A Comprehensive Guide to Reusing Materials: Embracing Sustainability Through Resourcefulness
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Reusing Materials: Embracing Sustainability Through Resourcefulness
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Reusing Materials: Embracing Sustainability Through Resourcefulness. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Reusing Materials: Embracing Sustainability Through Resourcefulness

The world today faces a myriad of environmental challenges, with resource depletion and waste generation standing as prominent concerns. Reusing materials emerges as a powerful solution, offering a path towards a more sustainable future. This practice transcends mere recycling; it involves extending the lifespan of existing materials, thereby minimizing the need for new production and reducing environmental impact.
This article delves into the diverse world of reusable materials, exploring various categories, their benefits, and practical applications. By understanding the potential of reuse, individuals and organizations can actively contribute to a circular economy, where resources are valued and utilized to their fullest potential.
Understanding the Scope of Reuse
The concept of reuse encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, each contributing to a more sustainable approach to material consumption. It is not limited to specific materials or categories but rather embraces a mindset of resourcefulness and innovation.
1. Everyday Objects:
The most common and readily accessible category of reusable materials encompasses everyday objects. These are items that have served their initial purpose but still possess value for other uses. Examples include:
- Glass Jars: Glass jars, once emptied of their contents, can be repurposed for storing food, organizing small items, or even as decorative elements.
- Plastic Containers: Plastic containers, often discarded after a single use, can be reused for storing leftovers, packing lunches, or organizing craft supplies.
- Paper Bags: Paper bags, commonly used for grocery shopping, can be reused for carrying items, wrapping gifts, or creating craft projects.
- Old Clothes: Old clothes, instead of being thrown away, can be donated, repurposed into new garments, or used as cleaning rags.
- Old Tires: Old tires can be transformed into planters, playground equipment, or even used for landscaping purposes.
2. Building Materials:
The construction industry generates substantial waste, but reuse offers a valuable solution. Various building materials can be salvaged and reused, contributing to sustainable construction practices:
- Reclaimed Wood: Reclaimed wood, salvaged from demolished buildings or old furniture, can be used for flooring, furniture, or decorative elements, adding character and sustainability to projects.
- Used Bricks: Used bricks, often available from demolished structures, can be cleaned and reused in new construction projects, reducing the need for new brick production.
- Concrete: Concrete can be crushed and reused as aggregate in new concrete mixtures, reducing the demand for virgin materials.
- Windows and Doors: Salvaged windows and doors can be refurbished and reused in renovation projects, adding vintage charm and promoting resource conservation.
3. Packaging Materials:
Packaging materials are often single-use items, contributing significantly to waste generation. However, reuse offers a practical alternative:
- Cardboard Boxes: Cardboard boxes, often discarded after deliveries, can be reused for storage, packing, or even as craft materials.
- Bubble Wrap: Bubble wrap, commonly used for protecting fragile items, can be reused for cushioning or as insulation.
- Styrofoam: Styrofoam, though often criticized for its environmental impact, can be reused for packing, insulation, or even as craft materials.
4. Electronic Devices:
Electronic devices, with their rapid obsolescence, present a significant waste challenge. However, reuse can extend their lifespan and reduce the demand for new production:
- Old Computers: Old computers can be refurbished and donated to schools, charities, or individuals who need them.
- Used Phones: Used phones can be sold, traded, or refurbished for resale, providing a more affordable option for consumers.
- Batteries: Rechargeable batteries can be reused multiple times, reducing the need for disposable batteries.
5. Industrial Materials:
Beyond everyday objects, reuse extends to industrial materials, offering a significant reduction in resource consumption and waste generation:
- Scrap Metal: Scrap metal, generated from manufacturing processes, can be recycled or reused in various industrial applications.
