substances are commonly used in cleaning, sanitation, industrial processes, medicine, and environmental remediation.
Q: Are all high pH substances dangerous?
A: Not all high pH substances are dangerous. Some, like baking soda, are safe for household use. However, highly concentrated alkaline substances, like lye, can be corrosive and harmful.
Q: How can I safely handle high pH substances?
A: Always wear protective gear, such as gloves, goggles, and a mask, when handling high pH substances. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Store these substances in a well-ventilated area, away from children and pets.
Tips for Using High pH Substances Safely
- Read the label: Always read the product label carefully before using any high pH substance. Follow the instructions for safe handling and storage.
- Wear protective gear: Always wear gloves, goggles, and a mask when handling high pH substances.
- Use in well-ventilated areas: Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes: Immediately wash any areas of skin that come into contact with high pH substances with plenty of water. If the substance gets in your eyes, flush them with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
- Store properly: Store high pH substances in a cool, dry place, away from children and pets.
Conclusion
High pH substances are ubiquitous in our daily lives, playing vital roles in various industries and aspects of our health. Understanding their properties, benefits, and risks is crucial for safe and responsible use. By following proper handling procedures and being aware of potential hazards, we can harness the power of high pH substances while minimizing their negative impacts.

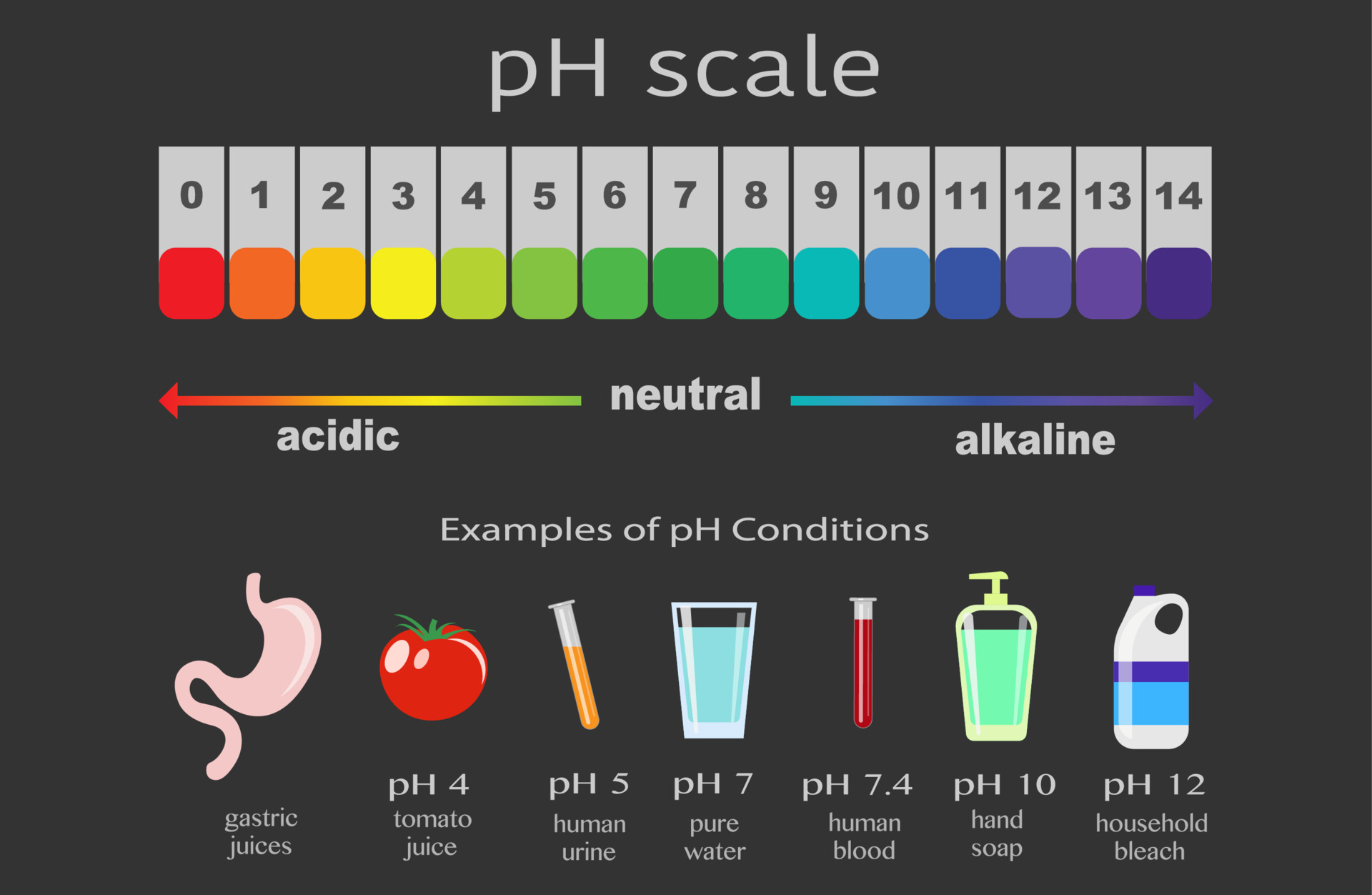
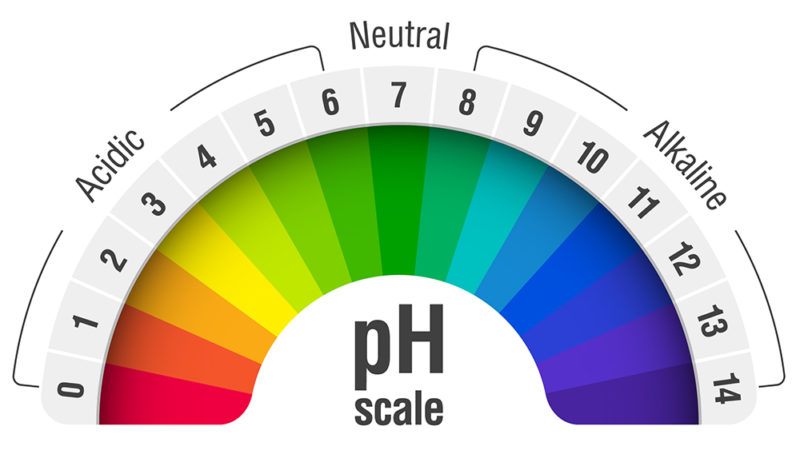



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power of High pH: Exploring the World of Alkaline Substances. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide To Materials That Cannot Be Recycled
The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled
Related Articles: The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled
- 3.1 Understanding the Recycling Process: A Foundation for Exclusion
- 3.2 The Unrecyclable: A Detailed Exploration
- 3.3 The Importance of Understanding the Unrecyclable: Environmental and Economic Implications
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 3.5 Tips for Responsible Waste Management
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled

Recycling is a cornerstone of sustainable practices, diverting waste from landfills and conserving valuable resources. However, not all materials are suitable for recycling, and understanding the limitations of this process is crucial for effective waste management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the unrecyclable, exploring the reasons behind their exclusion from recycling streams and highlighting the environmental and economic implications.
