A Perfluorinated World: Understanding the Prevalence of PFAS in Everyday Products
Related Articles: A Perfluorinated World: Understanding the Prevalence of PFAS in Everyday Products
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Perfluorinated World: Understanding the Prevalence of PFAS in Everyday Products. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Perfluorinated World: Understanding the Prevalence of PFAS in Everyday Products
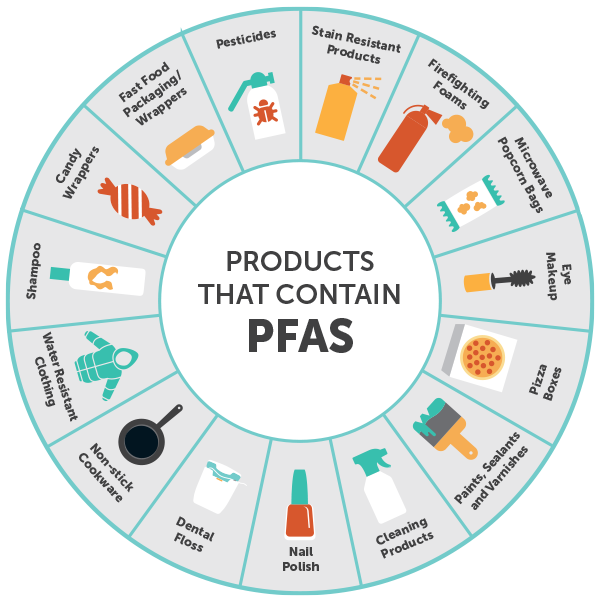
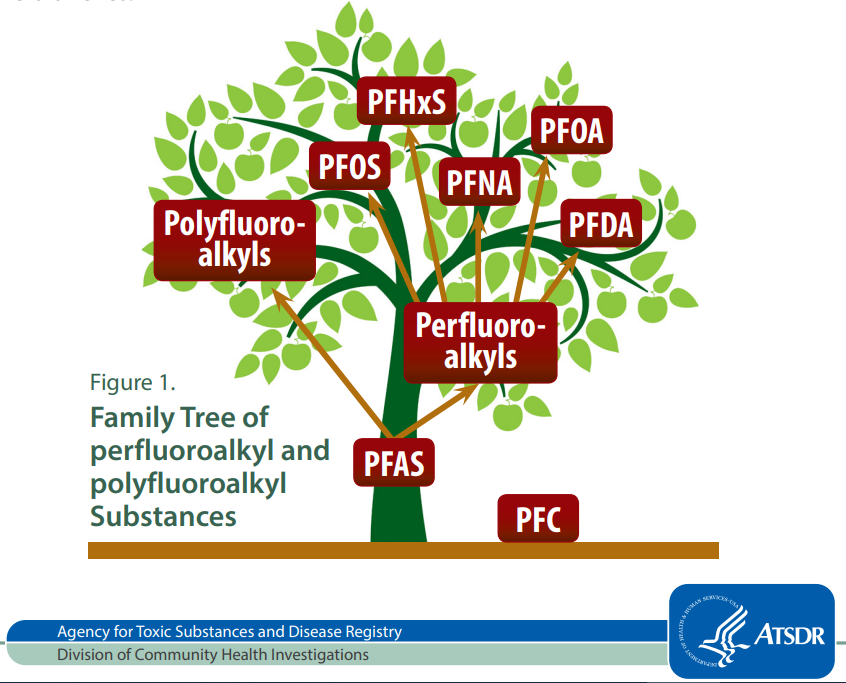
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, commonly known as PFAS, are a group of man-made chemicals characterized by their strong carbon-fluorine bonds. These bonds make PFAS incredibly stable, resistant to heat, oil, and water, qualities that have led to their widespread use in numerous industrial and consumer products. However, this very stability also makes PFAS persistent in the environment and poses significant health risks to humans and ecosystems.
This article explores the pervasive presence of PFAS in everyday products, shedding light on their diverse applications and highlighting the importance of understanding their potential risks.
The Many Faces of PFAS: A Diverse Range of Applications
PFAS’s unique properties have made them invaluable in a wide array of industries, leading to their incorporation into countless products we encounter daily. Here are some key areas where PFAS are commonly found:
1. Non-stick Cookware and Food Packaging:
PFAS, particularly PFOA and PFOS, have been widely used in the manufacturing of non-stick cookware and food packaging materials. Their ability to repel grease and water makes them ideal for creating surfaces that resist food sticking and prevent leaks.
2. Firefighting Foam:
PFAS are critical components of aqueous film-forming foam (AFFF), a type of firefighting foam used to extinguish flammable liquid fires. Their ability to suppress flames and prevent reignition has made them indispensable for airport fire departments, military installations, and industrial facilities.
3. Textiles and Apparel:
PFAS are incorporated into fabrics to create stain-resistant, water-repellent, and oil-repellent surfaces. This property makes them popular for outdoor gear, clothing, carpets, and upholstery, enhancing their durability and performance.
4. Personal Care Products:
PFAS are found in a variety of personal care products, including shampoos, conditioners, soaps, and cosmetics. Their ability to create smooth, silky textures and prevent water absorption makes them valuable ingredients for enhancing product performance.
5. Electronics and Manufacturing:
PFAS are used in various manufacturing processes, including the production of semiconductors, displays, and electronic components. Their ability to resist heat and corrosion makes them valuable for enhancing the performance and longevity of these products.