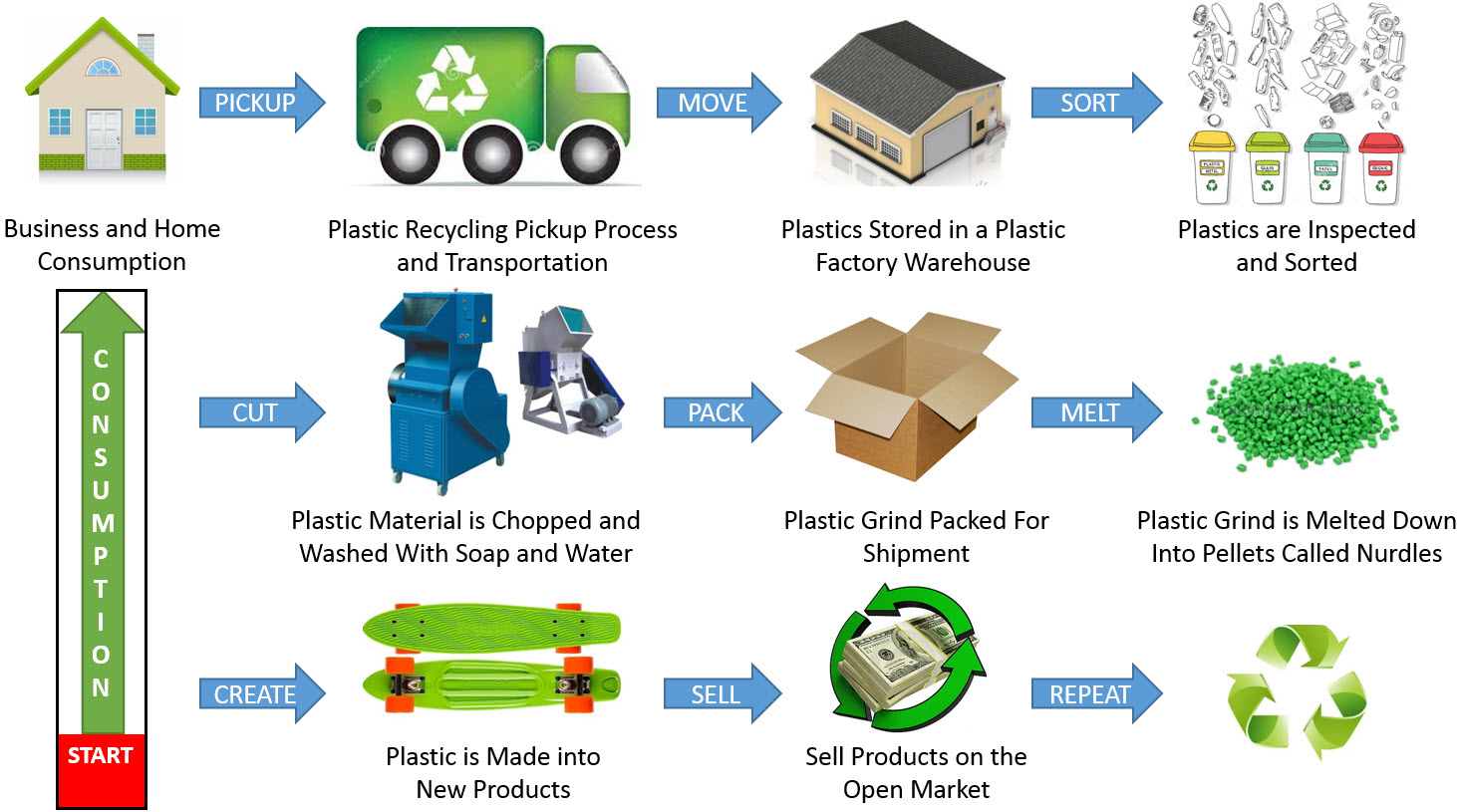
- Plastic Pellets: Plastic pellets, used in manufacturing processes, can be reclaimed and reused to create new products.
- Industrial Waste: Industrial waste, such as wood shavings or metal filings, can be reused as fuel or recycled into new products.
Benefits of Reuse
The benefits of reusing materials extend far beyond simply reducing waste. It offers a comprehensive approach to sustainability, encompassing economic, environmental, and social advantages:
1. Environmental Benefits:
- Reduced Resource Consumption: Reusing materials minimizes the need for new production, thereby conserving natural resources and reducing the environmental impact associated with extraction and processing.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reduced production processes translate to lower energy consumption and fewer emissions of greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Reduced Waste Generation: By extending the lifespan of materials, reuse significantly reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, mitigating the environmental impact of waste disposal.
- Conservation of Biodiversity: Reduced resource consumption and waste generation contribute to the protection of ecosystems and biodiversity, preserving valuable natural resources.
2. Economic Benefits:
- Cost Savings: Reusing materials often results in lower costs compared to purchasing new materials, providing financial benefits for individuals and organizations.
- Job Creation: The reuse industry creates jobs in collection, processing, and refurbishment, contributing to economic development and employment opportunities.
- Increased Value: Reused materials can often be more valuable than virgin materials, particularly in the case of reclaimed wood or vintage building materials.
3. Social Benefits:
- Community Engagement: Reuse initiatives often involve community participation, fostering a sense of shared responsibility and promoting social cohesion.
- Social Equity: Reusing materials can provide access to affordable goods and services for individuals and communities with limited resources.
- Educational Value: Promoting reuse practices can educate individuals about sustainability and responsible consumption, encouraging a more mindful approach to resource utilization.
FAQs about Reuse
1. What are the challenges associated with reuse?
While reuse offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges:
- Availability: Finding suitable reusable materials may be challenging, especially in areas with limited infrastructure or access to salvage resources.
- Quality: Reused materials may not always meet the same standards as new materials, requiring careful inspection and refurbishment.
- Cost: The initial investment in collecting, sorting, and processing reusable materials can be significant, potentially requiring financial incentives or government support.
- Logistics: Efficient transportation and storage of reusable materials require careful planning and logistical coordination.
2. How can I get started with reusing materials?
- Start small: Begin by reusing everyday objects, such as glass jars, plastic containers, and paper bags.
- Explore local resources: Search for local salvage yards, reuse centers, or community initiatives that offer reusable materials.