Understanding the Recycling Process: A Foundation for Exclusion
Recycling involves transforming used materials into new products, reducing the need for virgin resources. This process typically involves several steps:
- Collection and Sorting: Waste materials are collected from households and businesses, then sorted into different categories based on their composition.
- Processing: Sorted materials undergo various processes, such as cleaning, shredding, and melting, to prepare them for reuse.
- Manufacturing: The processed materials are then used to create new products.
While seemingly straightforward, this process is complex and reliant on specific material properties. Certain materials, due to their inherent characteristics or contamination, cannot be effectively recycled using current technologies.
The Unrecyclable: A Detailed Exploration
1. Contaminated Materials:
Contamination poses a significant challenge to the recycling process. When materials are mixed with other substances, it can interfere with the sorting and processing stages, making it difficult to extract and reuse the desired component.
- Mixed Plastics: Plastics are often categorized by their resin identification code (RIC), ranging from 1 to 7. However, mixing different types of plastics, especially those with varying melting points, creates a heterogeneous material that cannot be easily separated and recycled.
- Food-Contaminated Packaging: Food residues, grease, and oils can contaminate paper, cardboard, and plastic containers, making them unsuitable for recycling. These contaminants can degrade the quality of recycled materials and pose health risks if not properly removed.
- Dirty or Soiled Materials: Materials like textiles, paper, and cardboard that are heavily soiled with dirt, grease, or other substances cannot be recycled. The contamination can interfere with the recycling process and result in lower-quality recycled products.
2. Materials with Limited Reusability:
Some materials, while technically recyclable, have limited applications in the recycling process due to their inherent properties or the availability of suitable markets.
- Certain Types of Glass: Glass is generally recyclable, but certain types, such as tempered glass or heat-resistant glass, cannot be easily melted down and reused. These types of glass often end up in landfills.
- Polystyrene (Styrofoam): Styrofoam, a type of expanded polystyrene, is notoriously difficult to recycle. It can be recycled, but the process is energy-intensive and requires specialized facilities. Due to limited demand and processing challenges, Styrofoam is often landfilled.