6. Food Processing and Packaging:
PFAS are used in food processing and packaging to prevent food spoilage and maintain product quality. Their ability to repel water and oil makes them ideal for creating moisture-proof and grease-resistant packaging materials.
7. Construction and Building Materials:
PFAS are incorporated into building materials to create water-resistant, stain-resistant, and fire-retardant surfaces. This makes them valuable for applications like roofing membranes, sealants, and paints.
The Importance of Understanding PFAS: A Focus on Health and Environmental Concerns
While PFAS offer numerous benefits, their persistence in the environment and potential health risks have become major concerns. Studies have linked PFAS exposure to various health issues, including:
- Immune System Suppression: PFAS can interfere with the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases.
- Hormonal Disruption: PFAS can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, leading to developmental and reproductive problems.
- Liver and Kidney Damage: Long-term exposure to PFAS can damage the liver and kidneys.
- Increased Risk of Cancer: Some studies have linked PFAS exposure to an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
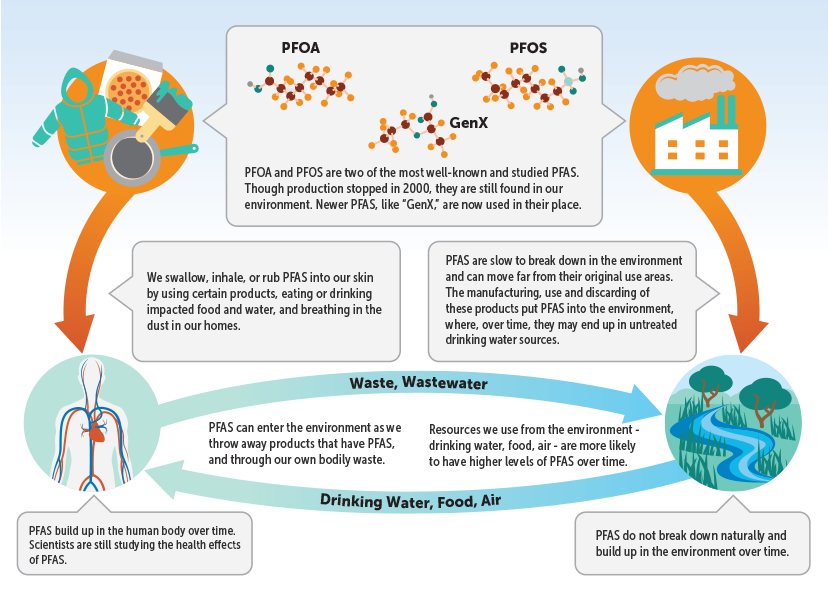
Moreover, PFAS are persistent in the environment, meaning they do not readily break down and can accumulate in water, soil, and wildlife. This poses a threat to ecosystems and human health through bioaccumulation, where PFAS levels increase as they move up the food chain.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about PFAS
1. Are PFAS found in all non-stick cookware?
Not all non-stick cookware contains PFAS. Some manufacturers have transitioned to using alternative materials, such as ceramic coatings, to achieve non-stick properties without relying on PFAS. However, it is essential to check product labels and research the materials used in cookware to ensure PFAS-free options.
2. Is it safe to use products containing PFAS?
The safety of PFAS-containing products is a complex issue that depends on several factors, including the specific type of PFAS, the concentration used, and the duration and frequency of exposure. While some PFAS may be considered safe at low levels, others are known to pose significant health risks. It is crucial to minimize exposure to PFAS by choosing products with alternatives and following product instructions carefully.
3. What can I do to reduce my exposure to PFAS?
Here are some tips for reducing PFAS exposure:
- Choose PFAS-free products: Look for products labeled as "PFAS-free" or "PFOA-free."
- Avoid using non-stick cookware at high temperatures: High heat can increase the risk of PFAS leaching into food.
- Use a separate pan for cooking fatty foods: Fatty foods can leach more PFAS from cookware.
- Wash cookware thoroughly after use: This can help remove any PFAS residue.
- Avoid using products containing PFAS in the home: This includes things like stain-resistant carpets and upholstery, waterproof clothing, and personal care products.
- Filter your drinking water: Some water filters can remove PFAS from drinking water.
4. How are PFAS regulated?
The regulation of PFAS varies by country and region. Some countries have implemented regulations limiting the use of specific PFAS, while others are still developing regulations. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States has set health advisories for PFAS in drinking water, but has not yet established legally enforceable standards.
5. What is being done to address the PFAS problem?
Efforts to address the PFAS problem include:
- Research and Development: Scientists are researching alternative materials and technologies to replace PFAS in products.
- Regulation and Policy: Governments are developing regulations and policies to limit the use and disposal of PFAS.
- Public Awareness: Efforts are underway to raise public awareness about the risks of PFAS and encourage safer product choices.
Conclusion: A Call for Collective Action
The widespread use of PFAS in countless products has created a complex challenge for human health and the environment. Understanding the presence of these chemicals in everyday items is crucial for making informed choices and minimizing exposure. By prioritizing research, regulation, and public awareness, we can work towards a future where PFAS are managed responsibly and their potential risks are mitigated.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Perfluorinated World: Understanding the Prevalence of PFAS in Everyday Products. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!