- Join online communities: Connect with online communities dedicated to reuse and upcycling, sharing ideas and resources.
- Educate yourself: Learn about the different types of reusable materials, their applications, and the benefits of reuse.
3. What are some tips for reusing materials effectively?
- Clean and sanitize: Before reusing any material, ensure it is thoroughly cleaned and sanitized to prevent contamination.
- Inspect for damage: Carefully examine reused materials for any signs of damage or wear, ensuring they are safe for their intended use.
- Consider durability: Choose materials that are durable enough for their new purpose, ensuring they will withstand the intended use.
- Be creative: Think outside the box and explore different ways to reuse materials, unleashing your creativity and resourcefulness.
Conclusion
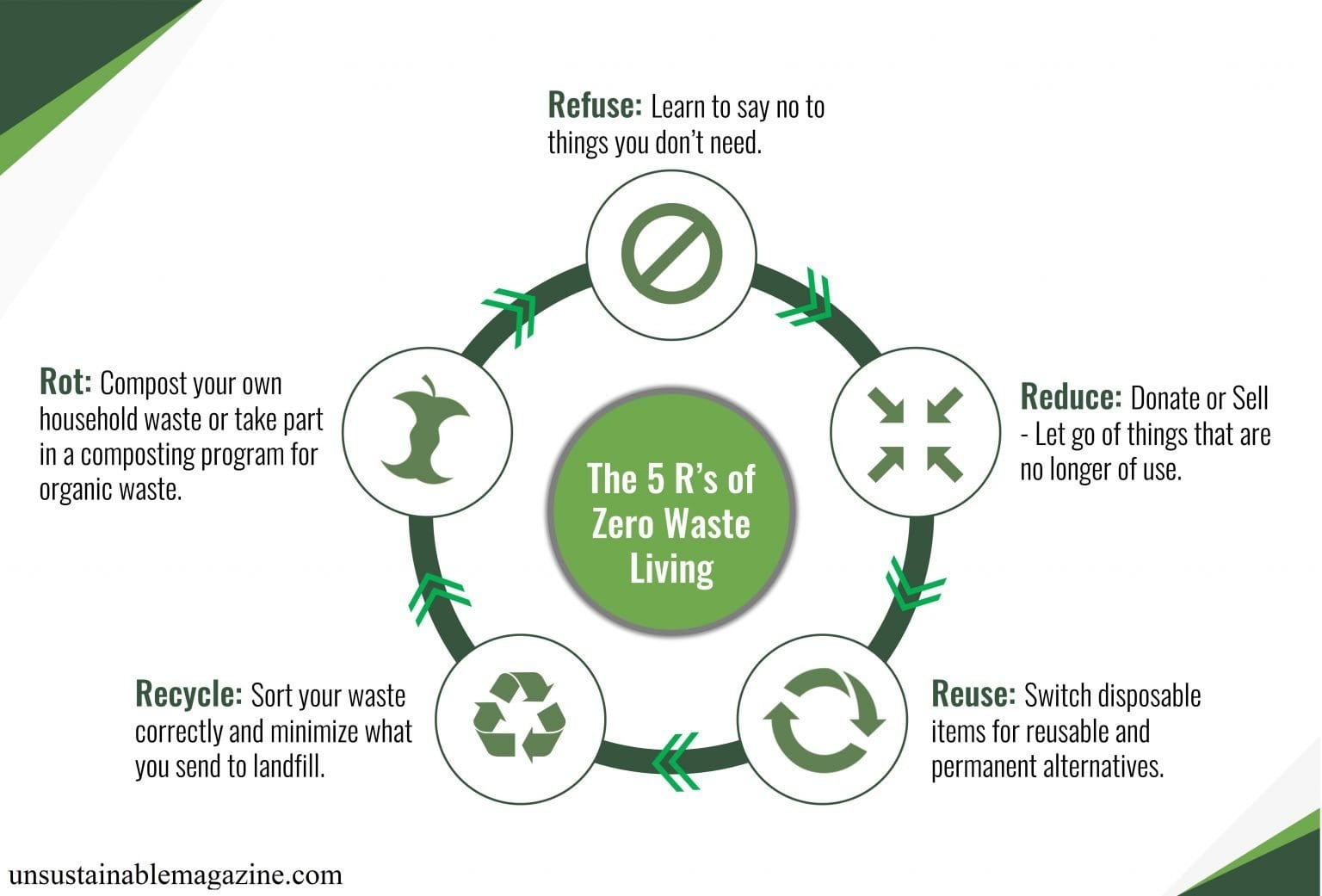
Reusing materials is not just a trend; it is a fundamental shift in our relationship with resources. It embraces resourcefulness, creativity, and a deep respect for the environment. By embracing reuse practices, individuals, communities, and organizations can contribute to a more sustainable future, where resources are valued, utilized to their fullest potential, and waste is minimized. The journey towards a circular economy begins with a simple act of reuse, transforming discarded materials into valuable assets and paving the way for a more sustainable world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Reusing Materials: Embracing Sustainability Through Resourcefulness. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!