- Composite Materials: Composite materials, such as those used in construction, are made from a mixture of different materials, making it difficult to separate and recycle them.
3. Materials with Hazardous Components:
Some materials contain hazardous substances that pose risks to human health and the environment. These materials are typically excluded from recycling streams to prevent contamination.
- Batteries: Batteries contain heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into the environment if not properly disposed of. Recycling batteries requires specialized facilities equipped to handle these hazardous materials.
- Electronics: Electronic devices, such as computers, smartphones, and televisions, contain a variety of metals, plastics, and other materials that can be difficult to separate and recycle. Many electronic components also contain hazardous substances, such as mercury and lead, which require specialized handling.
- Medical Waste: Medical waste, such as syringes, needles, and contaminated bandages, poses a significant health risk and must be disposed of separately through specialized medical waste disposal programs.
4. Materials with Limited Economic Viability:
Recycling is a commercially driven process, and the economic viability of recycling certain materials can be limited.
- Plastic Bags and Films: While technically recyclable, plastic bags and films can easily become entangled in recycling equipment, causing damage and disruption. Additionally, the demand for recycled plastic bags and films is limited, making their recycling economically unfeasible in many cases.
- Paper Products with Special Coatings: Paper products with coatings, such as wax-coated paper cups or glossy magazines, can be difficult to recycle due to the presence of these coatings. The coatings can interfere with the pulping process, resulting in lower-quality recycled paper.
- Certain Types of Cardboard: Cardboard boxes that are heavily soiled, grease-stained, or contain non-recyclable materials, such as plastic windows, are often excluded from recycling streams due to their limited economic value.
The Importance of Understanding the Unrecyclable: Environmental and Economic Implications
Recognizing the limitations of recycling is crucial for creating effective waste management strategies. By understanding what cannot be recycled, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their waste disposal practices, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource recovery.
- Reduced Landfill Waste: Proper waste separation and disposal practices, based on an understanding of the unrecyclable, can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. This helps conserve landfill space, minimize greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing waste, and reduce the environmental impact of landfilling.
- Conservation of Resources: By correctly identifying and separating unrecyclable materials, we can ensure that recyclable materials are processed effectively. This conserves valuable resources, such as timber, minerals, and energy, that would otherwise be used to produce new products from virgin materials.
- Economic Efficiency: Understanding the unrecyclable helps optimize recycling processes, reducing contamination and ensuring the quality of recycled materials. This contributes to the economic viability of recycling programs, promoting investment in infrastructure and technological advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What happens to unrecyclable materials?
A: Unrecyclable materials are typically sent to landfills. However, some materials, such as certain types of plastics, may be incinerated for energy recovery, though this process can release harmful emissions.
Q2: Can I recycle any plastic?
A: Not all plastics are recyclable. The recyclability of plastics depends on their type, composition, and contamination. Check the resin identification code (RIC) on the plastic item to determine its recyclability.
Q3: Can I recycle paper products with food residue?
A: No, paper products with food residue are not recyclable. The food residue can contaminate the recycling stream and degrade the quality of recycled paper.
Q4: Can I recycle batteries?
A: Batteries should not be recycled in household recycling bins. They contain hazardous materials and require specialized handling. Dispose of batteries properly through designated battery recycling programs.
Q5: What can I do with unrecyclable items?
A: Consider alternative disposal options, such as:
- Donate or repurpose: Donate items to charities or reuse them for creative projects.
- Compost: Compost food scraps and yard waste to create nutrient-rich soil.
- Specialized disposal programs: Utilize specialized programs for hazardous waste, electronics, and other materials that cannot be recycled through traditional means.
Tips for Responsible Waste Management
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Prioritize reducing waste generation, reusing items whenever possible, and recycling materials that are suitable for recycling.
- Check Local Recycling Guidelines: Consult your local municipality’s recycling guidelines to determine what materials are accepted for recycling in your area.
- Properly Sort and Separate: Sort waste materials into different categories, such as paper, plastic, metal, and glass, to ensure proper recycling.
- Minimize Contamination: Avoid contaminating recyclable materials with food residue, grease, or other substances. Rinse containers thoroughly and remove any non-recyclable components.
- Support Recycling Initiatives: Support local recycling programs and advocate for policies that promote sustainable waste management.
Conclusion
Understanding the limitations of recycling is crucial for effective waste management. By recognizing the materials that cannot be recycled, we can make informed decisions about our waste disposal practices, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource recovery. By embracing responsible waste management practices, we can contribute to a more sustainable future.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unrecyclable: A Comprehensive Guide to Materials That Cannot Be Recycled. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!